The document discusses the design and construction of pyramids in ancient Egypt. It provides details on:
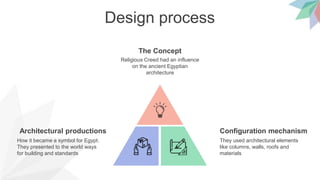
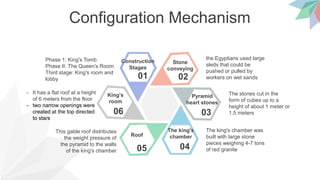
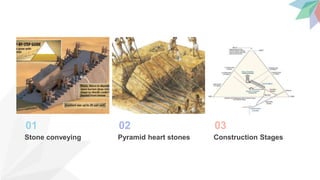
- The design process, which was influenced by religious beliefs and used architectural elements like columns and roofs. Over 100,000 workers and 20 years were sometimes needed to complete a pyramid.
- Means of expression in pyramid design including using the golden ratio for proportions, interior inscriptions, and tools like ropes and wood plates. Drawings guided the tunnels and chambers.
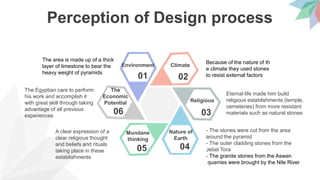
- Perceptions of the design process, which considered the environment, climate, economic potential of the area, and need for structures to represent religious thoughts and allow eternal life after death. Stones were sourced locally when possible.