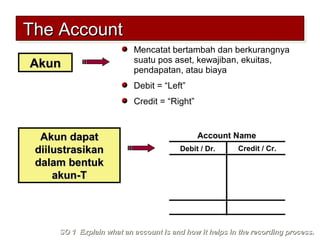
1) An account is used to record increases and decreases in assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses. Accounts help in the recording process by tracking changes to specific items.
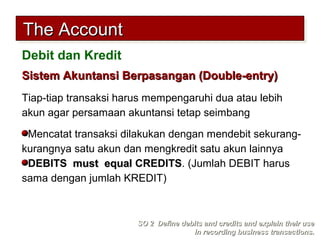
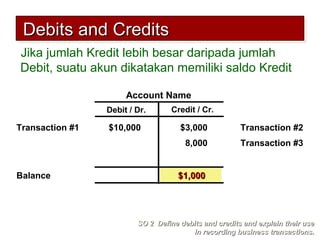
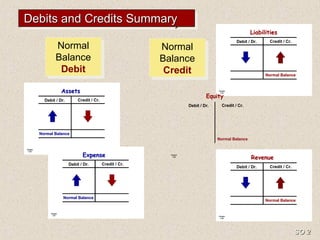
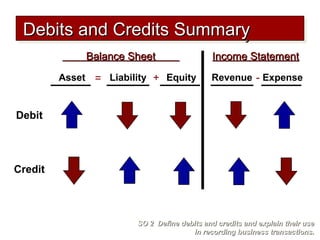
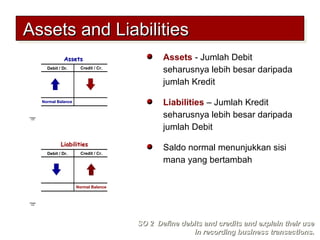
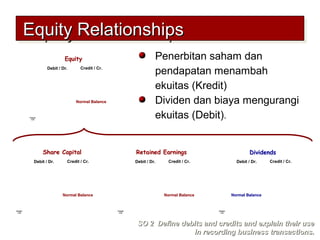
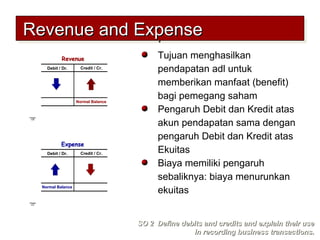
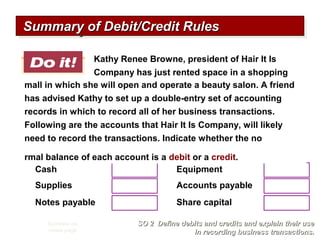
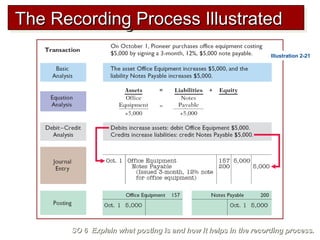
2) The double-entry system requires every transaction to affect at least two accounts to keep the accounting equation in balance. Transactions are recorded by debiting at least one account and crediting another account.
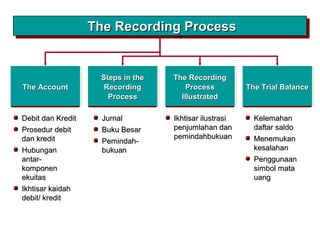
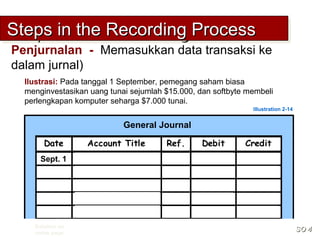
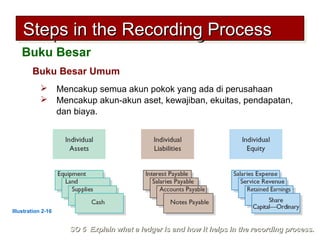
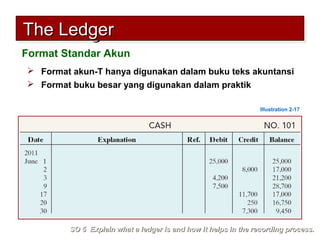
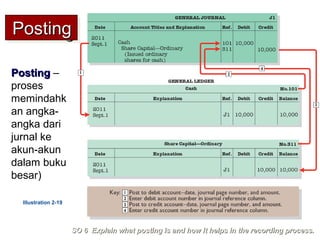
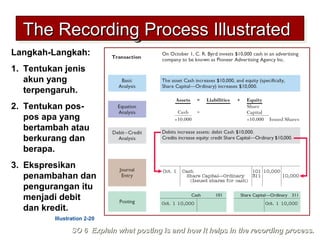
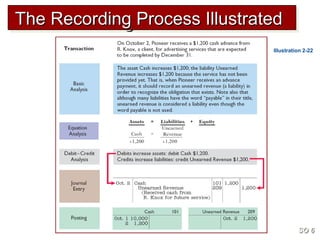
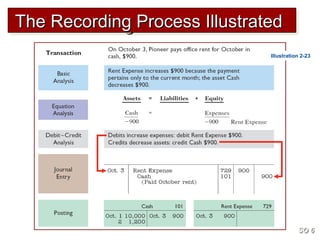
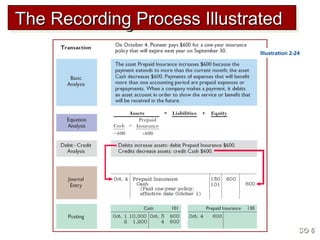
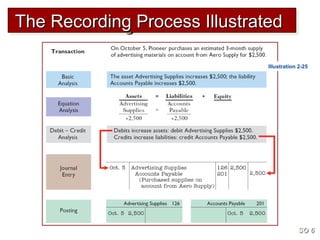
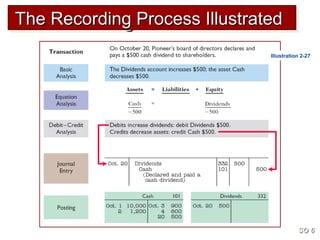
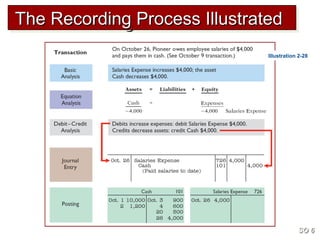
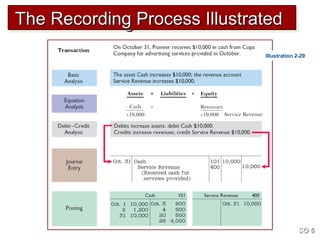
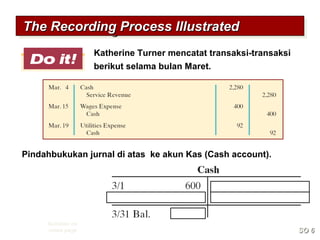
3) The basic steps in the recording process are to analyze each transaction, enter the transaction in a journal, and then transfer the journal information to individual ledger accounts.