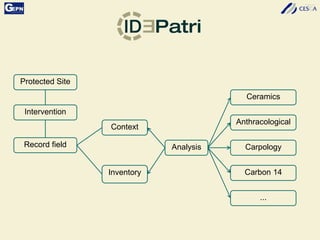
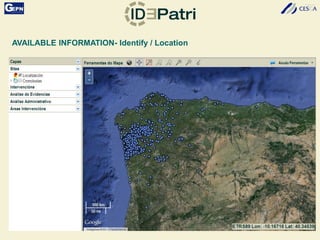
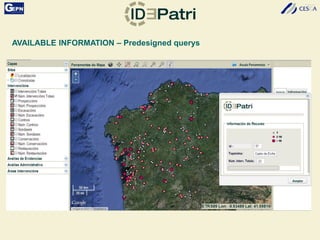
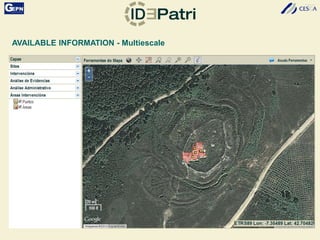
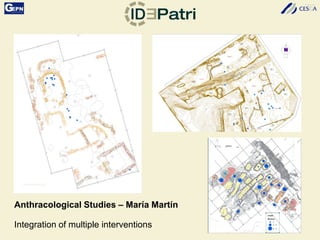
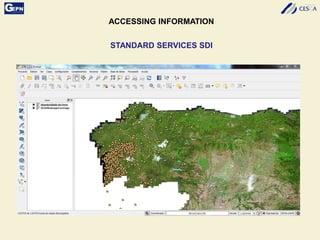
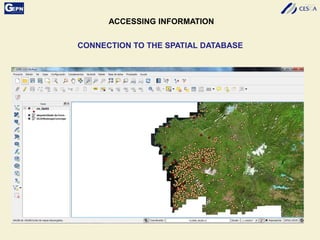
The document discusses the development of a Spatial Data Infrastructure (SDI) for managing and visualizing archaeological information, emphasizing the importance of standardized systems for accessibility and collaboration among researchers. It highlights the need for real-time data updates and ubiquitous access to enhance efficiency in archaeological research. Relevant European directives and laws, such as Directive 2007/2/EC, are mentioned as frameworks that support the establishment of SDIs to harmonize data across member countries.