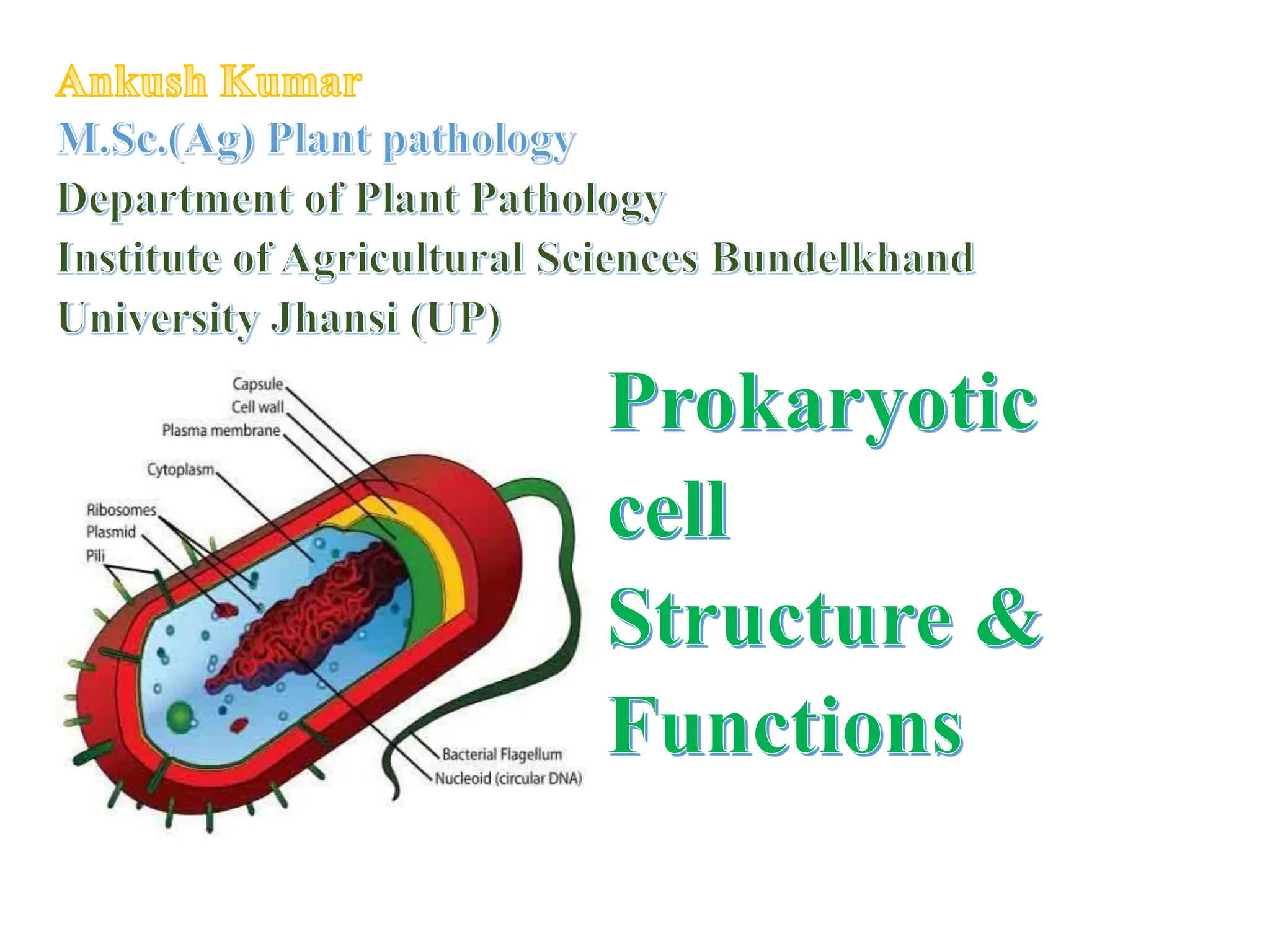
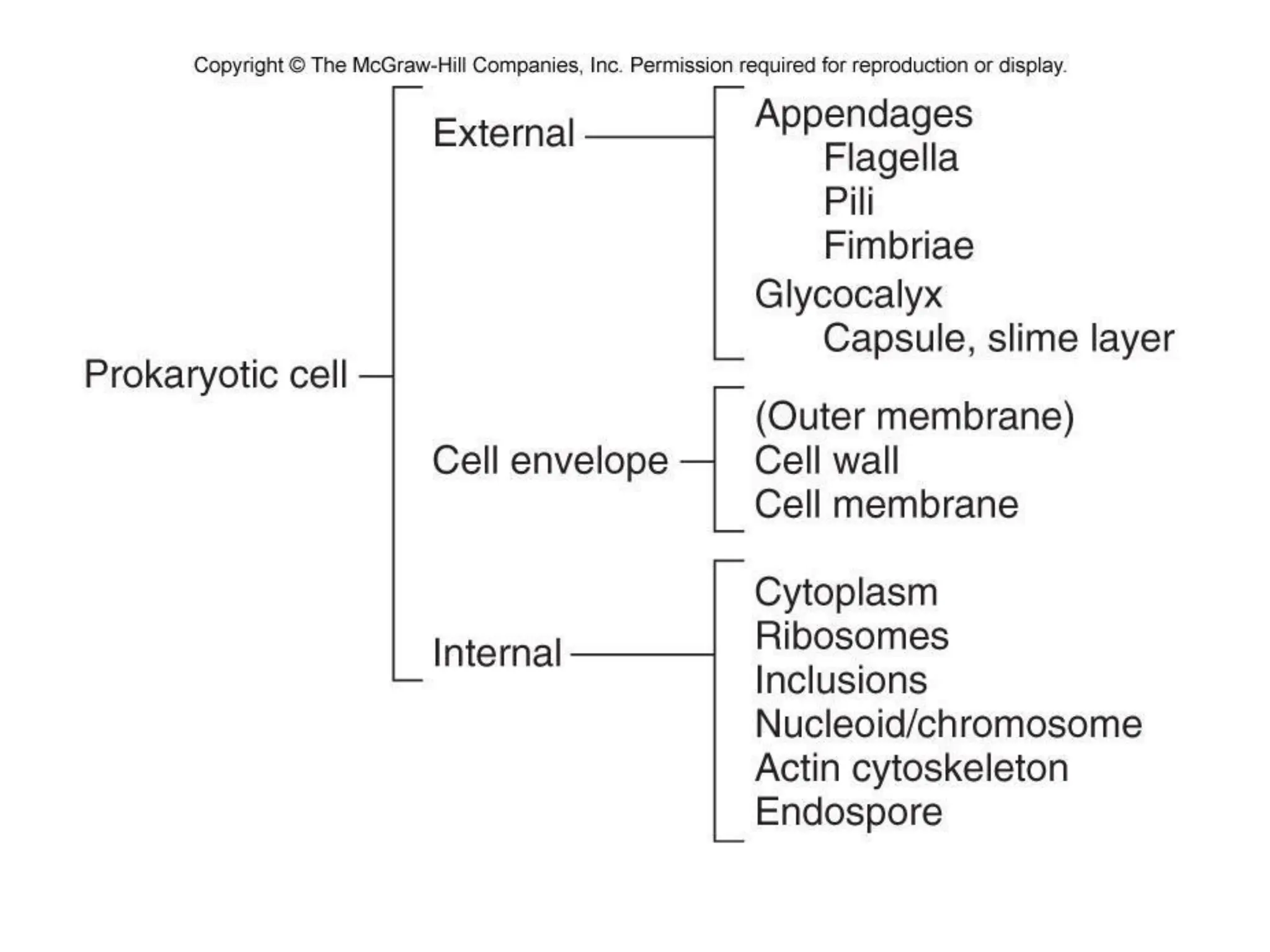
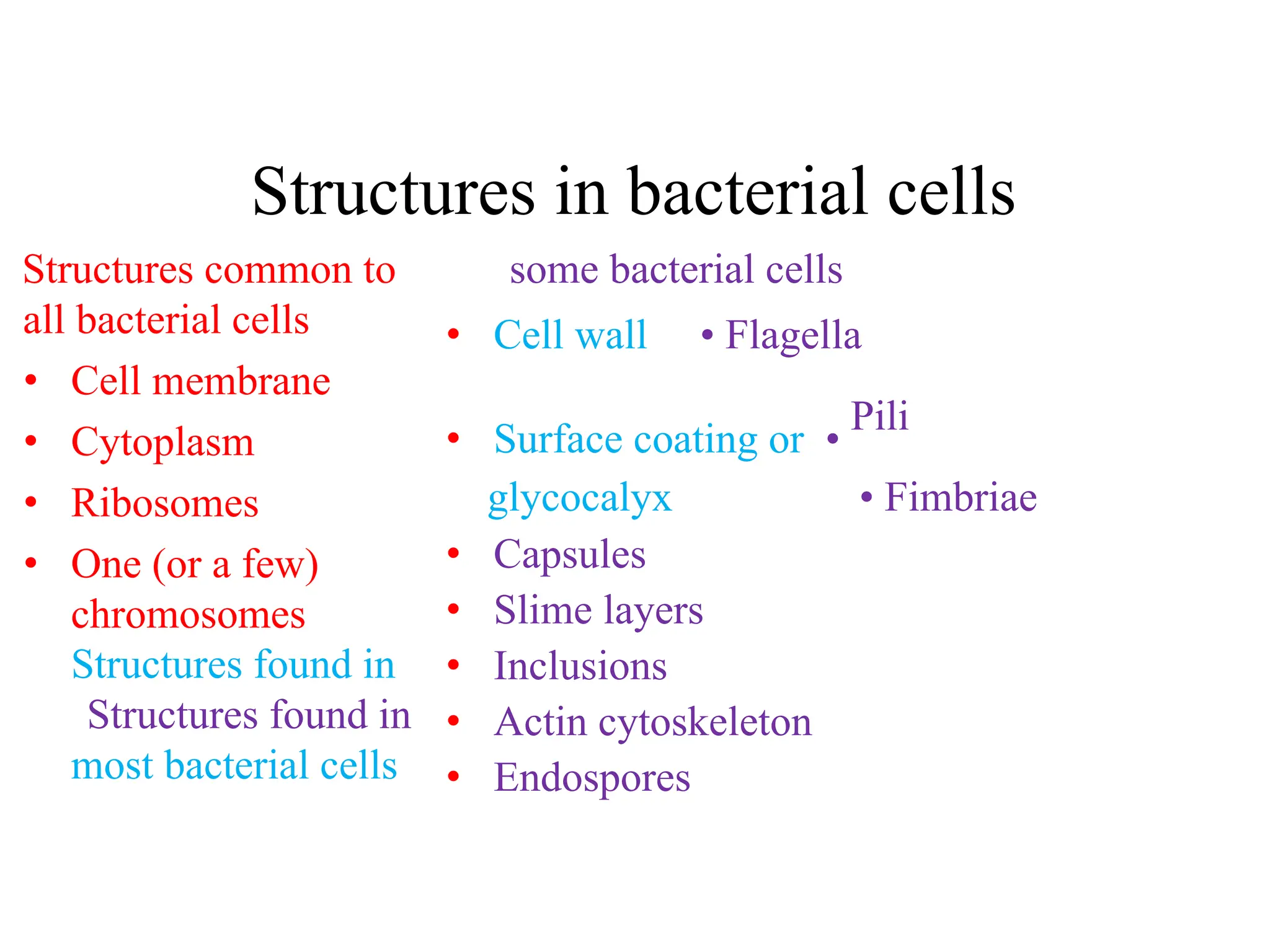
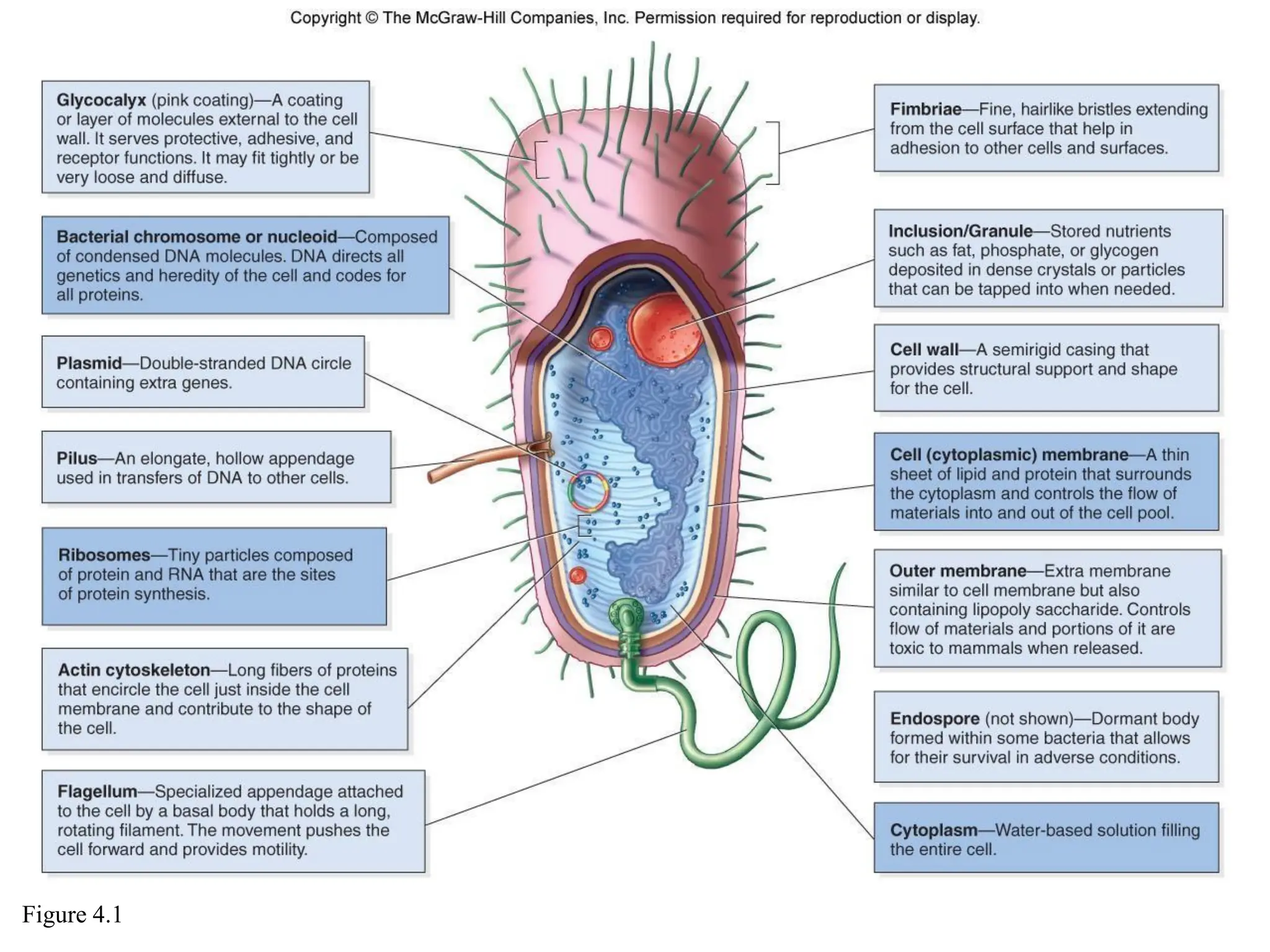
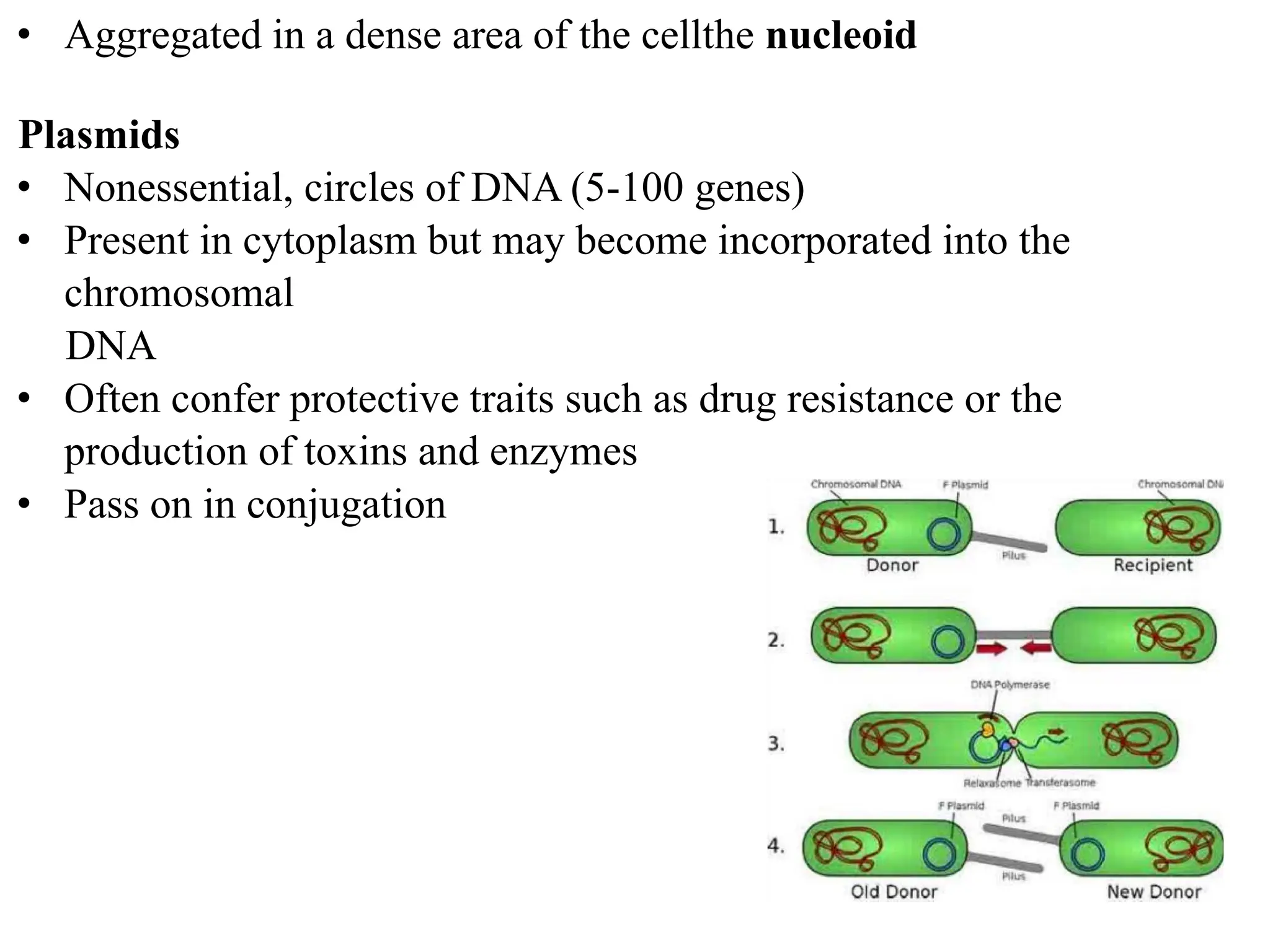
