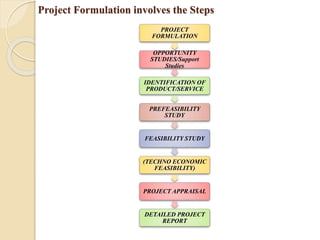
The document provides a comprehensive overview of project management, covering its definition, history, phases, and analysis facets including strategy and resource allocation. It outlines key figures in the evolution of project management, such as Frederick Winslow Taylor and Henri Fayol, and highlights significant methodologies and tools like Gantt charts and SWOT analysis. Additionally, it discusses the project life cycle, emphasizing the importance of thorough market, technical, financial, and ecological analyses for successful project execution.












![Project Life Cycle[PLC]
The project management life cycle is usually broken down into four phases:
initiation, planning, execution, and closure.
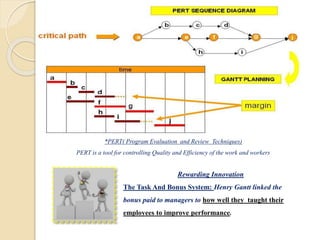
• Monitoring
• Controlling
closure
• Review
• Project Team
• Acquisition
• Development &
Management
• Detailed Planning
• Estimation &
Scheduling
• Project Definition
• Project constraints
• Problem Statement
Initiation
Phase
Planning
Phase
Project
Closure
Phase
Execution
phase](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-1pm-210309072314/85/Project-Management-17-320.jpg)
![Project Life Cycle [PLC]
Quality
Scope
Planning
Implementation
Checkout
Initiation
LIFE CYCLE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-1pm-210309072314/85/Project-Management-18-320.jpg)
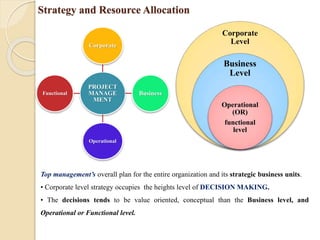
![Project Analysis: Facets of Project Analysis
Facets of Project Analysis
•Market Analysis
Technical Analysis
•Financial Analysis
Economic Analysis
•Ecological Analysis
Market Analysis
Demand
• Market Share
• Consumption
• Elasticity of
Demand
• Consumer
Behavior
• Legal constrains
Technical
Analysis
• Raw materials
• Scale
• Productions
• Layout
• Technology
• capacity
Financial
Analysis
• Cost of capital
• Project
profitability
• Cash flow
statements
• Break Even
Point[BEP]Risk
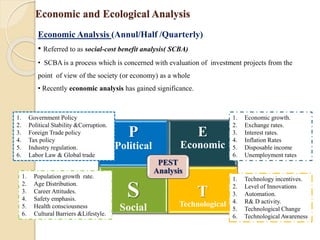
Economic
Analysis
1.Income of Society
2.Employment
3.Social order
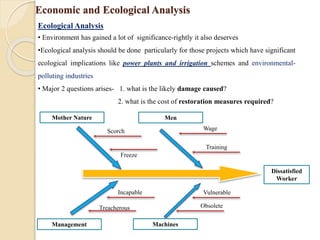
Ecological
Analysis
1.Damage on
Environment.
2.Limits on
Environment if any
3.Restoration
Measures](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-1pm-210309072314/85/Project-Management-19-320.jpg)



