Embed presentation
Download to read offline

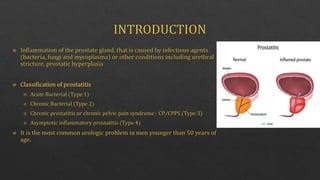
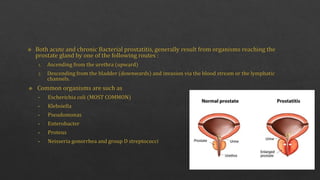






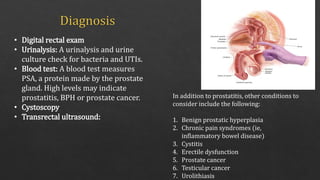


The document summarizes the microscopic and morphological features of prostatitis. Microscopically, the prostatic acini are dilated and filled with neutrophilic exudate, accompanied by diffuse acute inflammatory infiltrate, edema, hyperemia, and foci of necrosis. Morphologically, pathologic changes are similar in bacterial and abacterial prostatitis. The diagnosis of chronic prostatitis is made by finding lymphocytes, plasma cells, macrophages, and neutrophils within the prostatic substance, along with possible prostatic calculi or foci of squamous metaplasia. Seminal vesicles are invariably involved as well. A digital rectal exam, urinalysis, blood test, cystoscopy, and transrect











