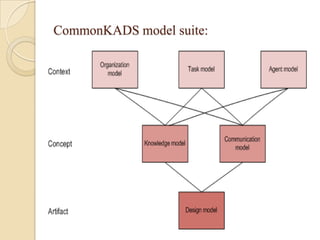
This presentation provides an overview of knowledge engineering and knowledge-based systems. It defines knowledge engineering as integrating knowledge into computer systems to solve complex problems requiring human expertise. The presentation discusses different views of knowledge engineering, trends in the field like the paradigm shift from transfer to modeling views, and modeling frameworks like CommonKADS. CommonKADS is highlighted as a leading methodology that supports structured knowledge engineering through detailed task and process analysis and developing knowledge systems to support business processes.