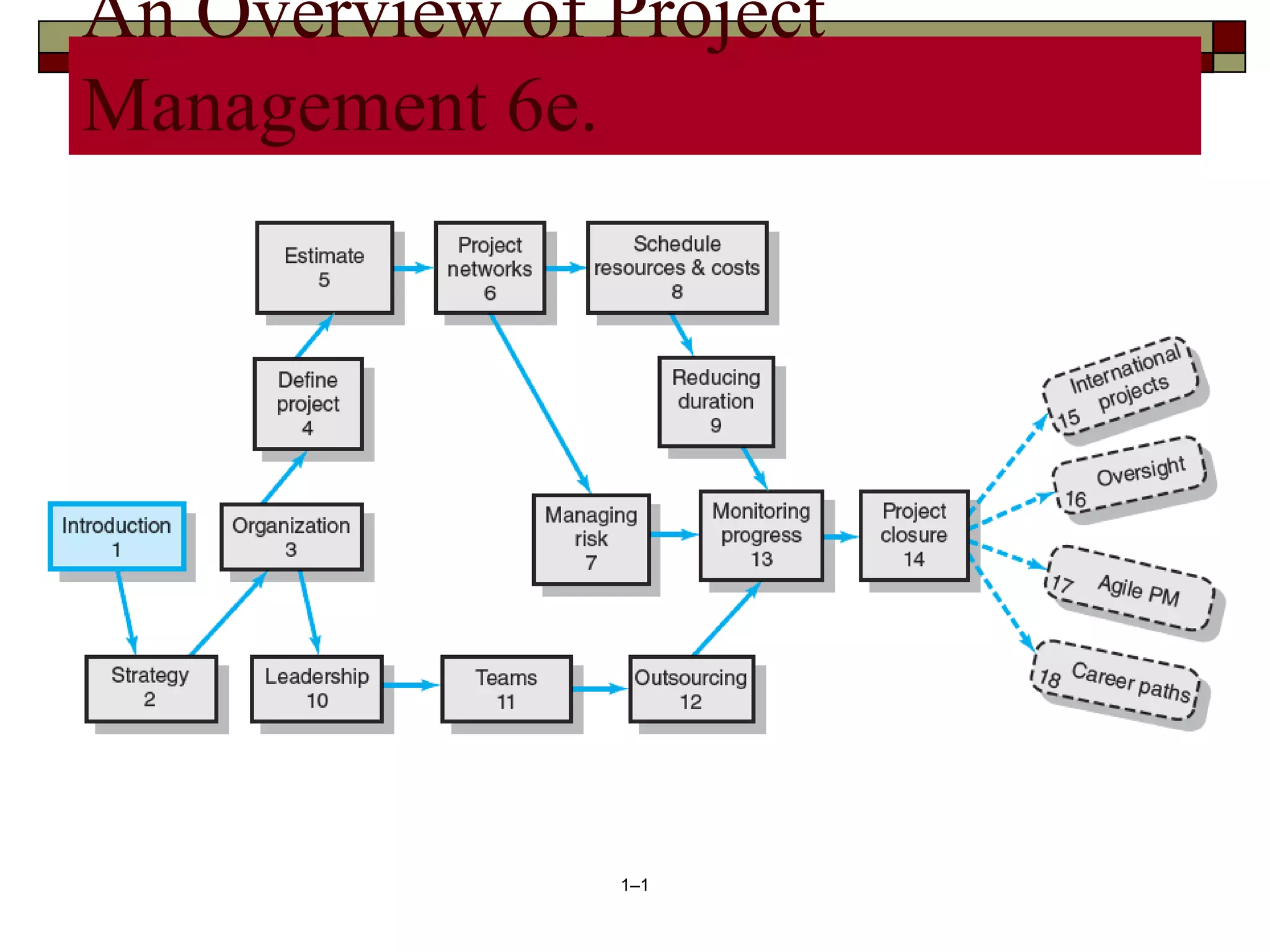
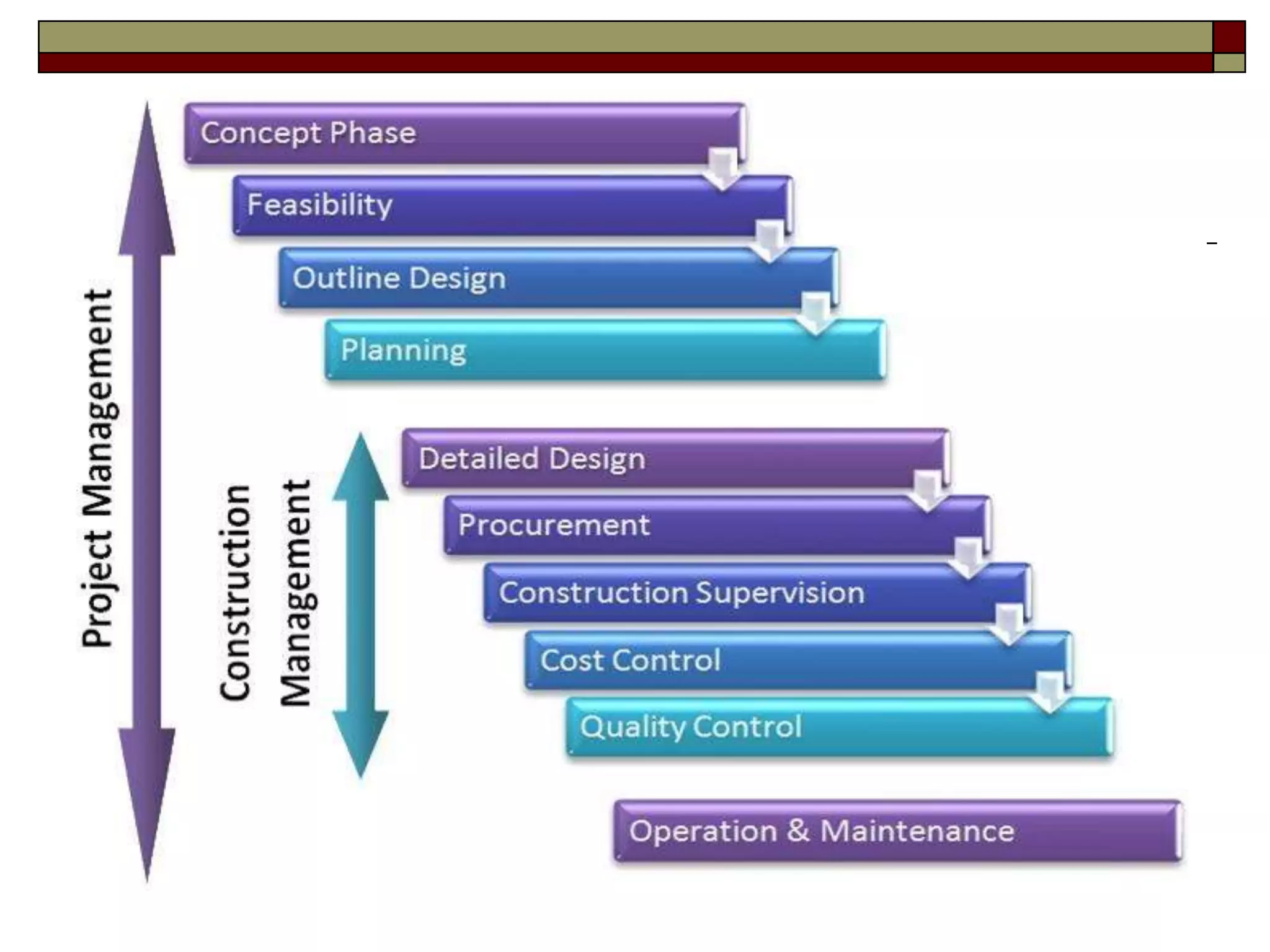
