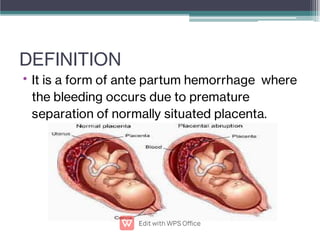
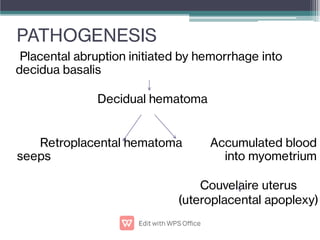
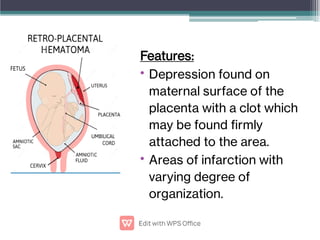
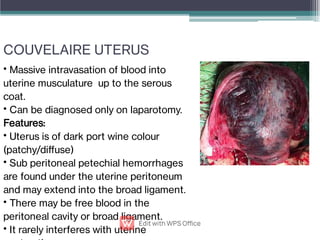
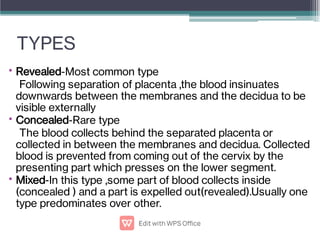
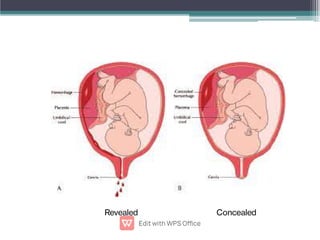
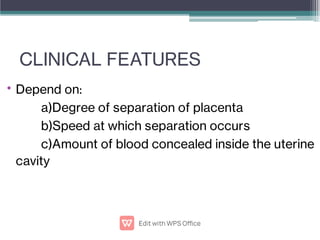
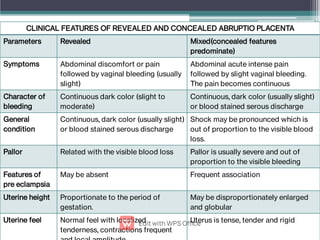
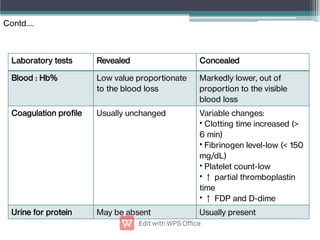
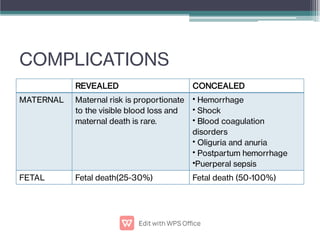
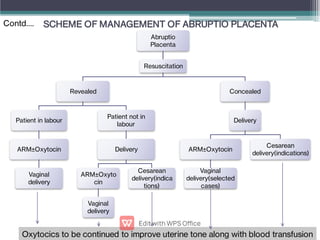
Abruptio placentae is premature separation of the placenta, which can cause bleeding. It occurs in about 1 in 200 pregnancies and carries risks of perinatal death (15-20%) and maternal mortality (2-5%). While the primary cause is uncertain, it is associated with hypertension, trauma, cocaine use, thrombophilias and other maternal risk factors. Clinically it presents as vaginal bleeding and abdominal pain and is diagnosed by ultrasound or MRI. Management involves resuscitation, monitoring for complications, and delivery depending on gestational age and whether the bleeding is revealed or concealed. Immediate delivery is often needed to prevent maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality.