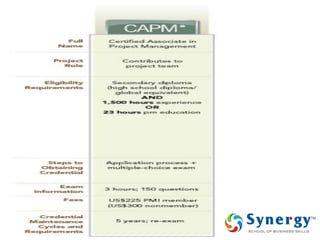
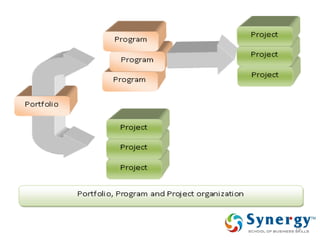
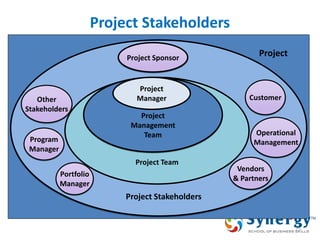
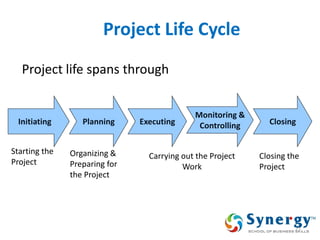
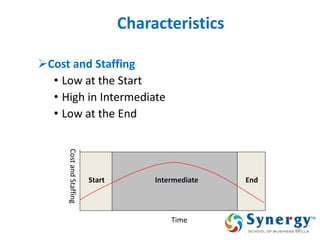
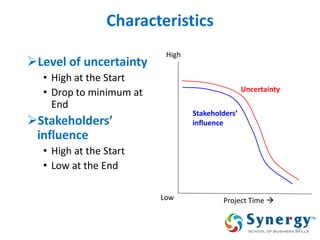
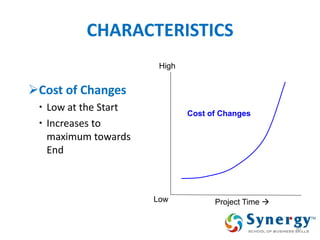
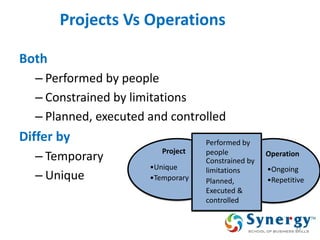
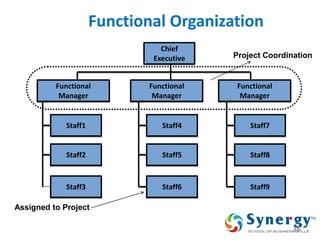
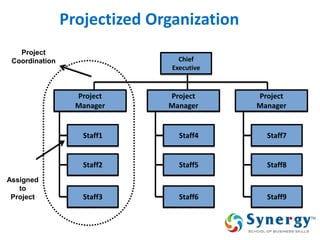
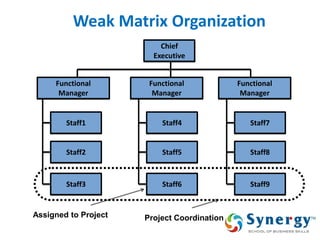
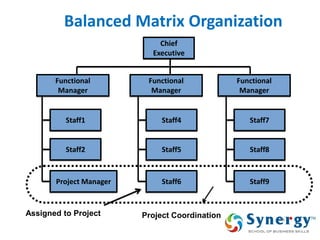
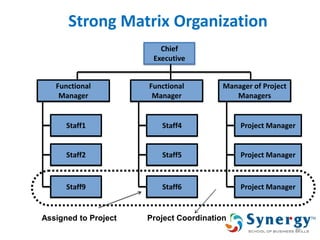
The document discusses project management concepts including the Project Management Institute (PMI), the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK), project lifecycles, and factors that influence project success and failure. It describes PMI as the body that developed best practices in project management and published the PMBOK guide. The PMBOK guide contains standard processes, tools, and techniques used in managing projects. Project management involves applying knowledge, skills, and techniques to meet requirements through activities like planning, executing, monitoring and controlling projects.