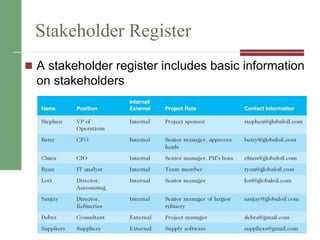
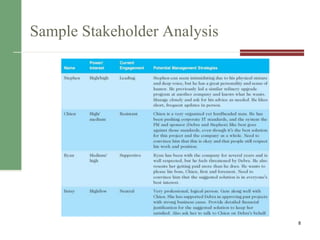
This document discusses stakeholder management, which is an important knowledge area for project managers. It identifies the key processes for managing stakeholders as identifying stakeholders, planning stakeholder management, managing stakeholder engagement, and controlling stakeholder engagement. The document provides examples of how to identify and classify stakeholders, as well as best practices for planning, engaging with, and controlling stakeholders over the course of a project. Managing stakeholders effectively is important for project success and addressing potential issues or changes that can impact organizations during a project.