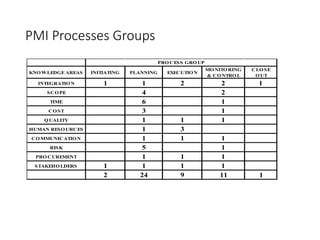
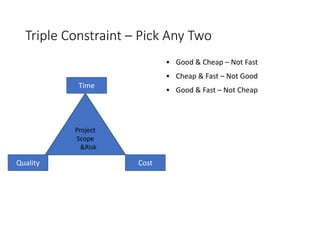
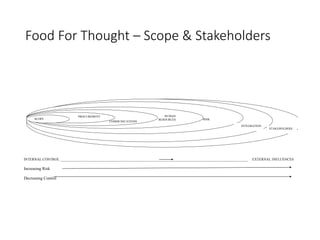
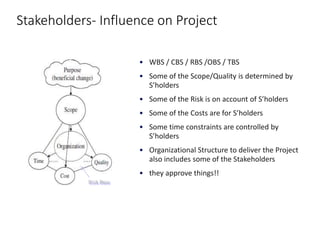
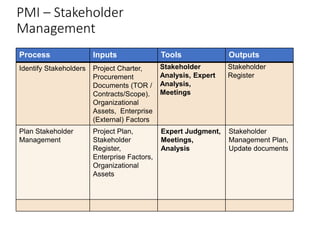
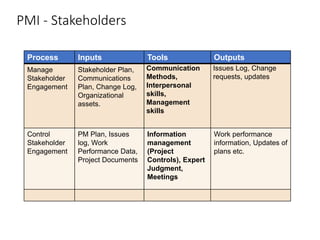
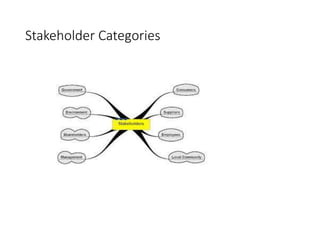
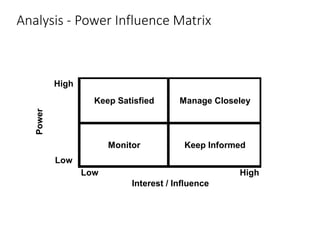
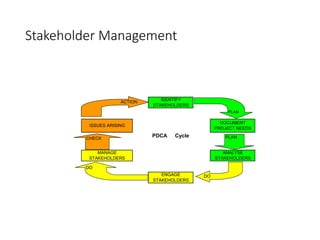
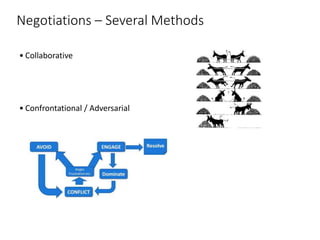
This document discusses stakeholder management in project management. It notes that stakeholder recognition has grown from a single page in 1996 to a full chapter in 2013 in PMI standards. Stakeholders can influence all aspects of a project including scope, risks, costs, timelines, and organizational structure. Effective stakeholder identification, engagement, and management is important for project success, while failure to manage stakeholders properly can lead to project cancellation or cost overruns. The document provides frameworks for analyzing stakeholders and engaging with them throughout the project lifecycle.