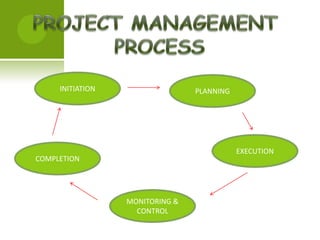
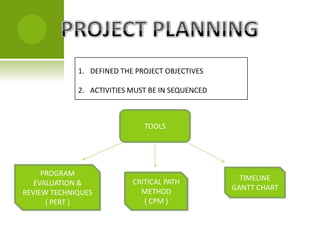
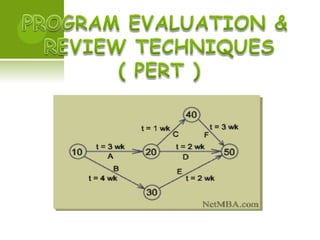
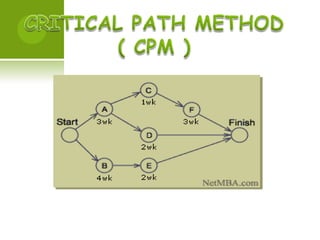
Project management involves planning, organizing, and managing resources to successfully complete specific business goals within constraints of time, cost and scope. The project life cycle includes initiation, planning, execution, monitoring/control and completion phases. Key aspects that must be managed include defining objectives, sequencing activities, evaluating techniques like PERT and Gantt charts, coordinating resources, and monitoring performance against the plan to control deviations.