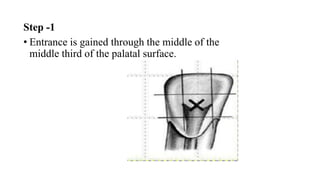
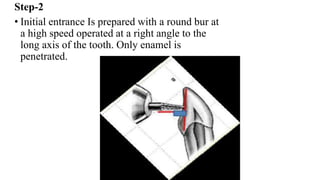
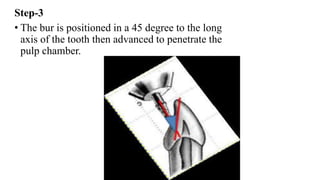
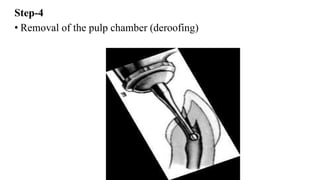
This document provides information on pulpectomy procedures for primary teeth. It defines pulpectomy and discusses guidelines for the procedure. It outlines the indications and contraindications for pulpectomy. Details are given on access opening and root canal anatomy in primary teeth. The document discusses techniques for pulpectomy, including one-stage and two-stage procedures. It also covers working length determination, instruments used, and cleaning and shaping of the root canals.





























































![Related articles
Allen KR (1979) Endodontic treatment of primary teeth. Aust Dent J
24: 347-51.
• Speculated that the resorption rate of zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE) and the root
differed, resulting in small areas of ZOE paste possibly being retained.
Garcia-Godoy [1987] Reported deflection of developing permanent tooth bud
because of its hardness
Sadrian R, Coll JA (2013) A long-term followup on the retention rate of zinc oxide
eugenol filler after primary tooth pulpectomy. Pediatr Dent 15: 249-253.
• Demonstrated that none of the retained ZOE particles caused observable
pathology and were also not related to treatment failure(success rate of 80%).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pulpectomy-copy-210708190200/85/Pulpectomy-copy-86-320.jpg)




















![• Dr. Barry Musikant [1998]
• Developed a new obturation technique with bi-directional
spiral.
• This technique ensures that a minimal amount of obturating
material will pas the apex.
• This controlled coverage is achieved because the spirals at
the coronal end of the instrument spin the material down
the shaft towards the apex, while the spirals at the apical
end spin the material upward towards the coronal end
• Where they meet (about 3-4 mm from the apical end of the
shaft), the material is thrown out laterally.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pulpectomy-copy-210708190200/85/Pulpectomy-copy-109-320.jpg)
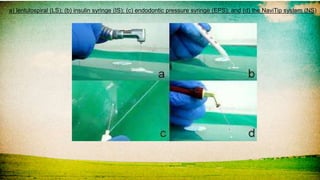
![• Muskant et al. [1998] observed that the bi-directional spiral
prevented the apical extrusion of the sealer from the root
canals of permanent teeth.
• Grover et al. ( 2013) The highest number of voids was seen in
canals filled with the lentulo spirals and bidirectional spiral
• Gibson et al. (2008) Ca(OH)2 injected into canal with
NaviTip consistently produced better results than the spirally
placed dressings](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pulpectomy-copy-210708190200/85/Pulpectomy-copy-110-320.jpg)