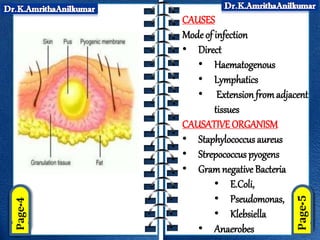
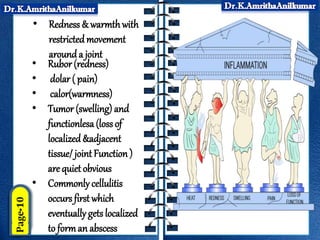
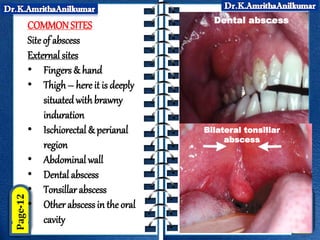
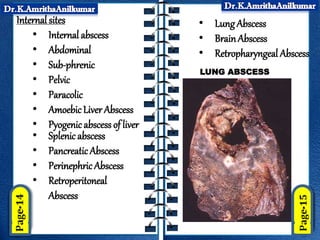
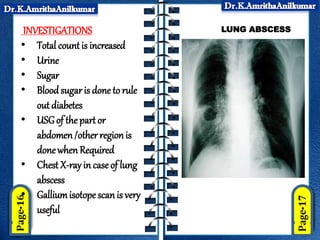
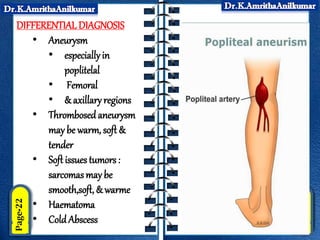
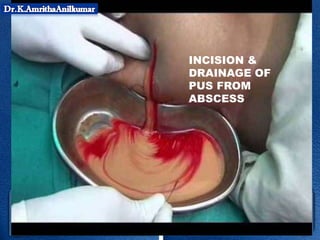
This document discusses pyogenic abscesses, which are localized collections of pus caused by bacterial infection. It defines pyogenic abscesses and describes their causes, signs and symptoms, common sites, investigations, complications, differential diagnosis, and treatment, which involves incision and drainage after antibiotics. Common causative organisms are Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. Investigations may include blood tests and imaging like ultrasound or chest X-ray. Complications can include sepsis if not treated properly. Treatment is incision and drainage of the abscess after it has formed, along with antibiotics.