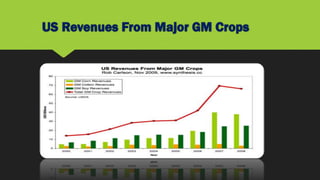
This document discusses genetically modified foods (GMFs). It provides a brief history of genetic modification, including the creation of the first transgenic plant in 1983. Commercially, four GMF crops - soybeans, maize, cotton, and canola - dominate global agriculture. While GMFs promise benefits like increased nutrients and crop protection, there are also risks to human health from allergic reactions and toxic effects. Additionally, GMFs can reduce biodiversity and lead to environmental problems through increased pesticide and herbicide use. The economic and social impacts of GMFs are an ongoing topic of debate.