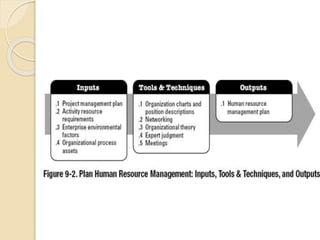
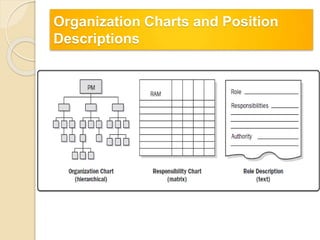
This document discusses human resource management processes for projects. It describes planning human resource management which involves identifying roles, responsibilities, required skills and creating a staffing plan. It outlines acquiring the project team by obtaining necessary resources according to the project proposal. This involves negotiation, pre-assignment, acquisition from outside if needed, and use of virtual teams. It also covers developing the project team to improve competencies, interactions and environment. Managing the project team includes tracking performance, providing feedback, resolving issues and allocating resources properly. The key benefits and outputs of these processes are also summarized.