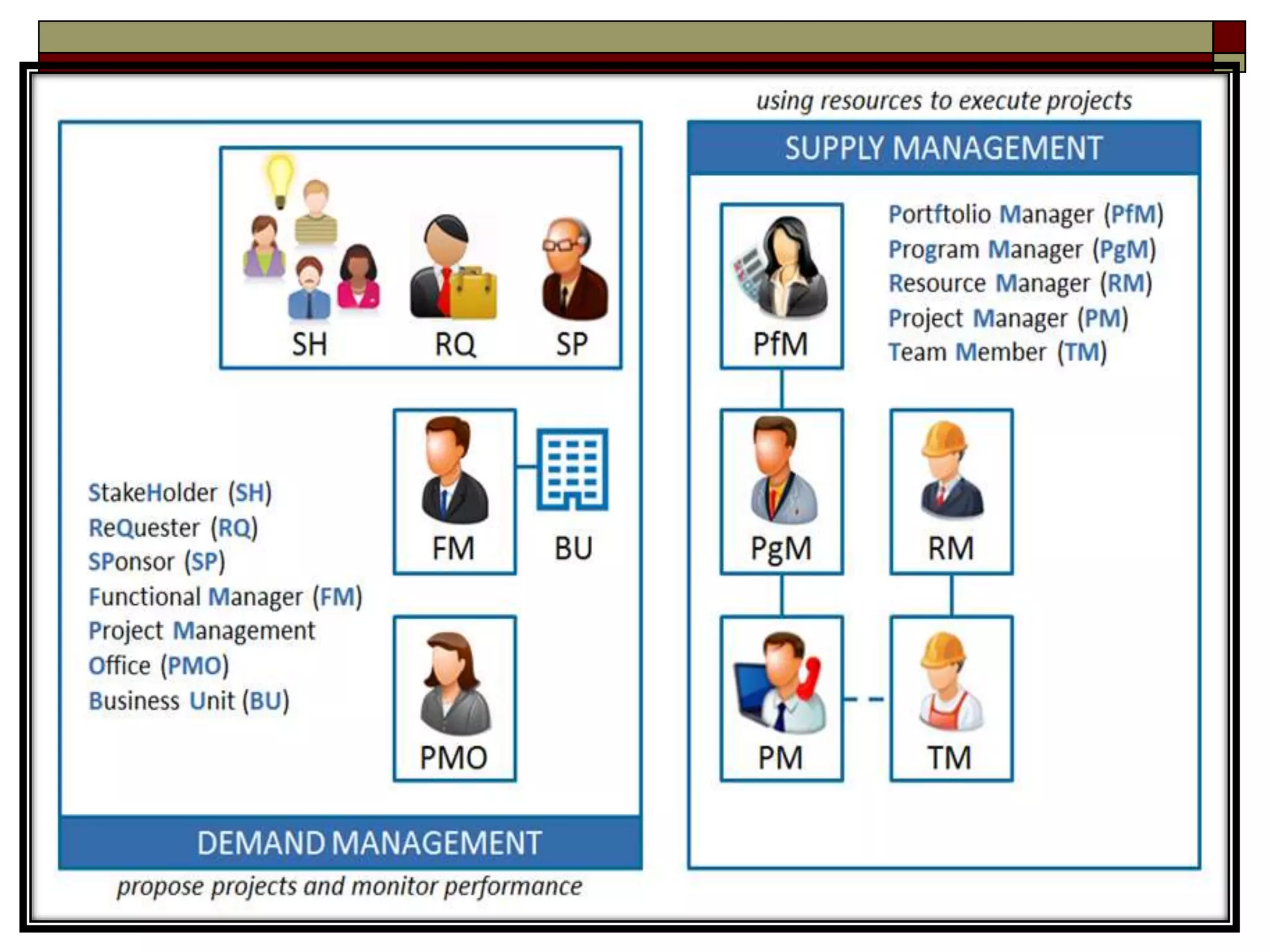
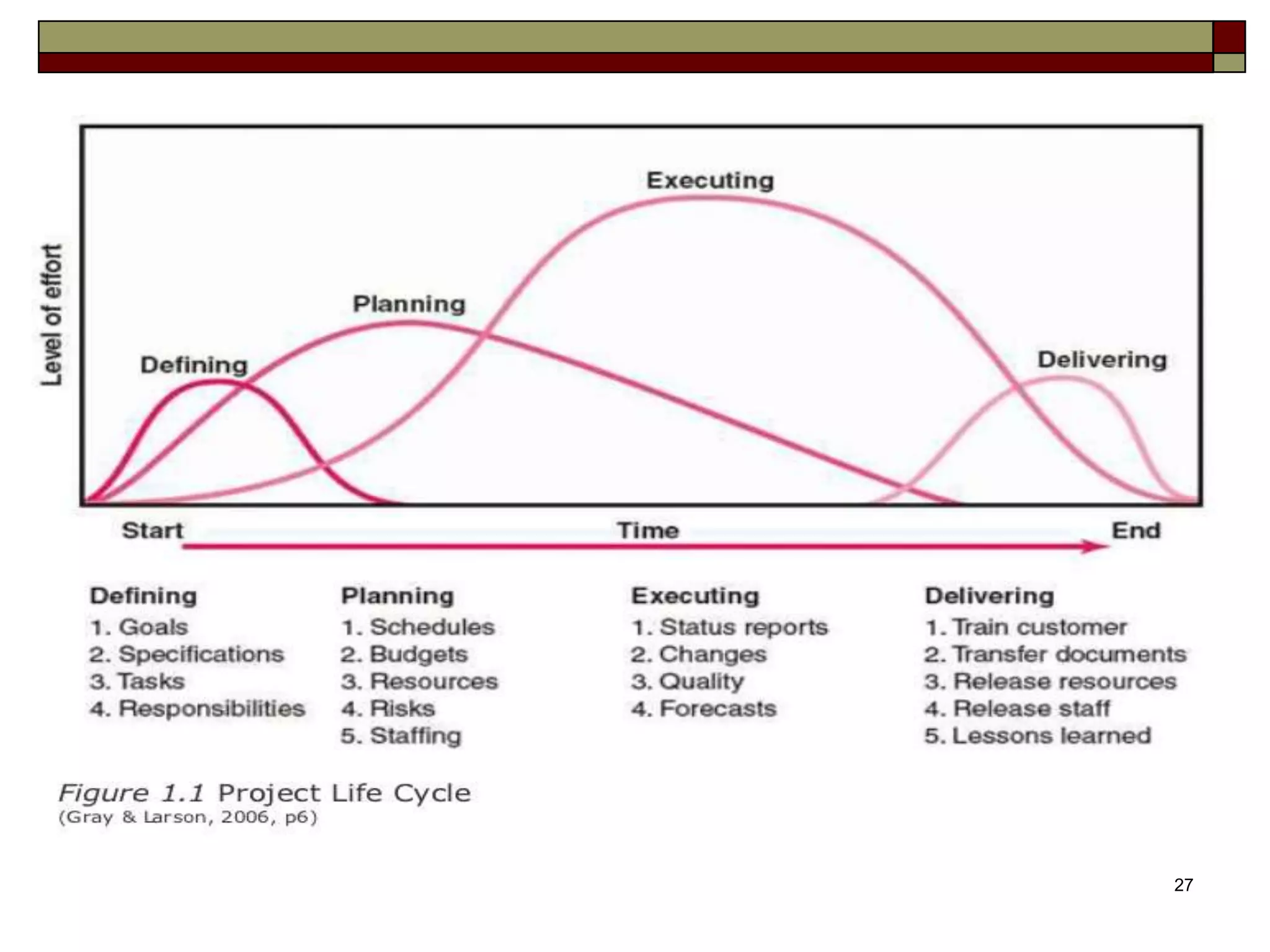
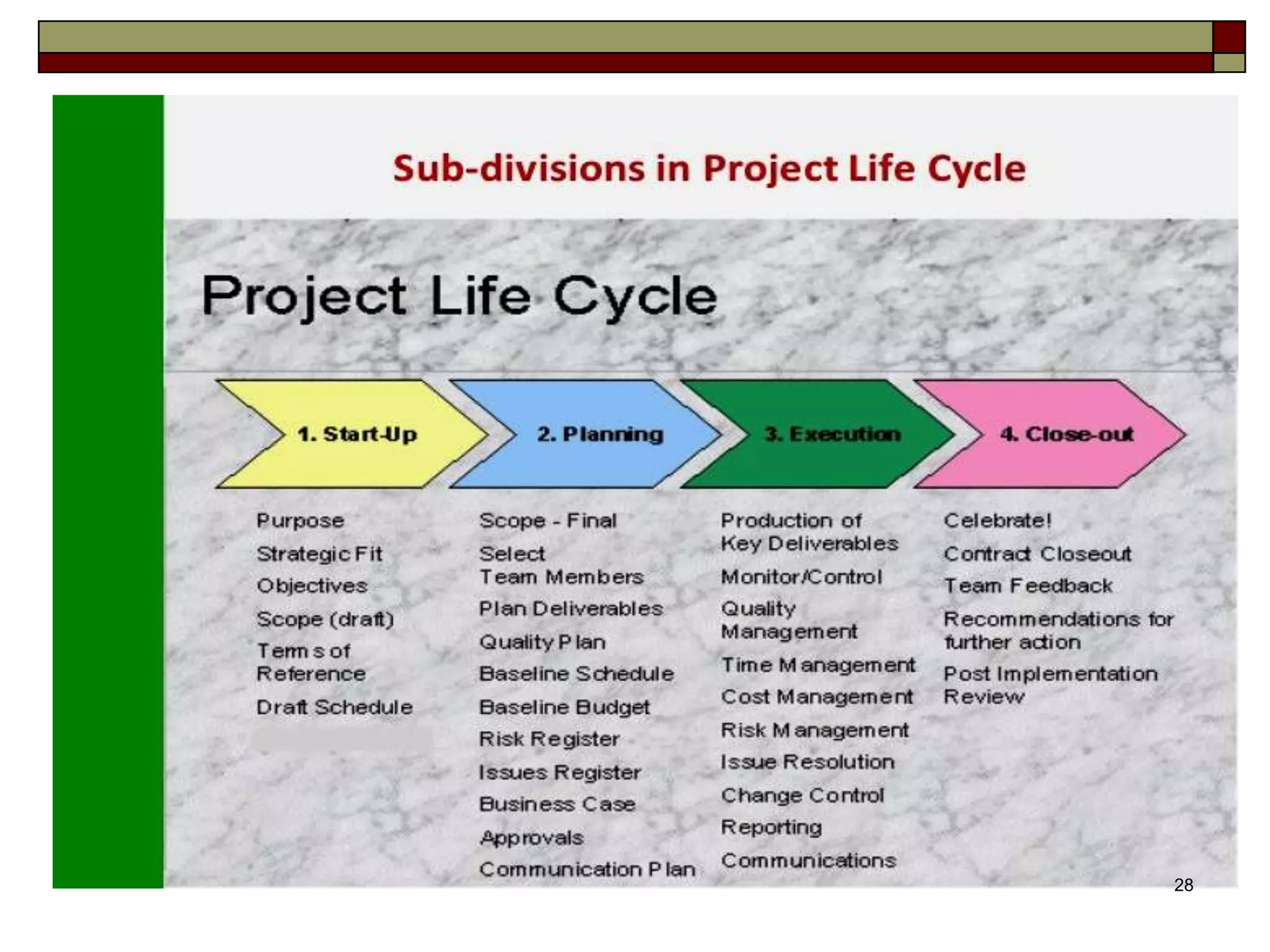
