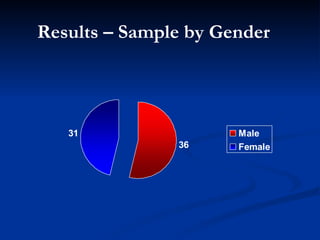
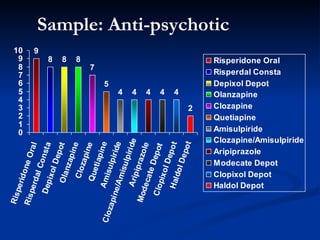
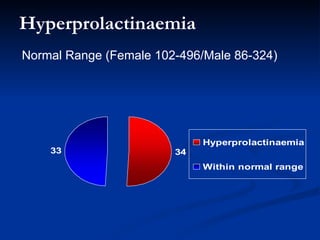
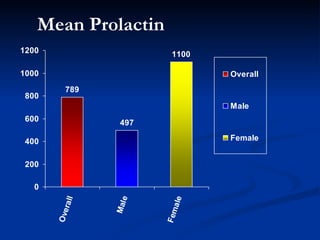
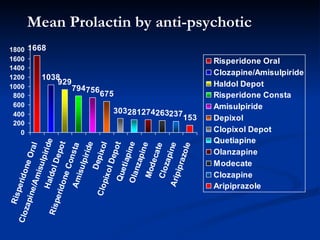
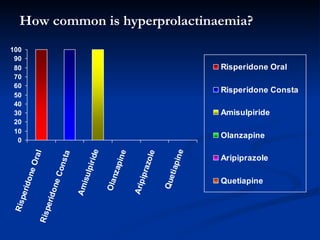
This document presents a study on prolactin levels in schizophrenia patients in Birmingham, revealing that 51% of the cohort had hyperprolactinaemia, with significant concerns for those on specific antipsychotics. The findings suggest that routine prolactin screening is warranted for patients on prolactin-elevating medications. A case study illustrates improvement in symptoms after switching medication, supporting the recommendation for monitoring and possible medication adjustments.