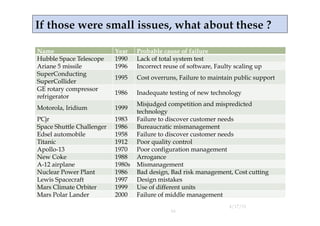
The document outlines the key stages of a typical project according to Conway's Law. It lists the 6 stages as: 1) enthusiasm, 2) disillusionment, 3) panic, 4) search for the guilty, 5) punishment of the innocent, and 6) praise and honors for the non-participants. The document suggests projects typically progress through these stages from an initial period of optimism to a later phase of blame and punishment before concluding.


![Key
Knowledge
Areas
Topics
Strategic
Management
Introduc1on,
Linking
Strategic
Planning
to
new
product
development
New
Product
Development
New
Product
Development
/
New
Service
Development,
selec1ng
the
right
project,
Cost-‐Benefit
Analysis,
Financial
Ra1os
(CF,
DCF,
NAV,
IRR),
Project
Lifecycle
Project
Ini1a1on
Charter,
Contract,
Preparing
a
Business
Case
Project
Planning
Scoping,
SoW,
WBS,
Es1ma1on,
Iden1fy
Stakeholders,
Risk
Management,
Organiza1on
Structure
(including
people
issues,
repor1ng
rela1onships,
etc.),
Staffing,
Budge1ng,
Scheduling,
PERT,
CPM,
GanT
Chart,
Quality
Project
Communica1ons
(Mee1ng,
Repor1ng),
Sobcotractor
Management
Project
Execu1on
Project
Execu1on,
Managing
Stakeholders
and
influencing
key
stakeholders,
Communica1on
Strategies
(including
using
modern
tools
like
Social
networking,
Video
conf,
TwiTer,
web
based
PM
tools,
Online
query
of
project
status
etc),
Overcoming
Poli1cal
Resistance
Project
Control
Project
Control:
EVM,
Metrics,
Project
Reviews,
Change
Management,
Project
Survival
Strategies
Project
Closure
Closure,
Evalua1on,
Post-‐closure
Misc.
Topics
Project
Manager
Competencies,
Project
Success
Factors,
Managing
Troubled
Projects
Introduc1on
to
addi1onal
PMBOK,
So]ware
Development
Lifecycles,
Agile
/
Scrum,
Megaprojects,
TOC,
topics
(1me
&
interest
willing)
PRINCE2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectmanagement01-1303008072032-phpapp01/85/Project-Management-01-3-320.jpg)