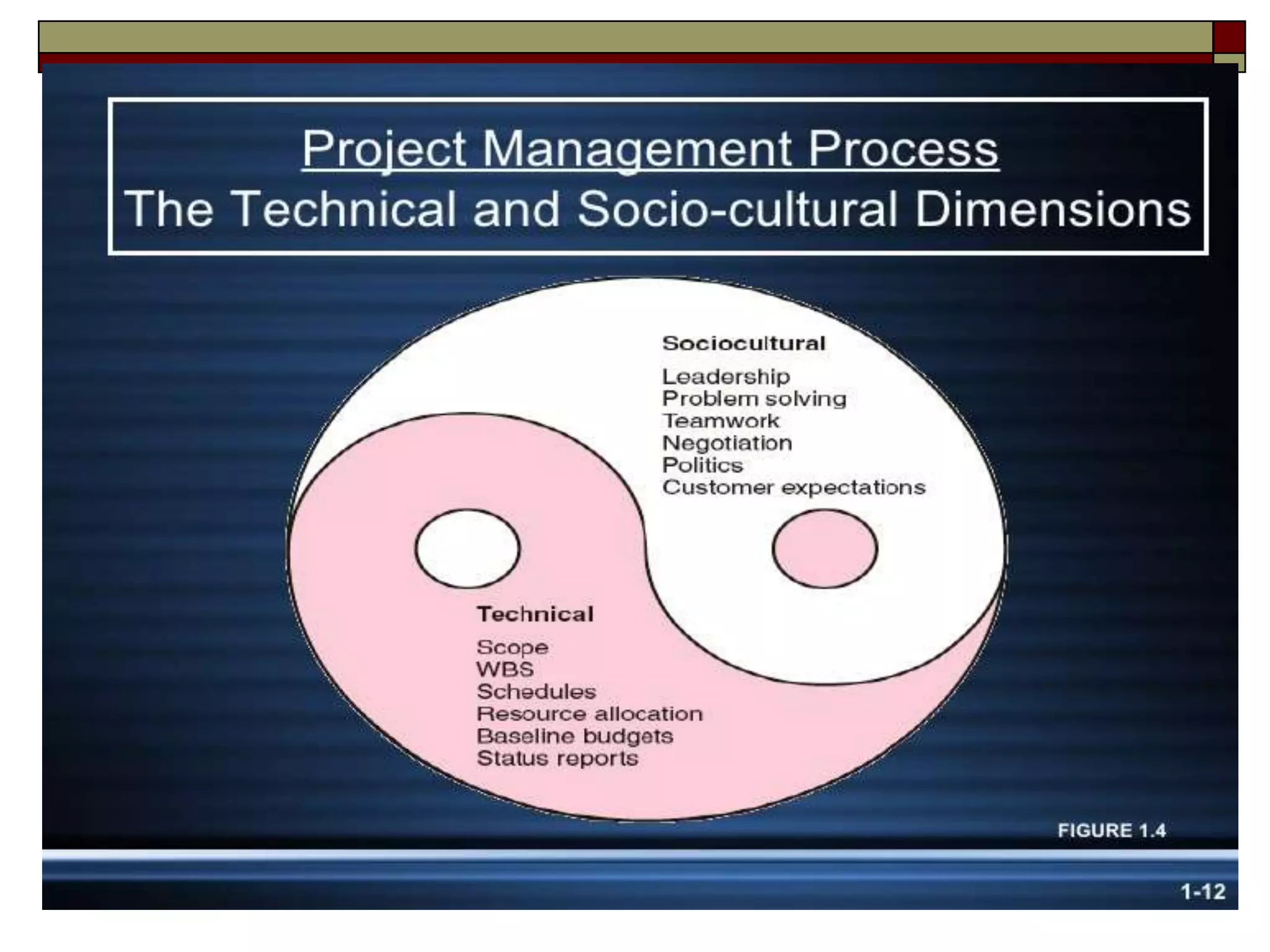
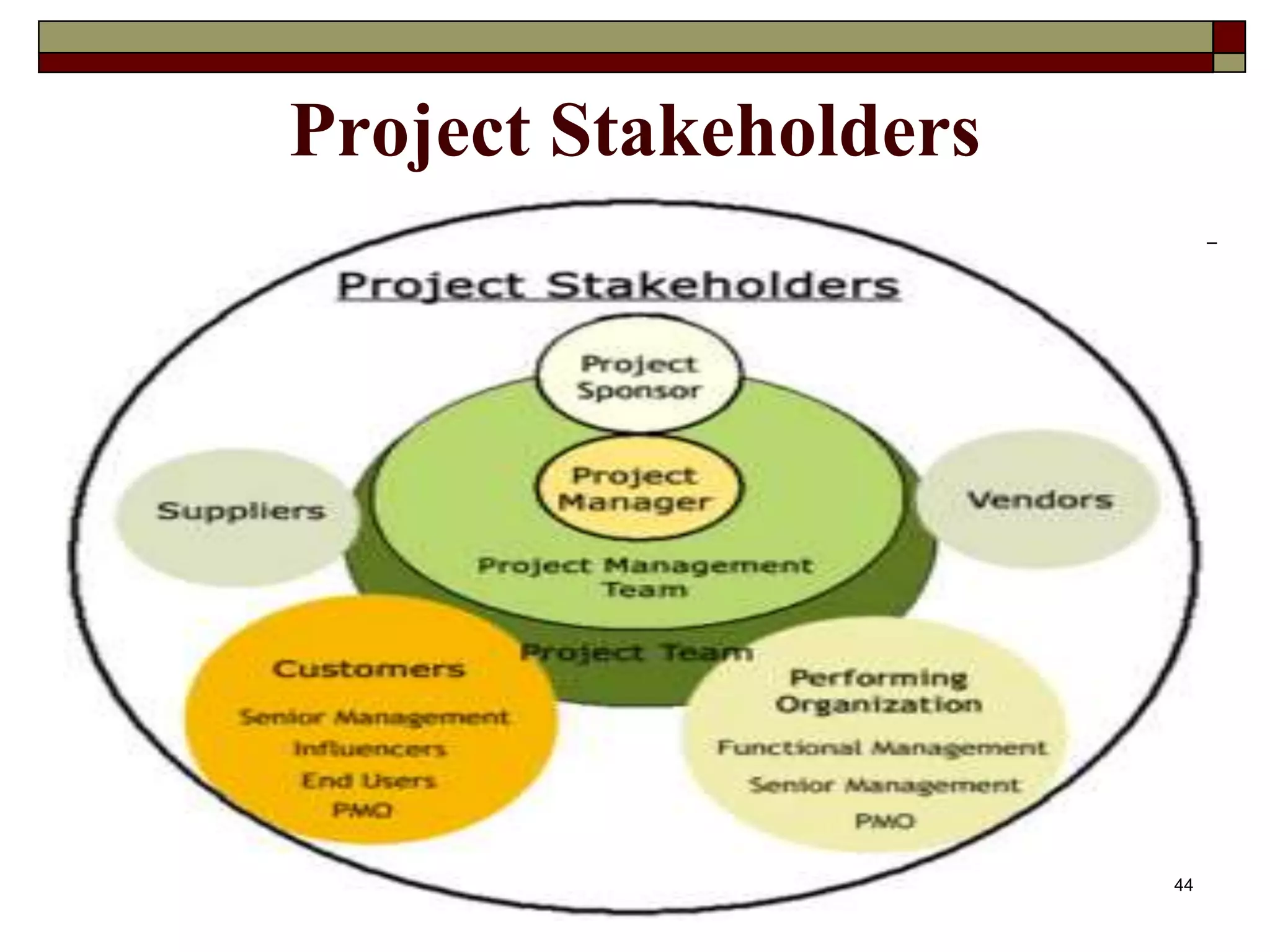
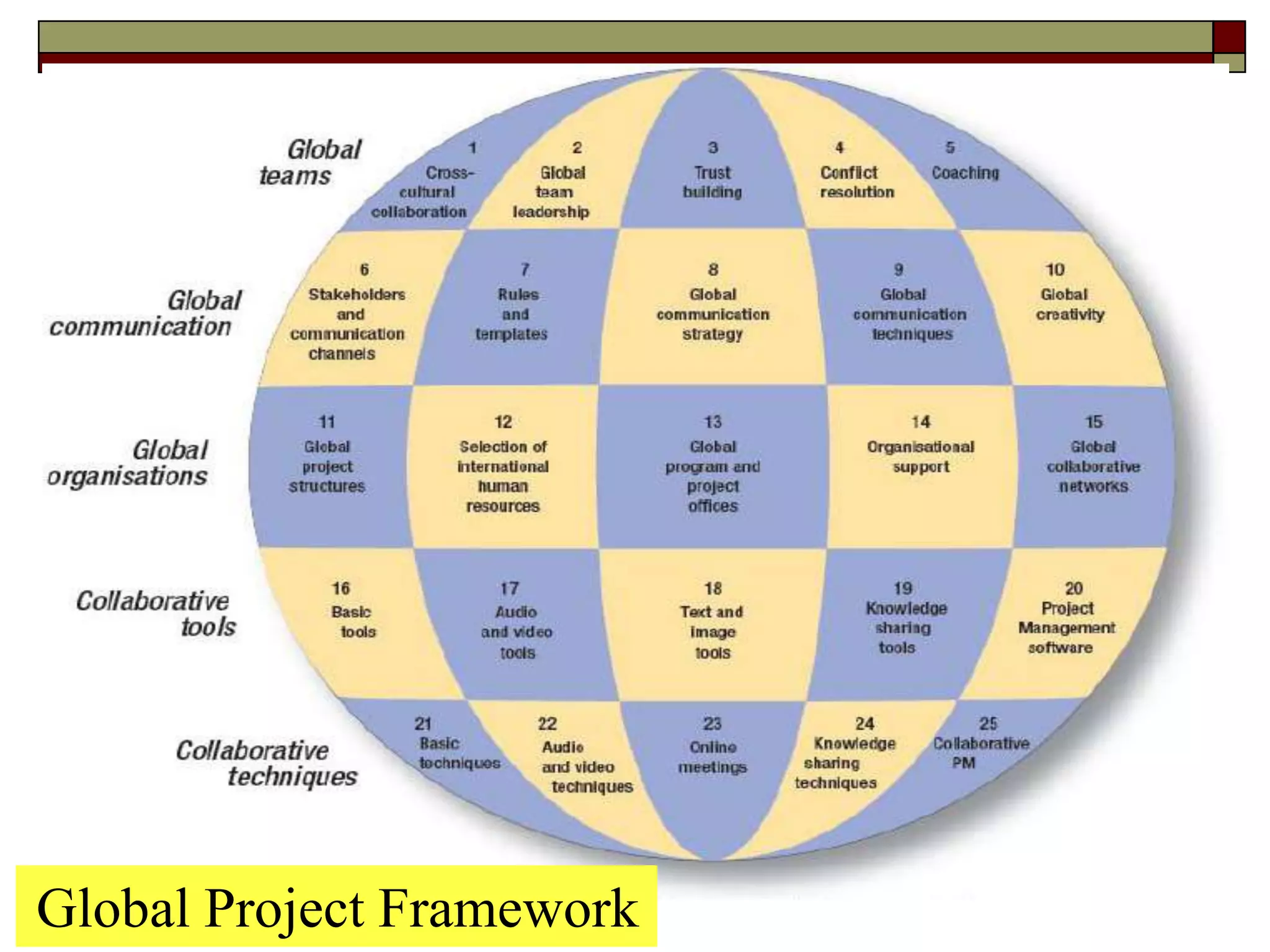
The document provides an in-depth overview of project management, detailing its framework, life cycle, characteristics, and the importance of effective management. It outlines the roles of project stakeholders, emphasizes the need for strategic alignment and teamwork, and highlights current drivers influencing project management practices. Additionally, it explains the socio-technical approach to project management, emphasizing the balance between technical and socio-cultural dimensions.