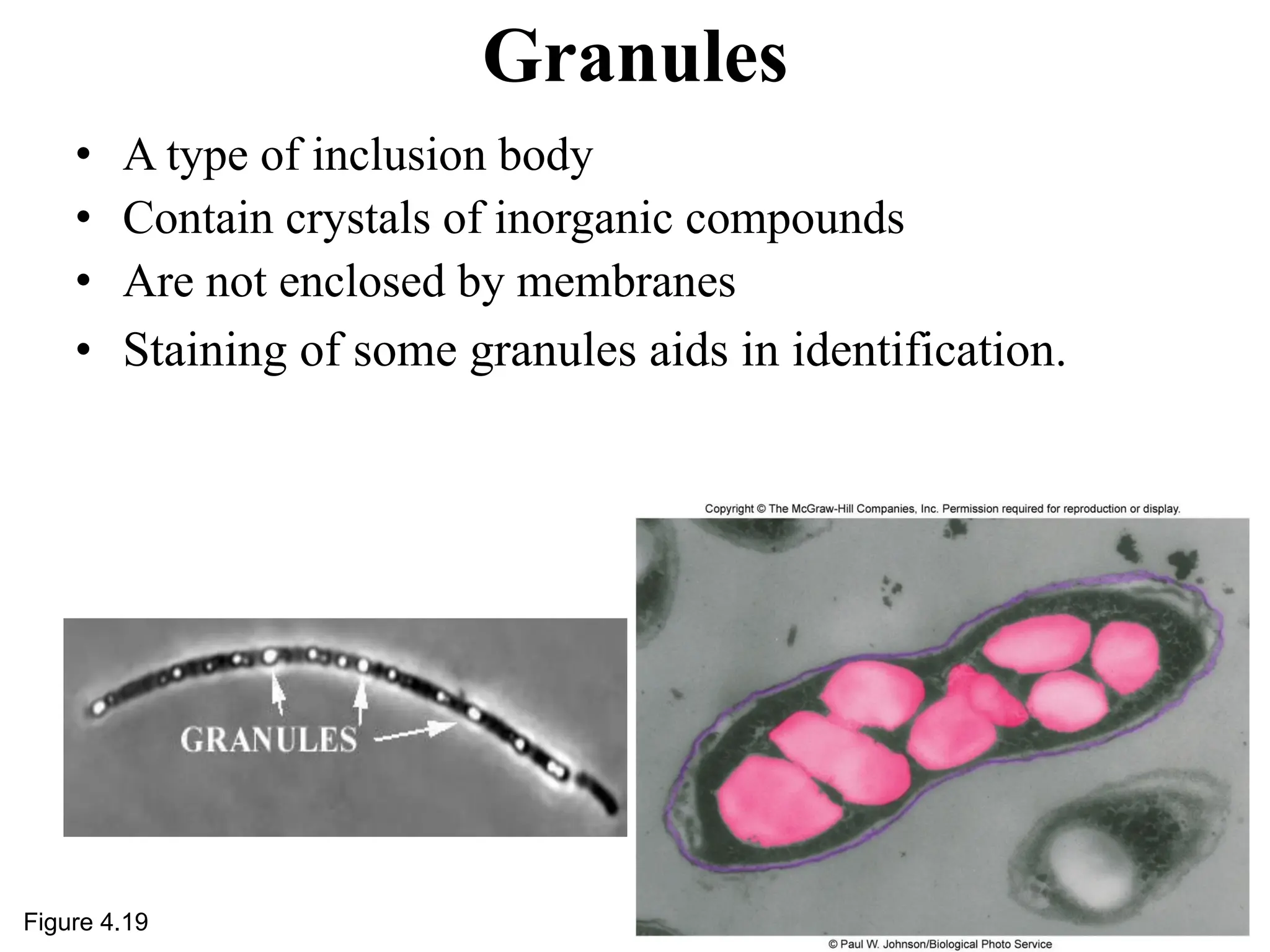
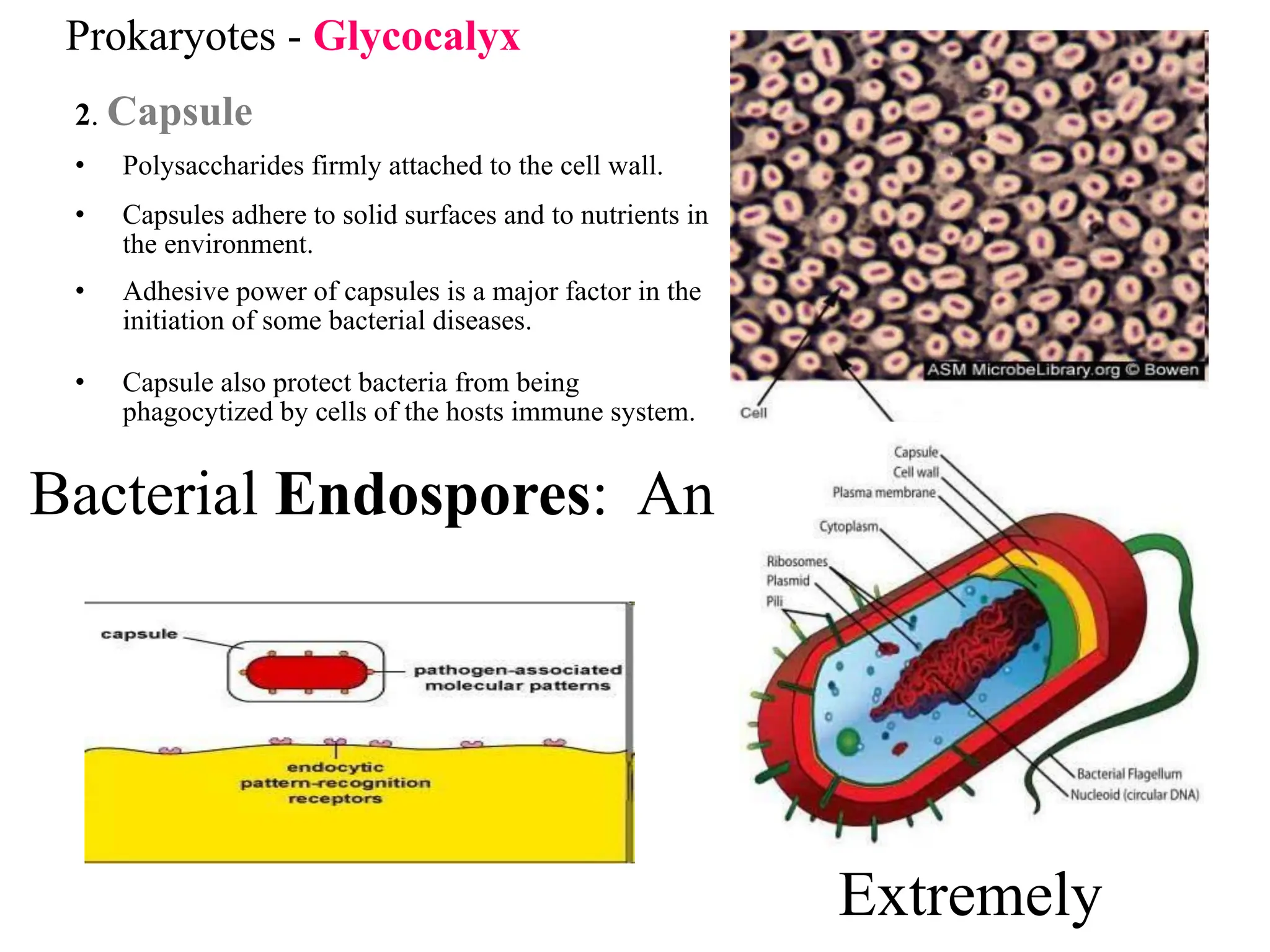
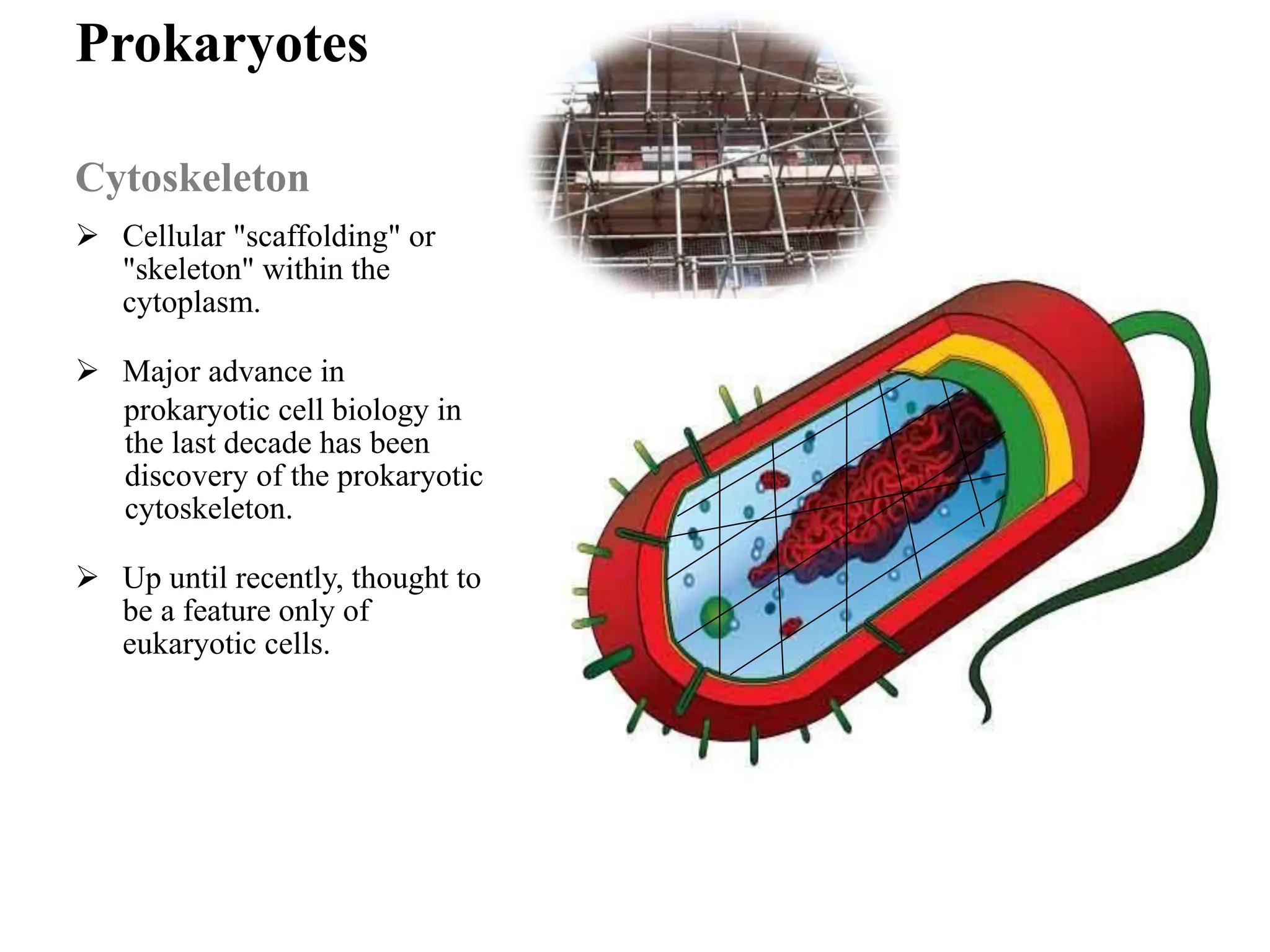
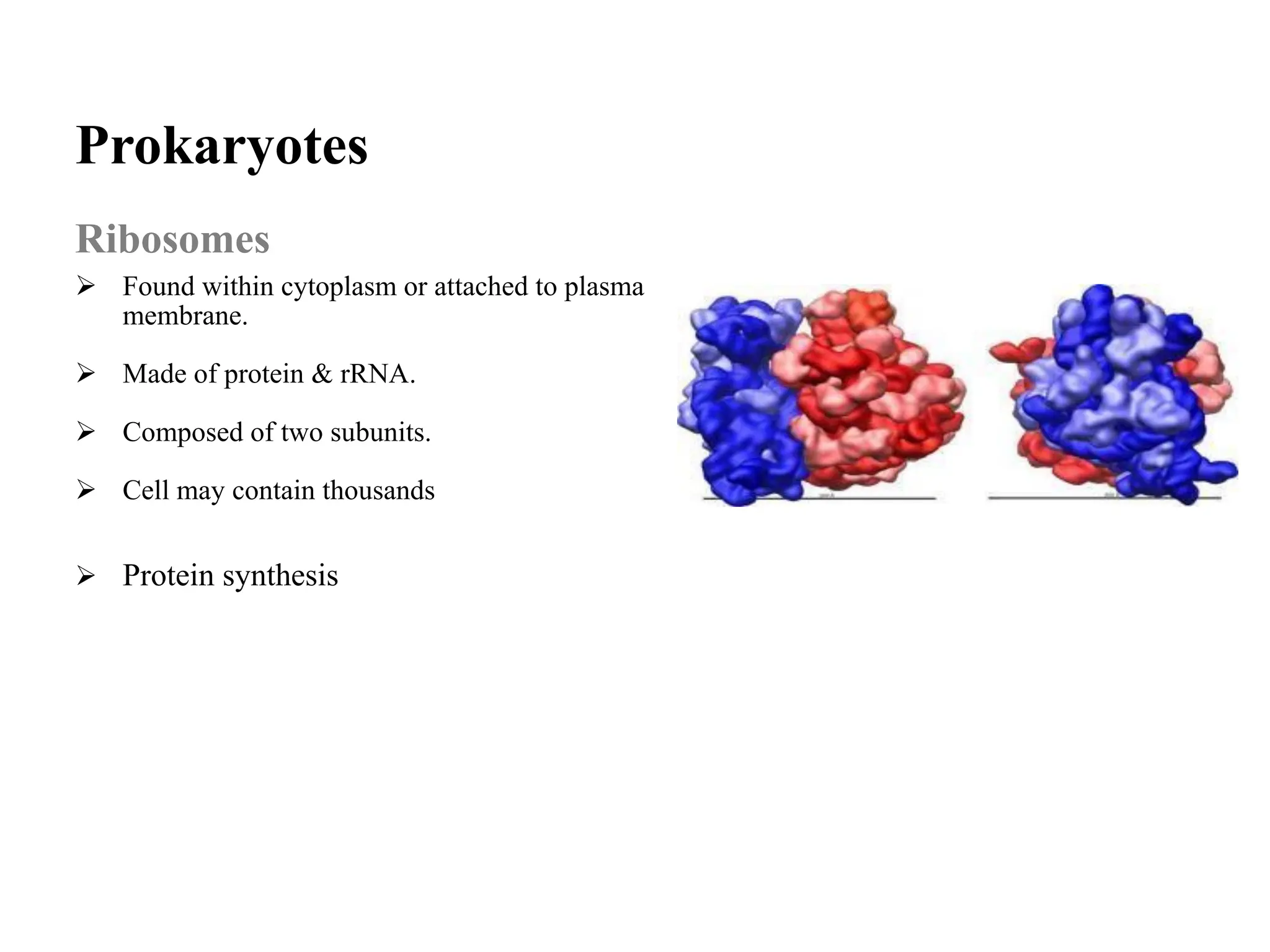
