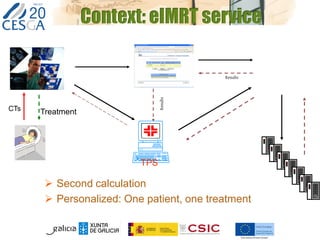
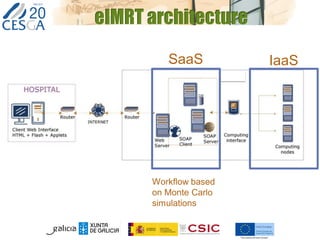
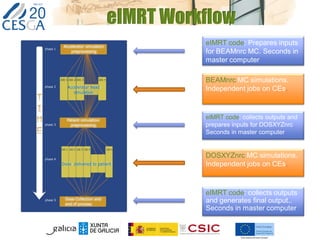
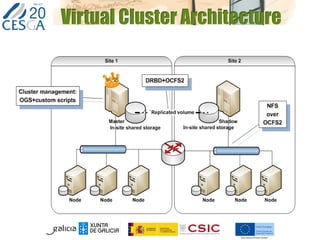
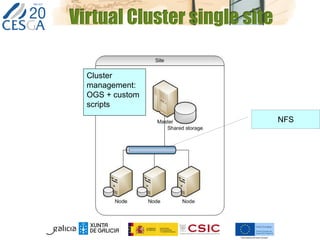
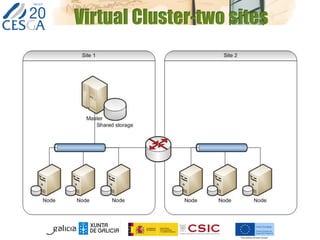
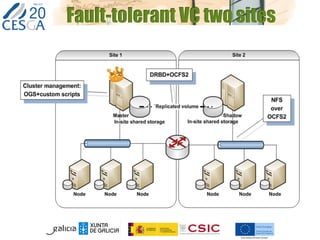
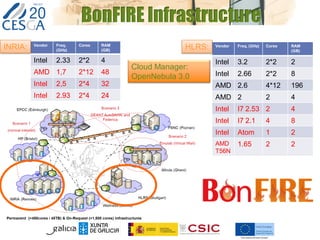
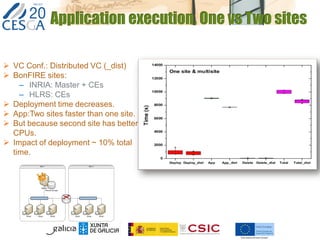
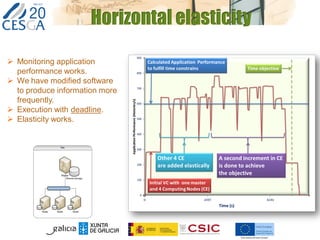
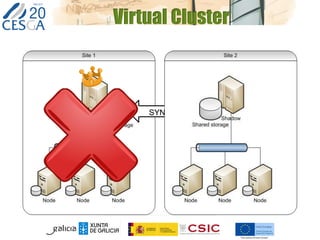
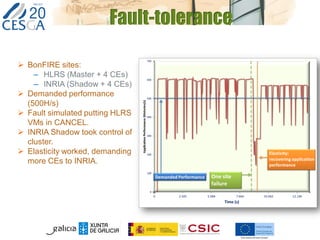
The document discusses the application of federated HPC clouds in radiation therapy, focusing on virtual cluster architectures and experimental results from a project funded by the EU's FP7 program. It addresses challenges related to resource sharing, application performance variability, and fault tolerance in cloud environments, proposing an autonomous virtual cluster architecture to enhance performance and reduce costs. The findings indicate that distributed virtual clusters can accelerate HTC applications while maintaining high quality of service through elasticity and monitoring mechanisms.