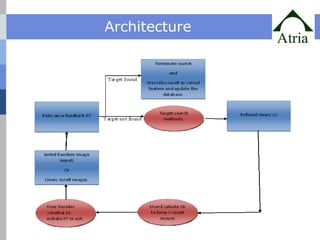
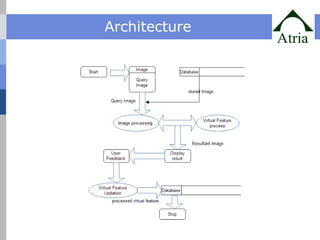
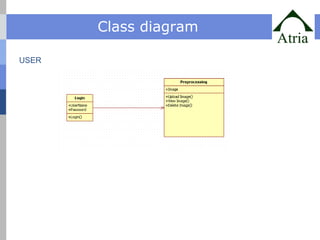
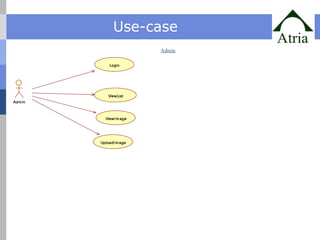
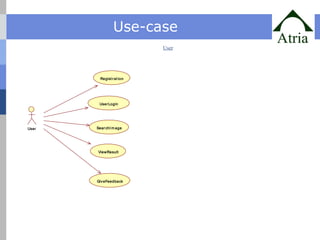
The document outlines advanced techniques for improving target search in content-based image retrieval (CBIR) systems, addressing limitations of existing methods such as slow convergence and inefficiency in handling user feedback. Proposed solutions include new query point movement methods and an innovative index structure aimed at enhancing retrieval speed and accuracy. The system is designed to provide users with a responsive interface and effectively process image searches based on user relevance feedback.