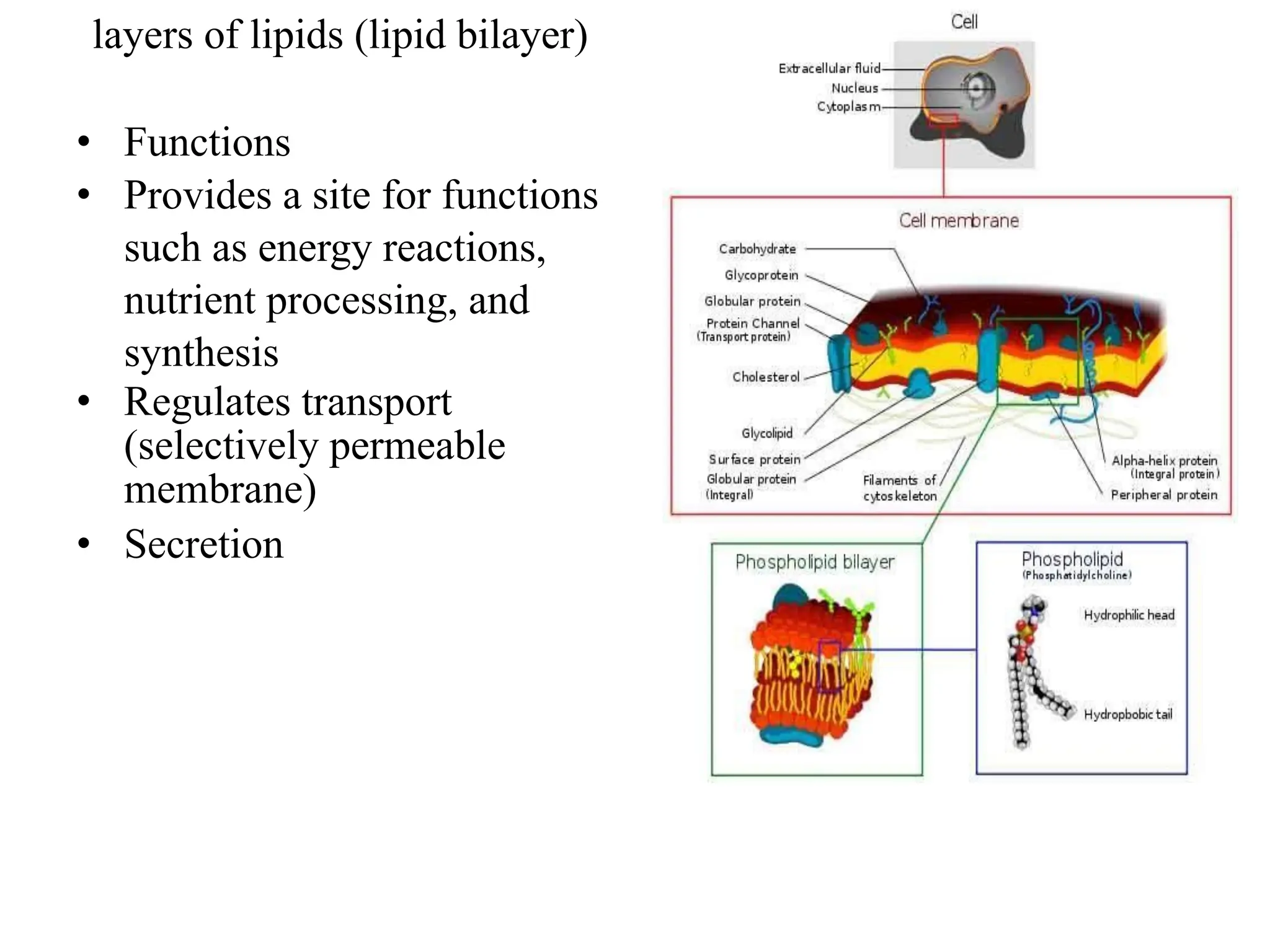
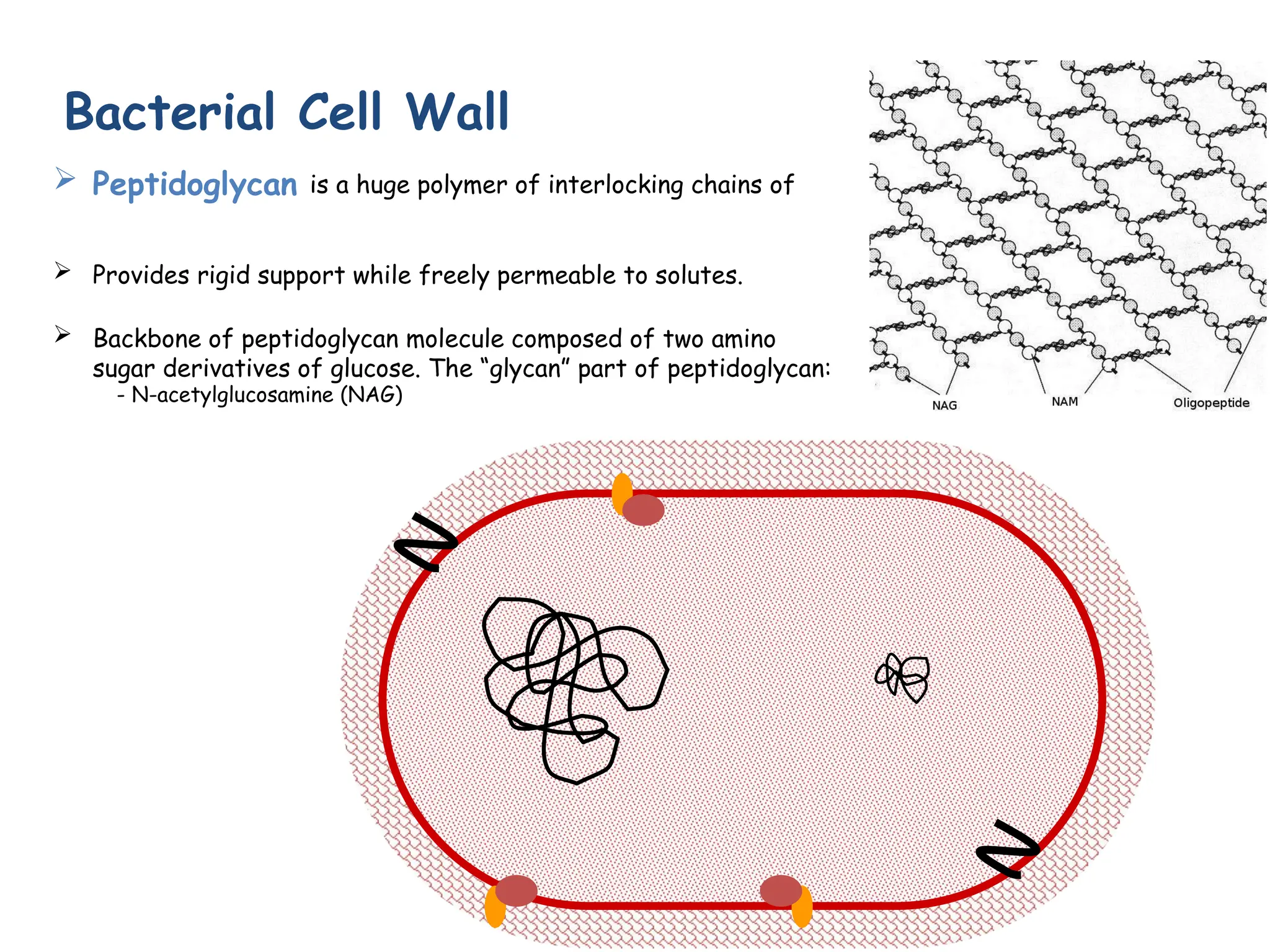
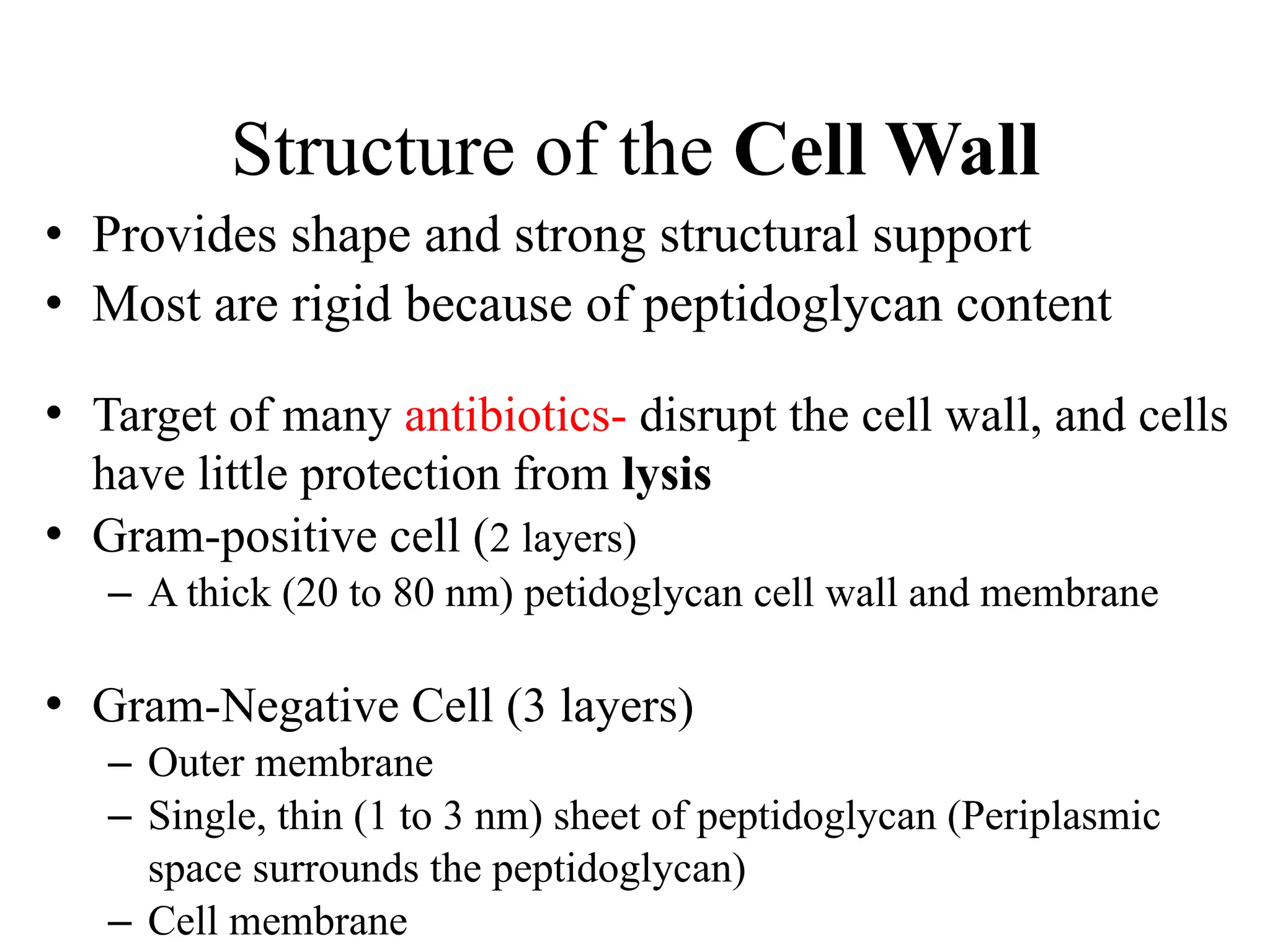
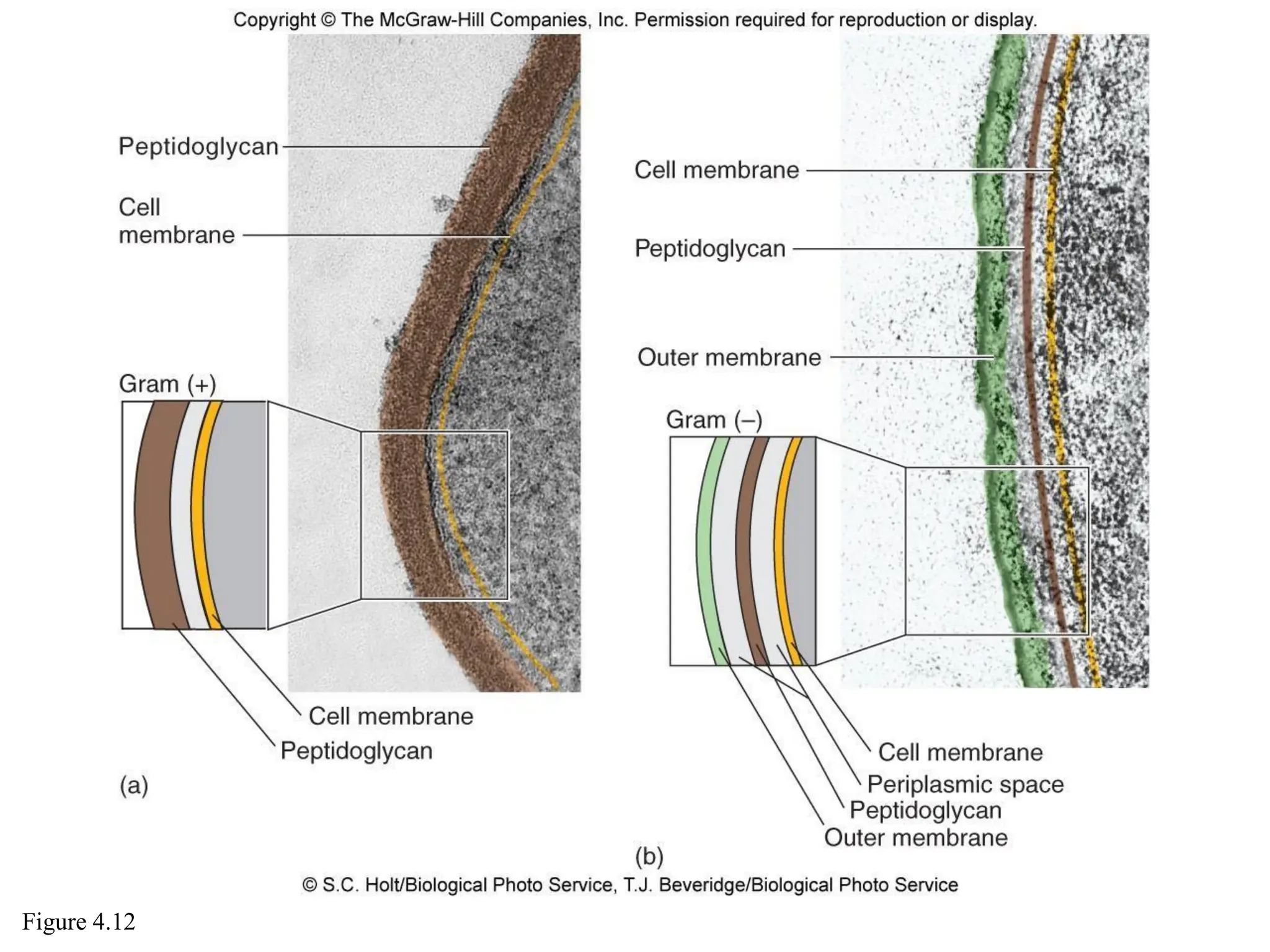
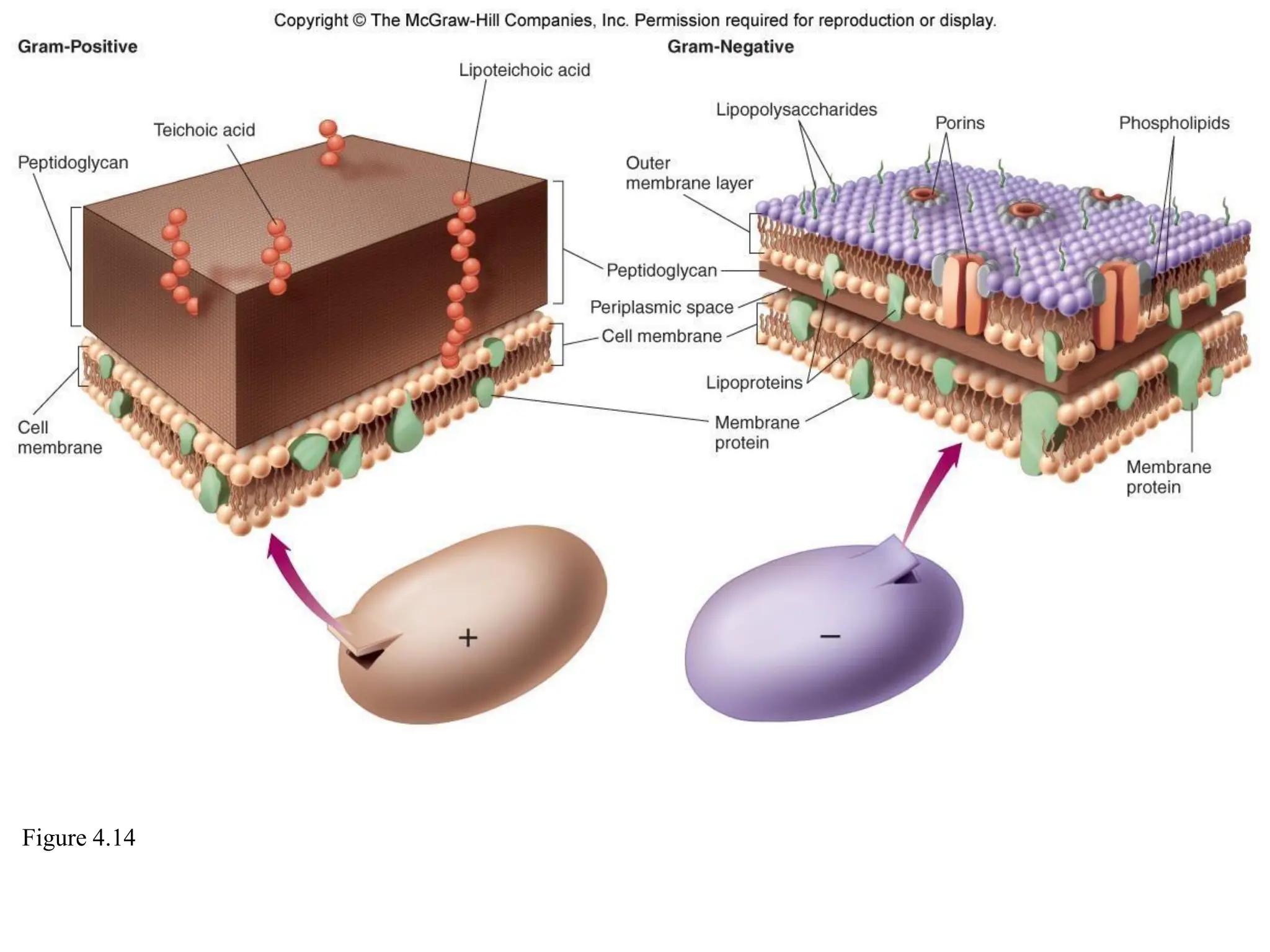
