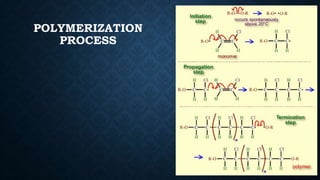
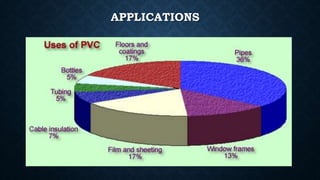
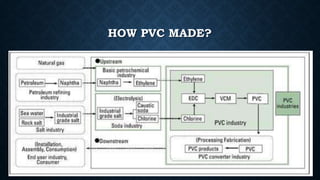
This document provides an overview of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), including its production, physical properties, applications, and disadvantages. PVC is the third most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer after polyethylene and polypropylene. It exists in both rigid and flexible forms. PVC is produced through the polymerization of vinyl chloride monomer, which is derived from petrochemical sources like ethylene. It has properties like fire retardancy, durability, and chemical resistance but also has disadvantages like difficulty recycling and sensitivity to heat and UV light.