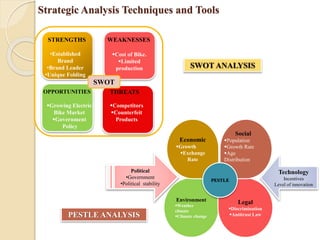
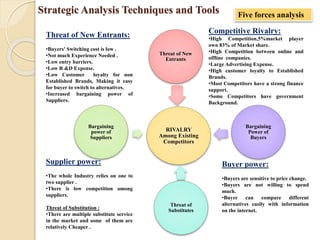
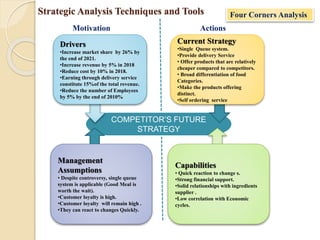
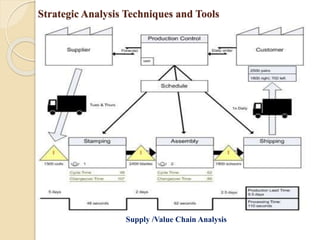
![Strategic Analysis Techniques and Tools
Strategist Many techniques and tools available for strategy analysis
1. SWOT[Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats] Analysis technique developed at
Stanford in the 1970s
2. PEST Analysis useful tool for understanding market growth or decline, and as such the position,
potential and direction for a business. PEST is an acronym for Political, Economic, Social and
Technological factors. PESTLE Analysis PESTLE (i.e. PEST + Legal & Environment).
3. Supply /Value Chain Analysis is a way to visually analyze a company's business activities to see
how the company can create a competitive advantage for itself.(Originated in the 1980s by Michael
Porter)
4. Five Forces Analysis Michael Porter developed the Five Forces Model in 1980,a powerful
competitive analysis tool market. within an industry.
5. Four Corners Analysis developed Michael Porter, is a model well designed to help company
strategists assess a competitor's intent and objectives, and the strengths it is using to achieve them.
6. Business Motivation Model (BMM) an enterprise prescribes a certain approach for its business
activity, it ought to be able to say why and what result(s) is the approach meant to achieve., modeling
notation for support of business decisions about how to react to a changing world.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-1pm-210309072314/85/Project-Management-24-320.jpg)
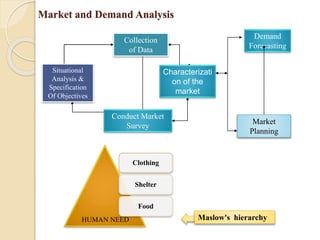

![Market and Demand Analysis
Conduct Market Survey :
Secondary information, though useful, often does not provide a wide-ranging basis
for market and demand analysis
There is a need to be supplemented with the primary information through market
survey
A market survey is useful in determining the total market demand, growth rate in
different segments of the market, understanding the inner motives of the customer and
measuring the unsatisfied needs of the customers
Characterization of the market :
-Heterogeneity of the Geographical Division - Multiplicity Consumer Groups – Design
of Questionnaire Nature of Product (Marred)
Effective Demand in the earlier period and current
Production + Imports – Exports – Change in stock level
[1. Price 2. Methods of Distribution and Sales Promotion 3.Consumers 4. Supply and
Competition 5.Government Policy].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-1pm-210309072314/85/Project-Management-31-320.jpg)


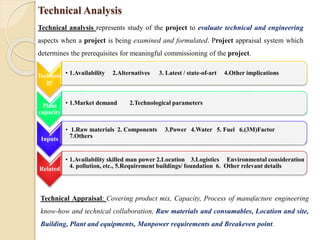
![TEWI-TOTAL EQUIVALENT WARMING IMPACT
GWP=GLOBAL WARMING POTENTIAL ; ODP =OZONE DEPLECTION POTENTIAL
TEWI=(GWP x L x n)+(GWP x m[1-αRecovery])+(n x Eannual x β)
Leakage Recovery losses Energy Consumption
Direct global warming potential Indirect global warming potential
*Reference :Bitzer International, Germany
*GWP=Global Warming potential [CO2-related]
L =Leakage rate per year [Kg]
N =System operating time [Years]
M = refrigerant charge [kg]
αRecovery =Recycling factor
Eannual =Energy consumption per year [kWh]
β =CO2 –Emission per kWh (Energy-Mix)
*ODP =OZONE DEPLECTION POTENTIAL
Ecological Analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-1pm-210309072314/85/Project-Management-37-320.jpg)