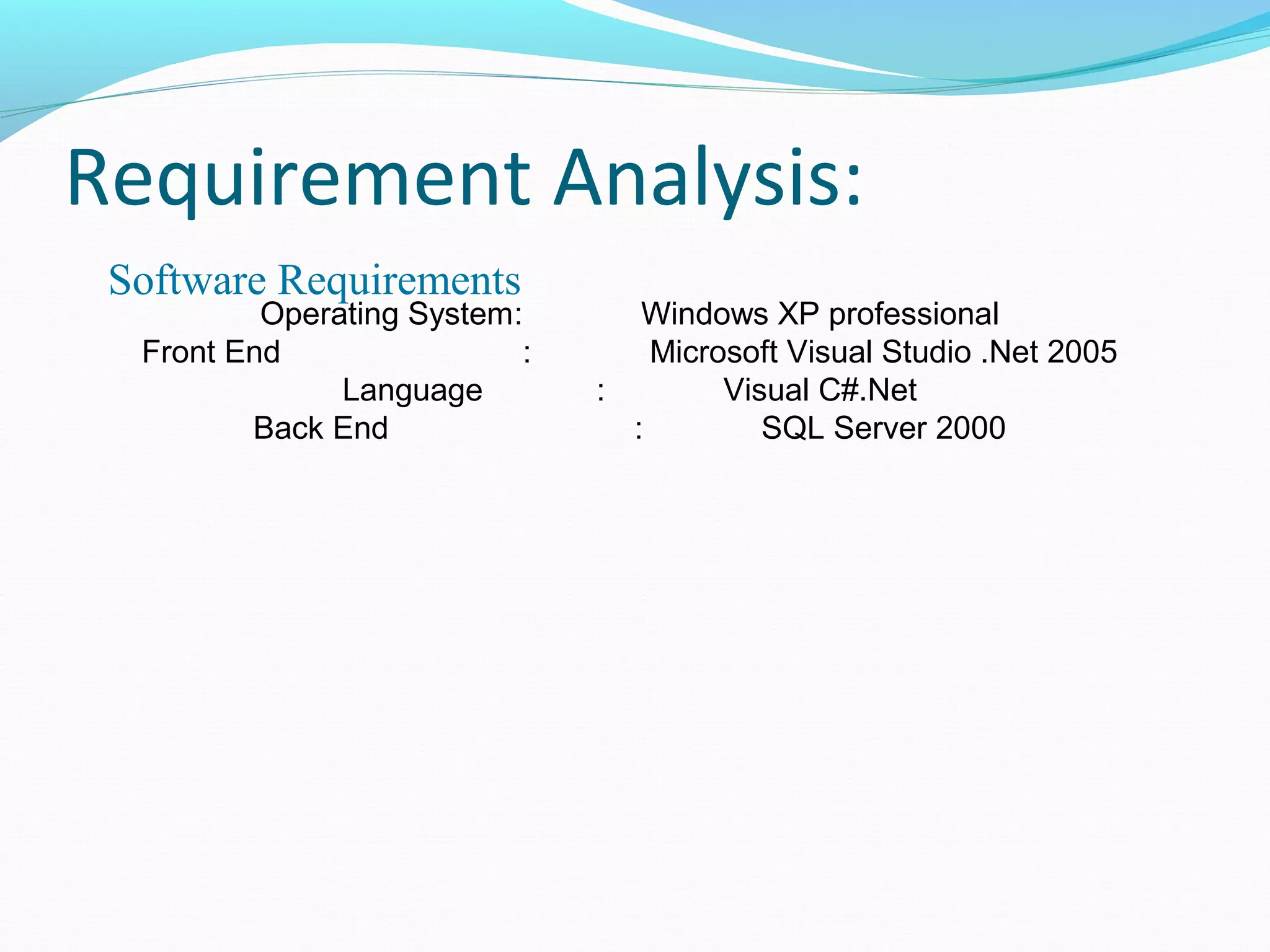
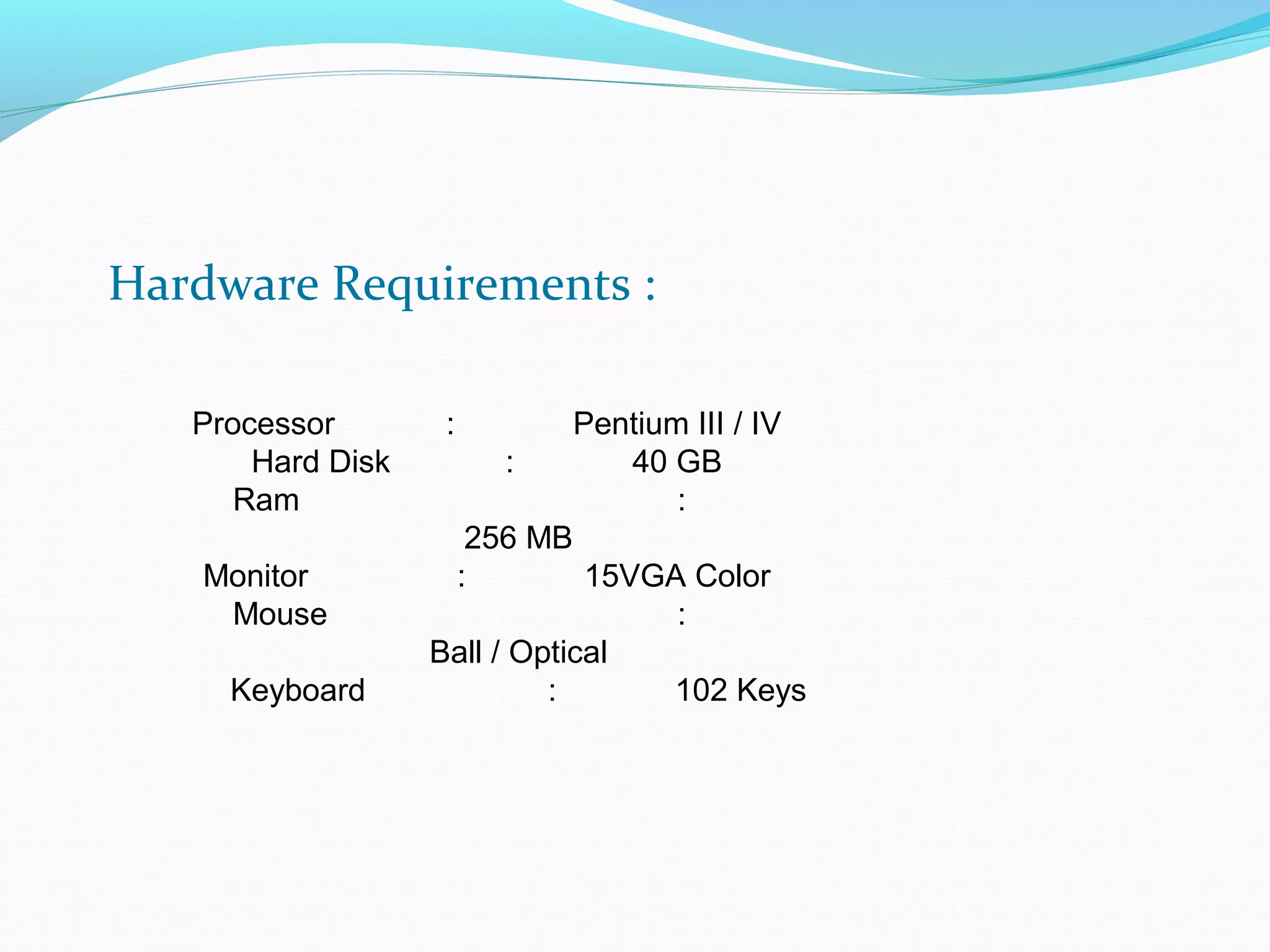
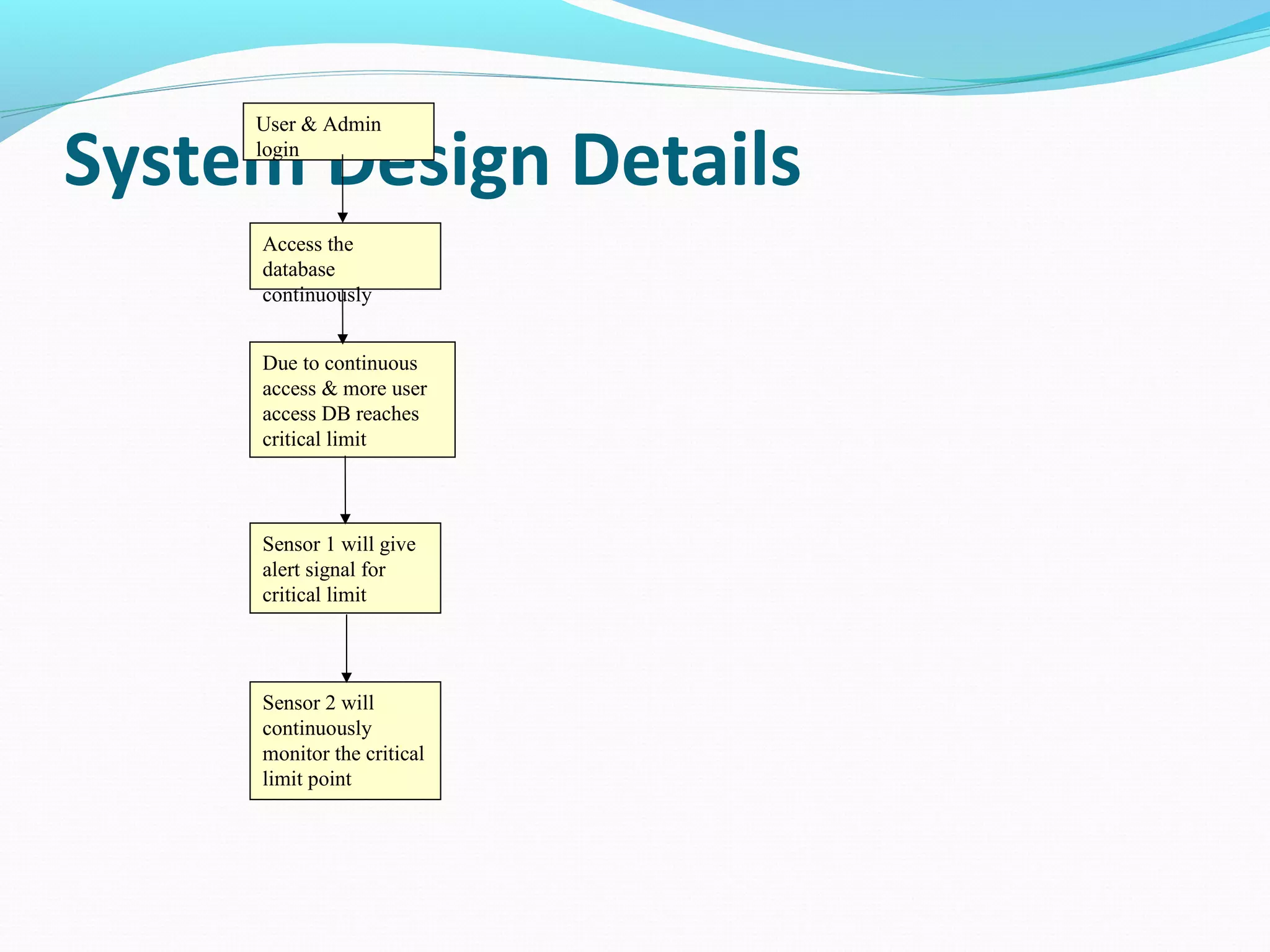
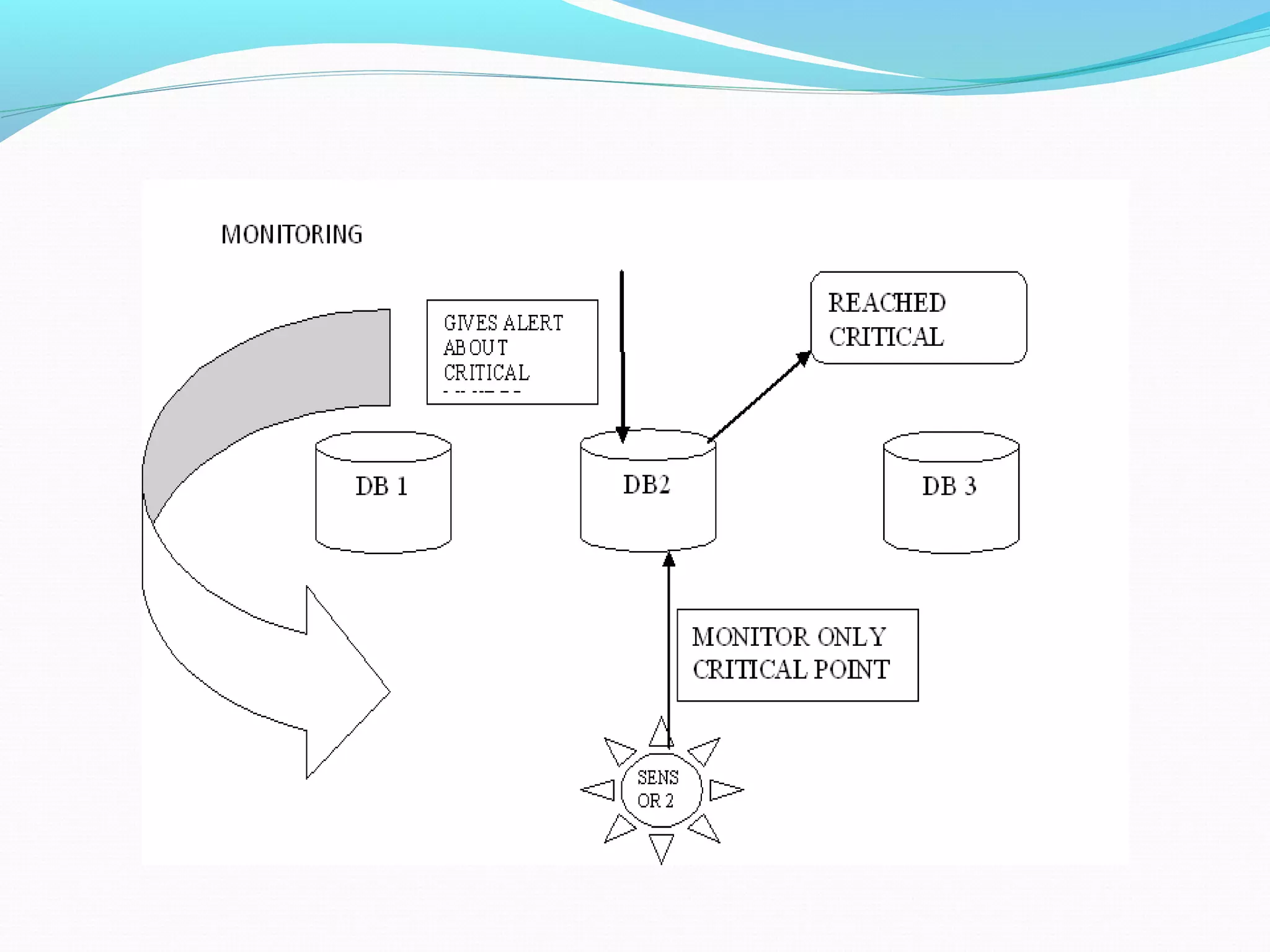
This document discusses energy efficient processing of reverse skyline queries in wireless sensor networks. It proposes using a full skyband approach to minimize communication costs among sensor nodes when evaluating range reverse skyline queries. It also discusses optimization mechanisms for improving the performance of multiple reverse skyline queries, including vertical and horizontal optimizations. Extensive experiments on real and synthetic data demonstrate the efficiency and effectiveness of the proposed approaches.