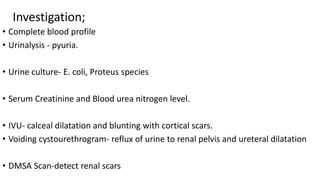
This document discusses acute and chronic pyelonephritis, which are inflammations of the kidney that can be caused by bacterial infections traveling up the urinary tract. It describes the etiology, pathogenesis, clinical features, investigations, and management of both conditions. Acute pyelonephritis is typically caused by gram-negative bacteria and can range from mild to severe with symptoms like fever and flank pain. Chronic pyelonephritis is characterized by recurrent infections and scarring of the kidney over time. Imaging tests can identify abnormalities and complications are treated with antibiotics or sometimes surgery.