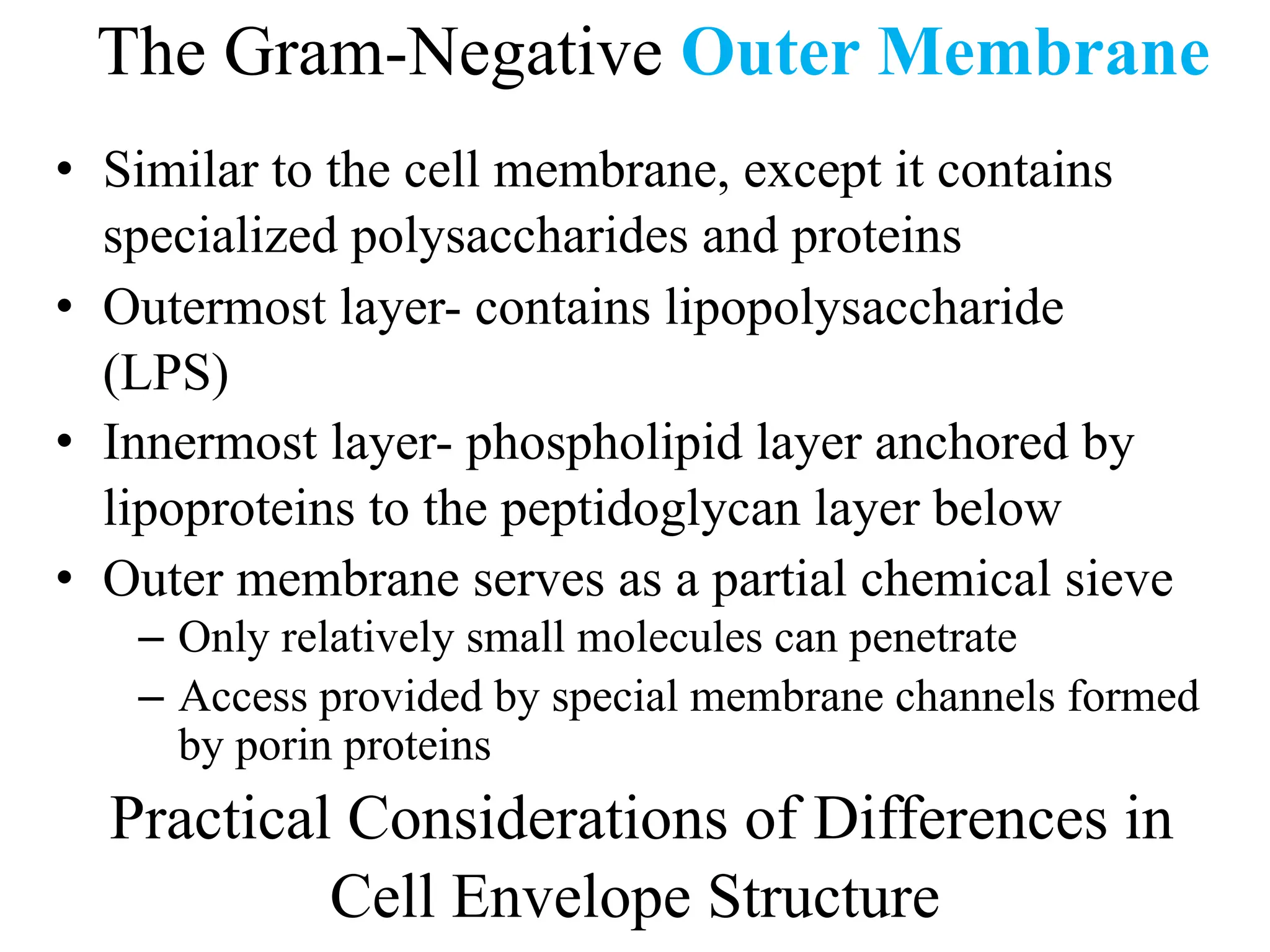
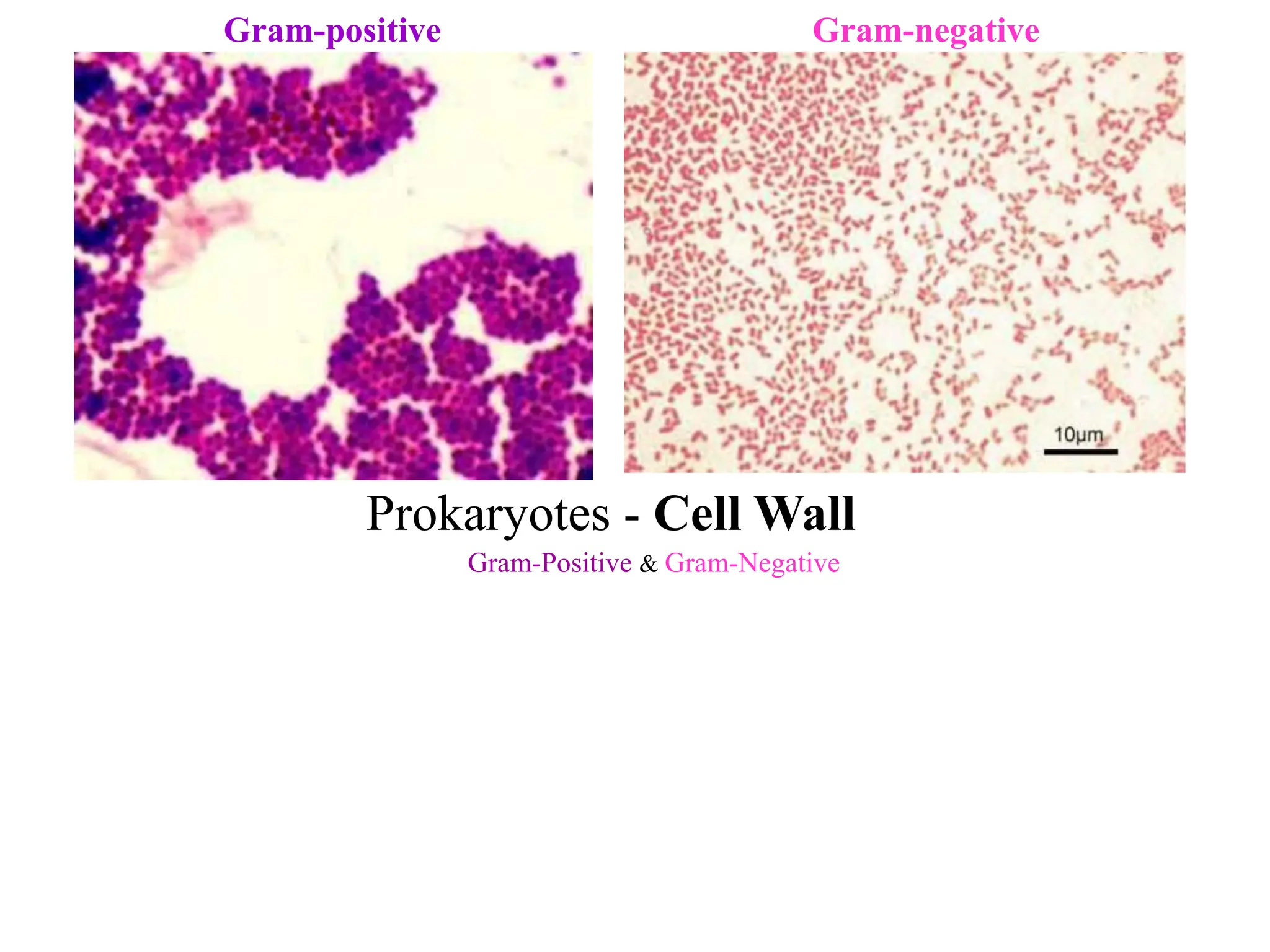
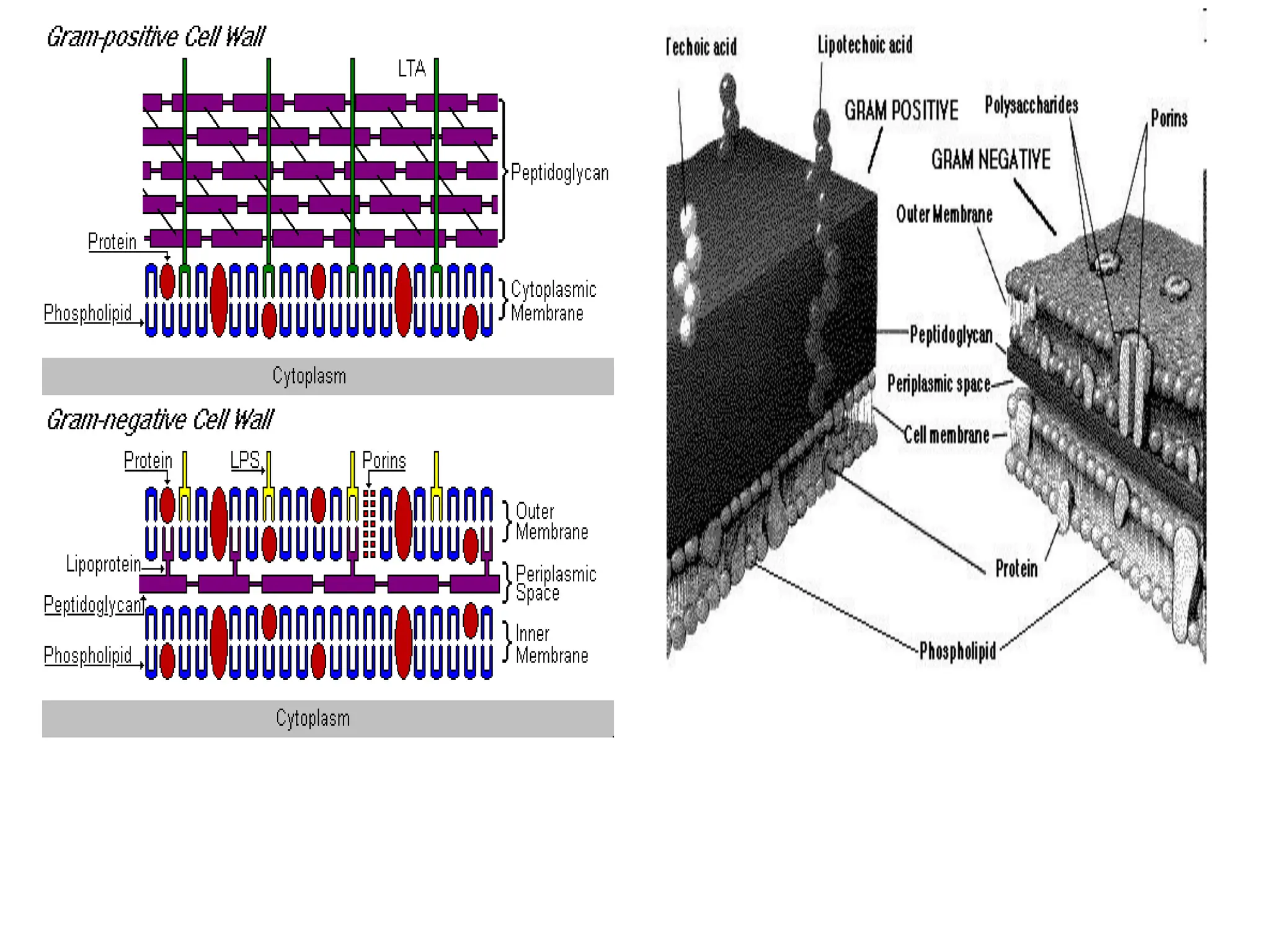
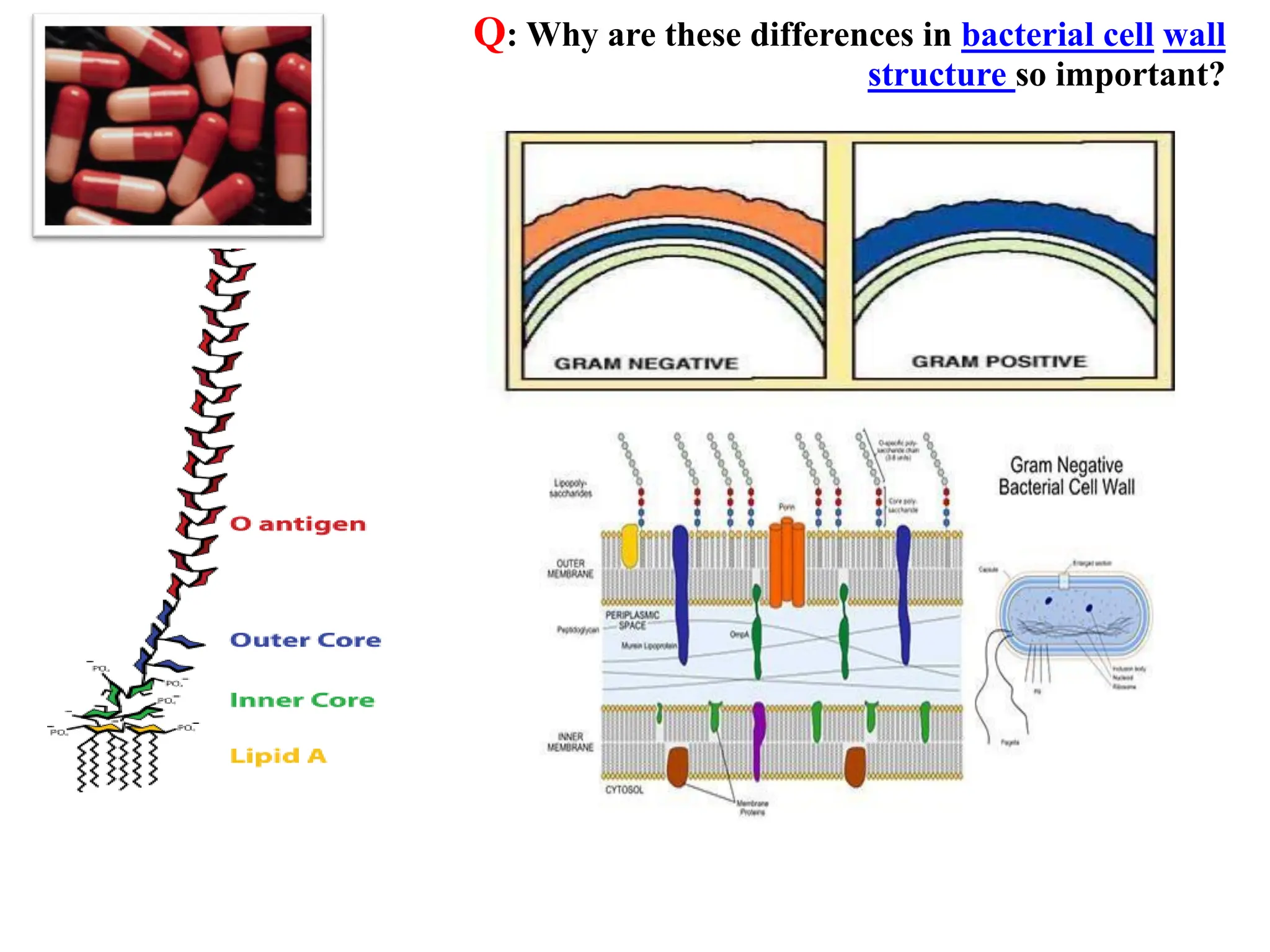
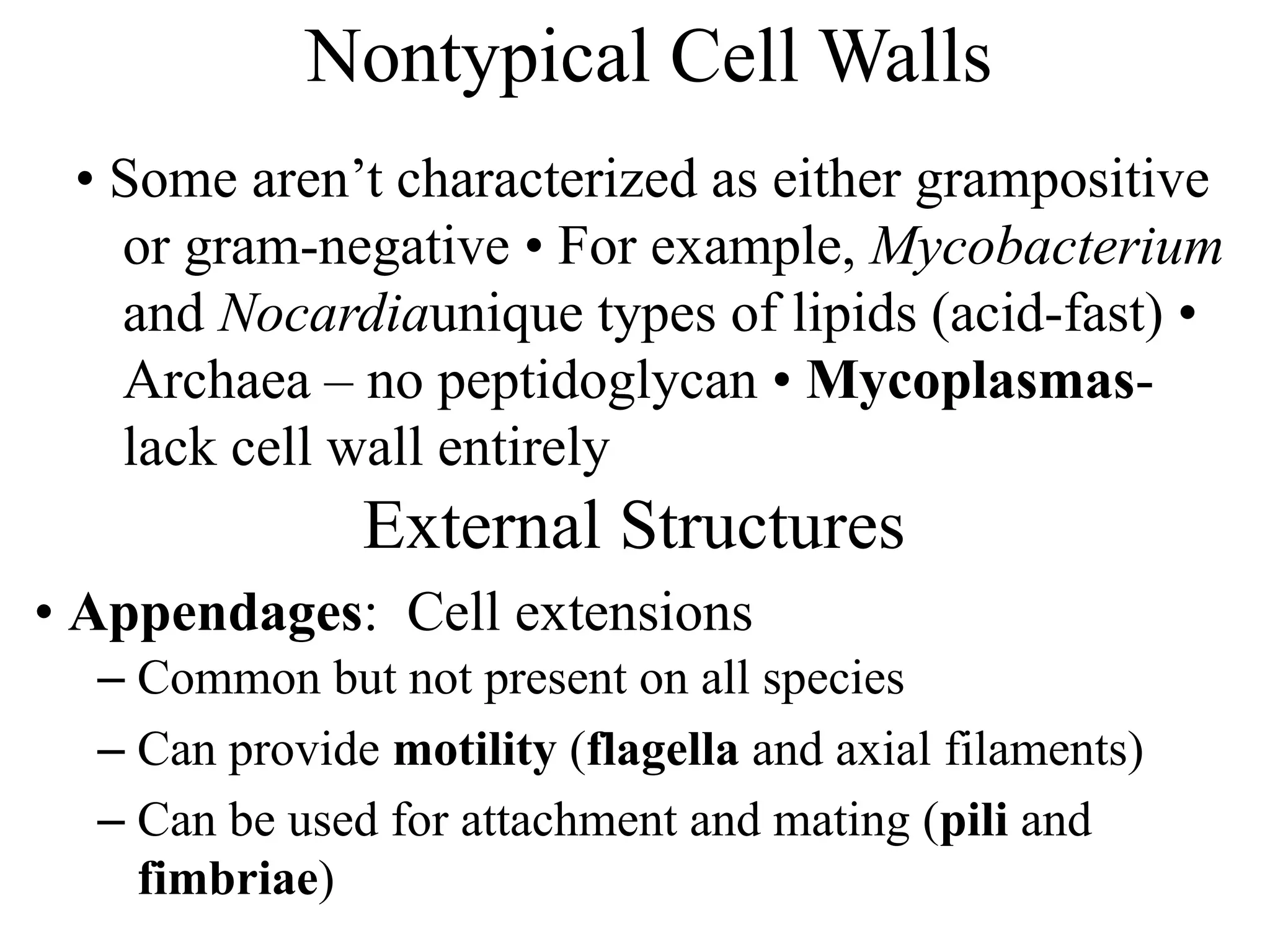
