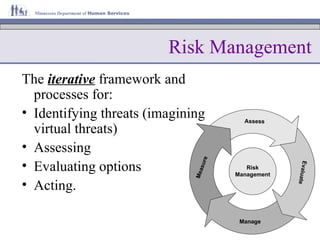
This document summarizes a presentation on risk management 101. It defines key terms like threat, vulnerability, risk, and types of risk. It outlines the components of risk management frameworks including identifying threats, assessing risk, evaluating options, and taking action. It discusses different risk management standards and frameworks. Finally, it provides an overview of information risk management practices at the Minnesota Department of Human Services.