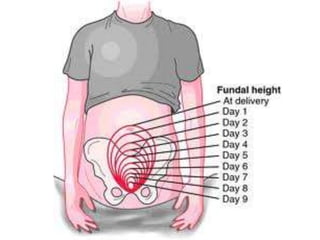
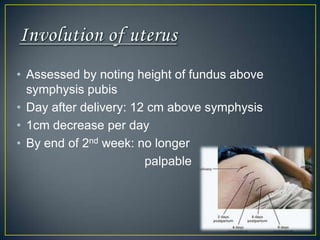
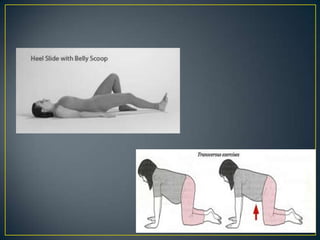
The normal puerperium period lasts 6 weeks following childbirth. During this time, the pelvic organs and body return to their pre-pregnant state. Physiological changes include the involution of the uterus, shedding of the endometrium and lochia discharge, closing of the cervix, and normalization of other organs and systems. Care during this period involves monitoring for complications, encouraging rest and early ambulation, perineal care, lactation support, nutrition, immunizations, contraception counseling, and postnatal checks to ensure full recovery.