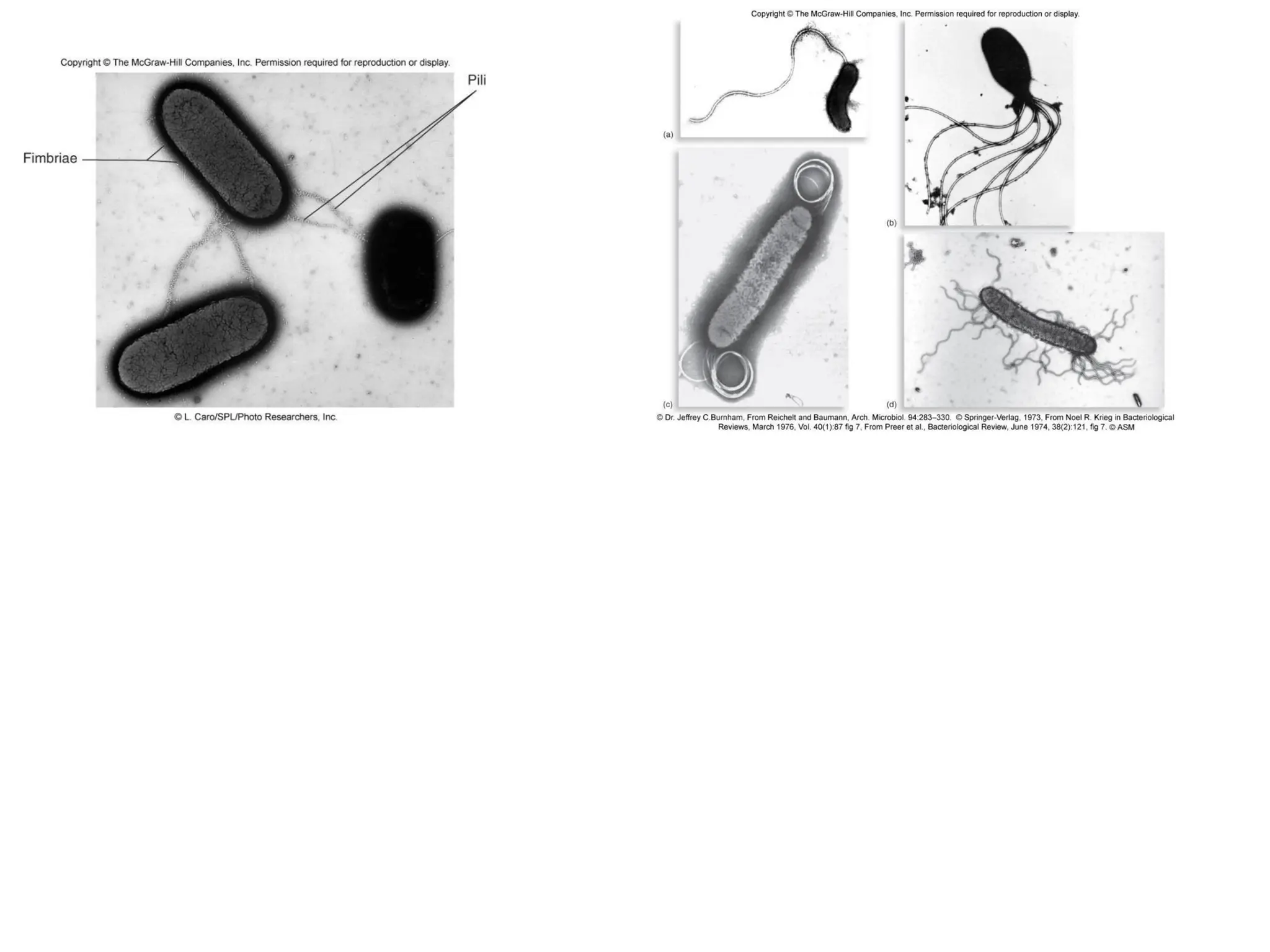
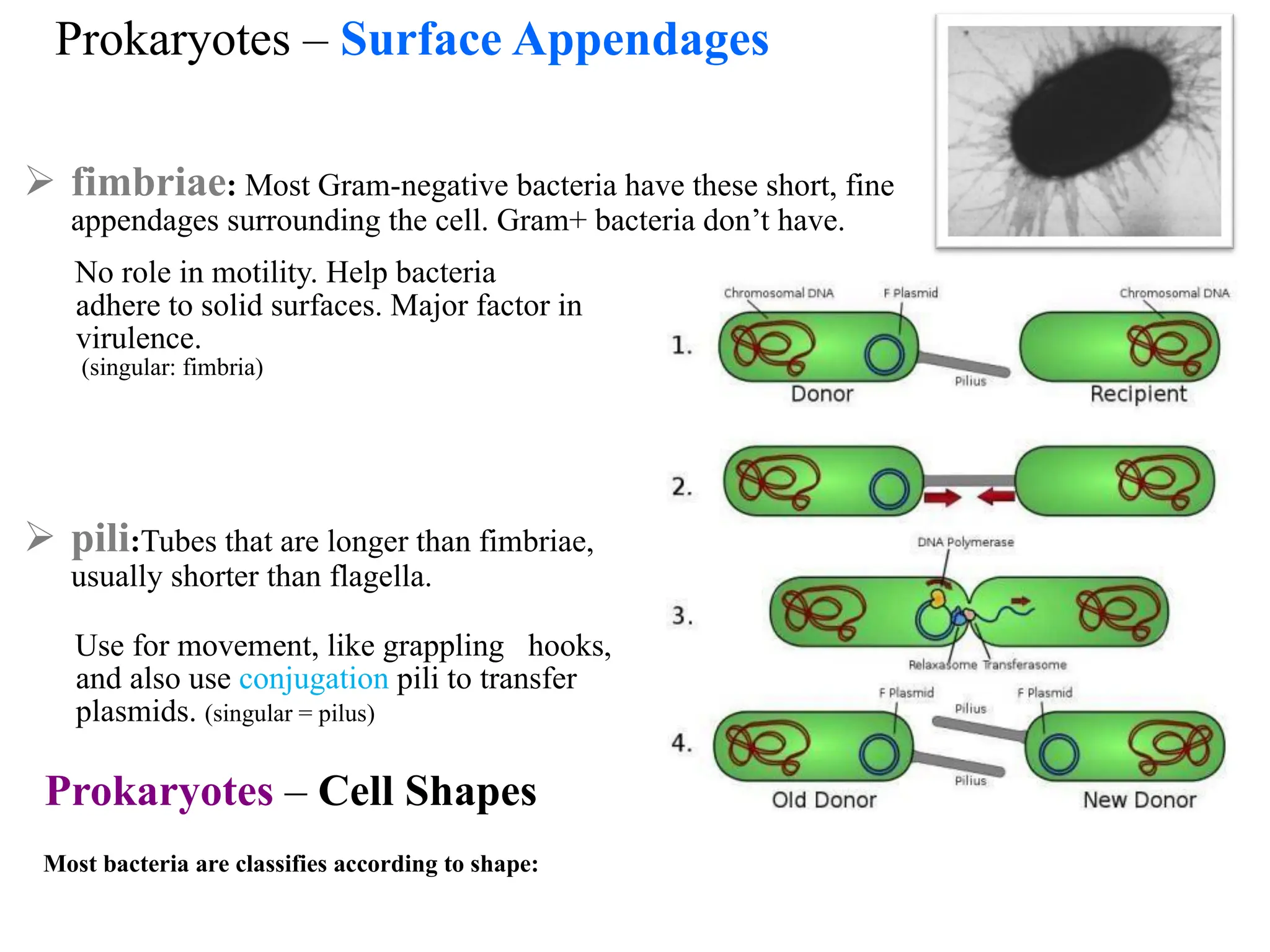
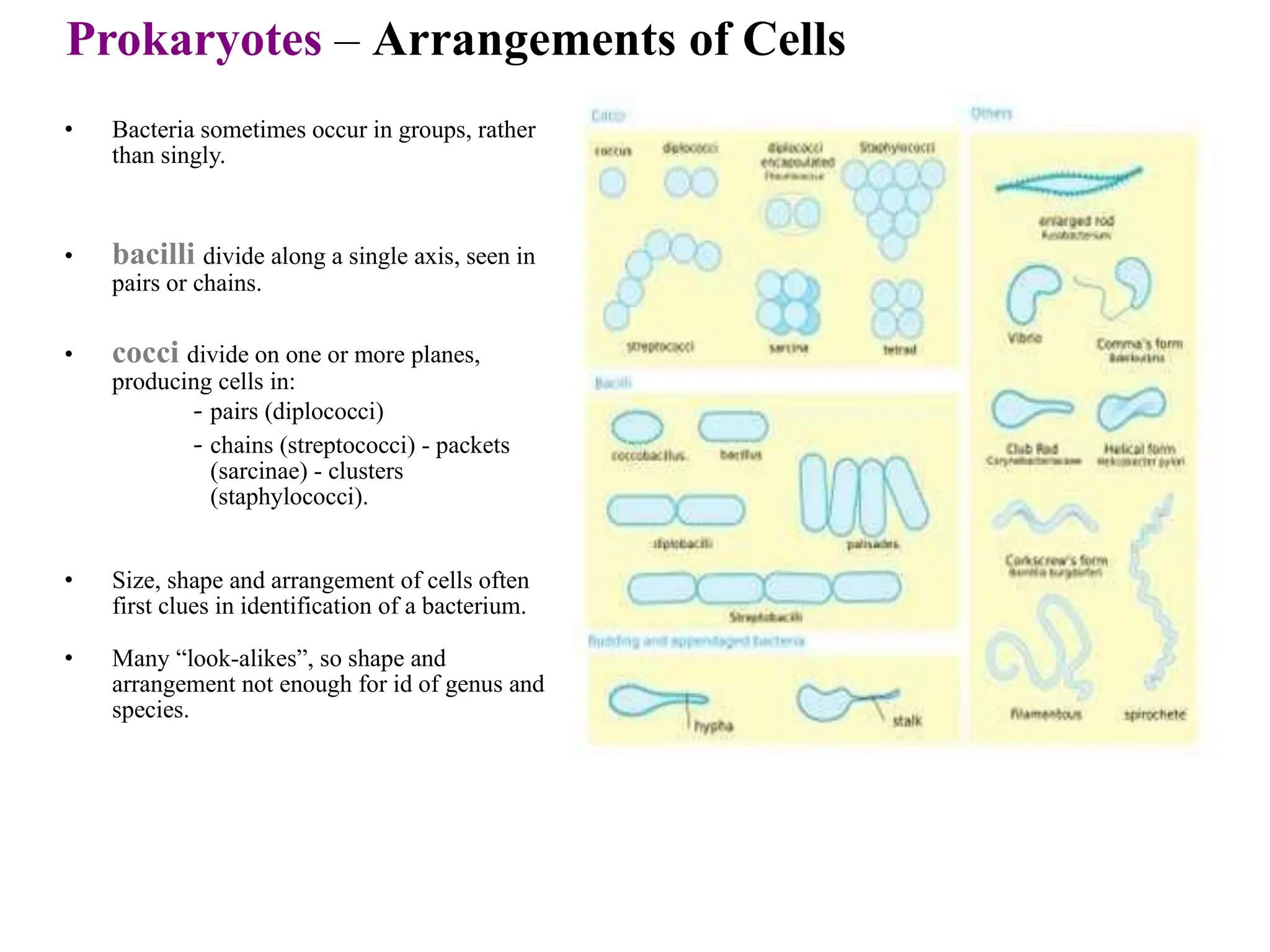
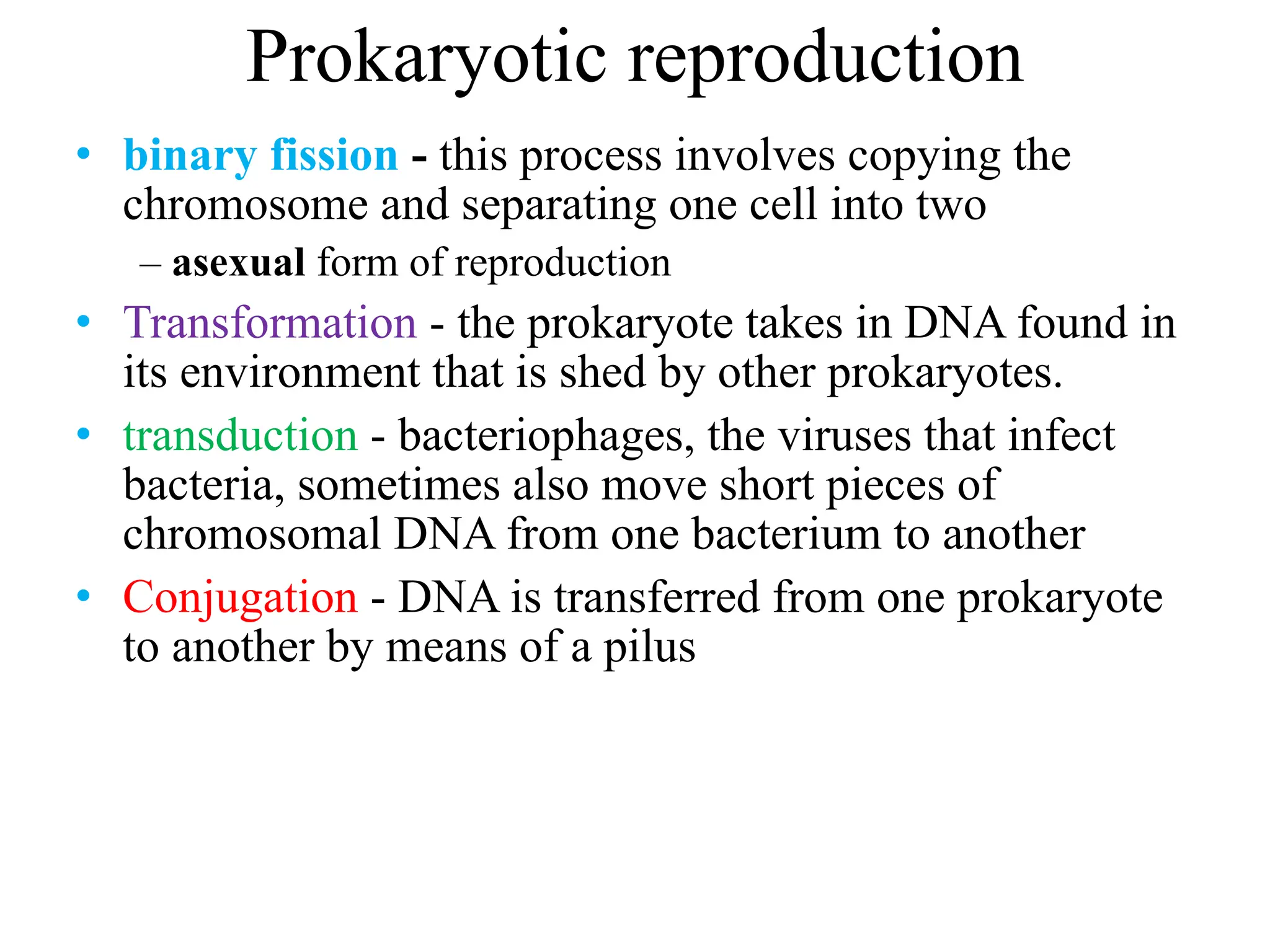
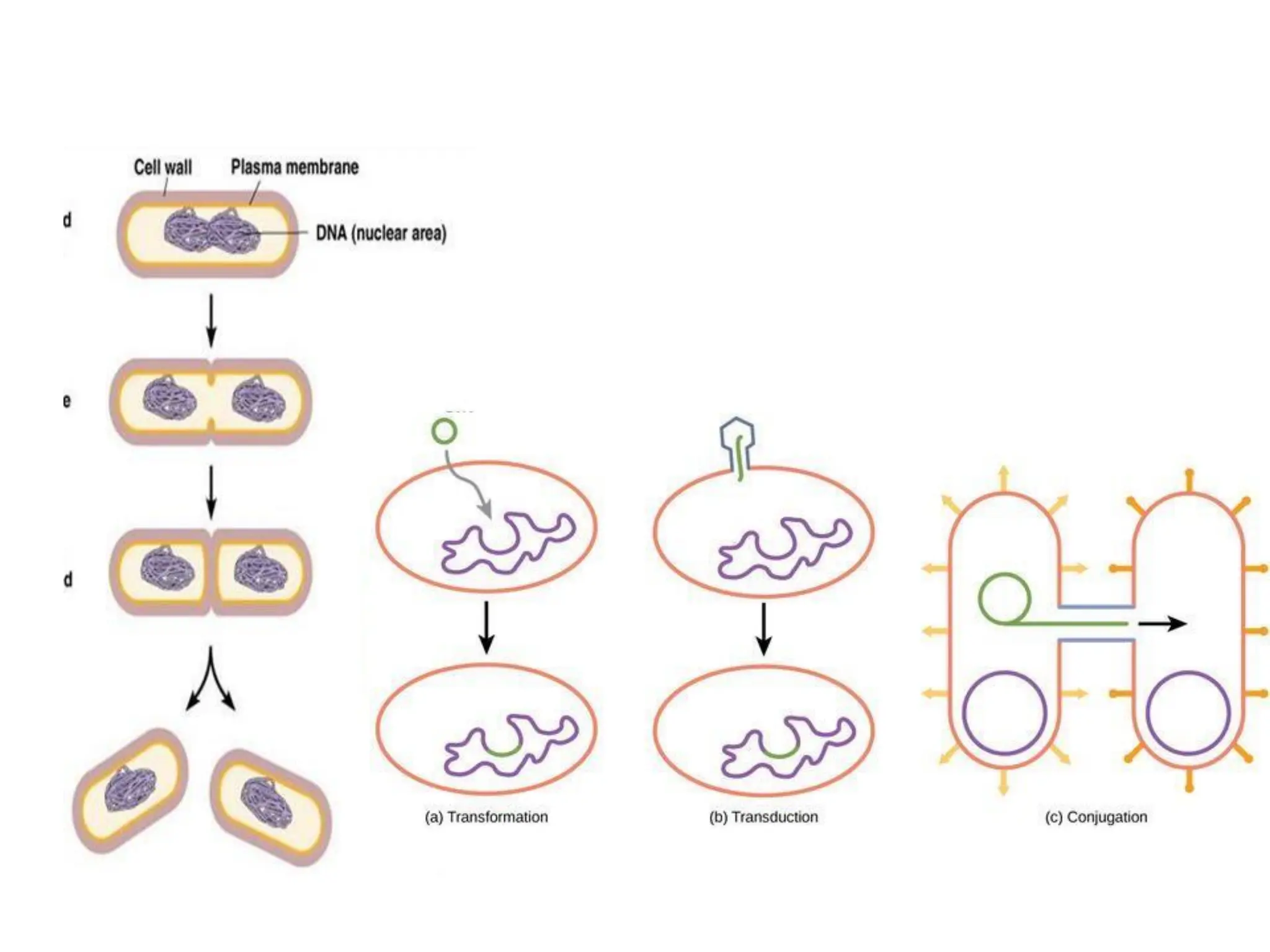
Prokaryotic cells have several key structural differences from eukaryotic cells: they lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, and their DNA is not associated with histones. Their cell walls are composed of peptidoglycan in bacteria or other compounds in archaea. Internal structures include the cytoplasm, ribosomes, plasmids, and inclusions. The cell membrane and glycocalyx coat the outside of the cell and provide protection. Reproduction occurs through binary fission or horizontal gene transfer like transformation, transduction, and conjugation.