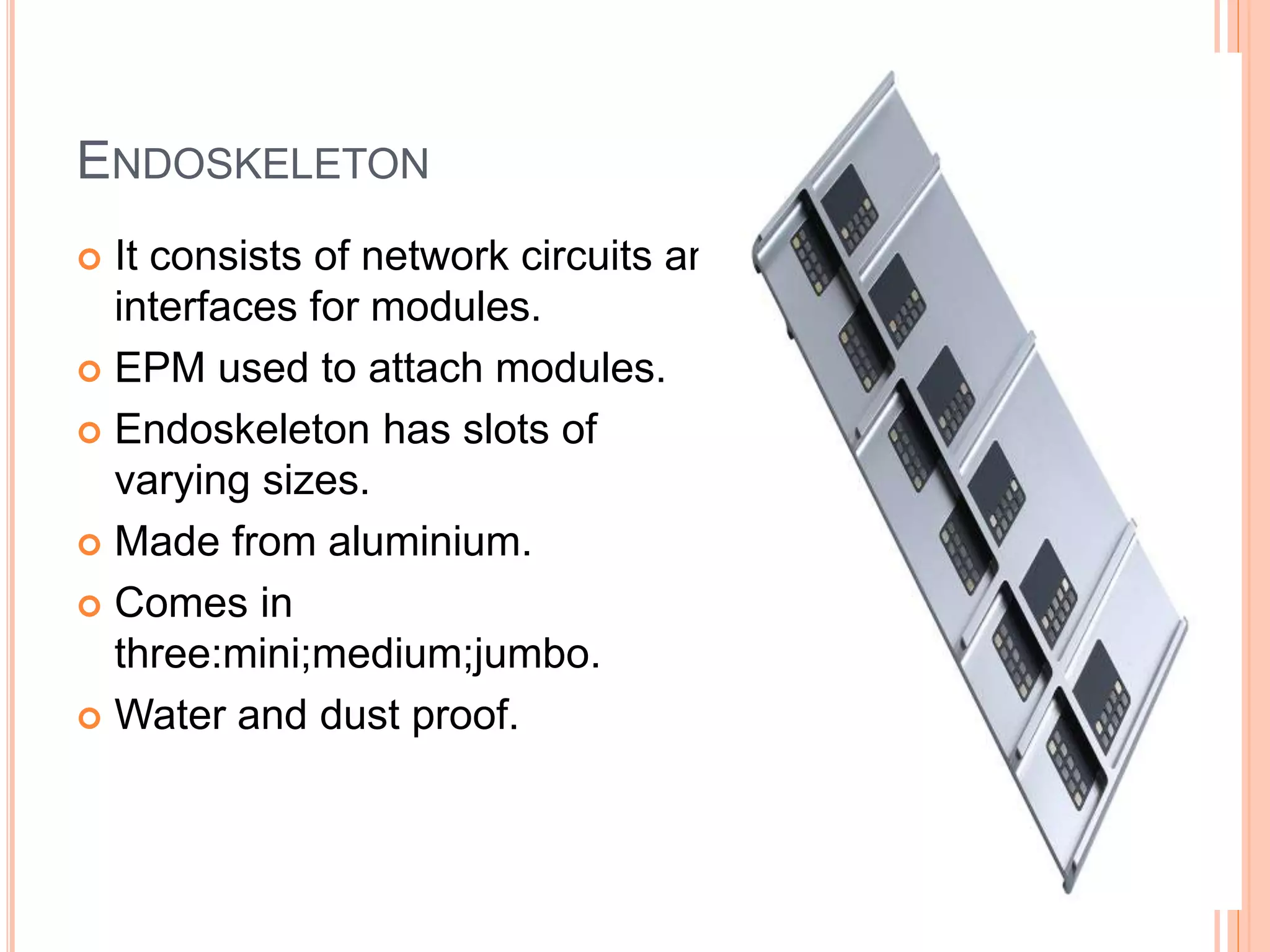
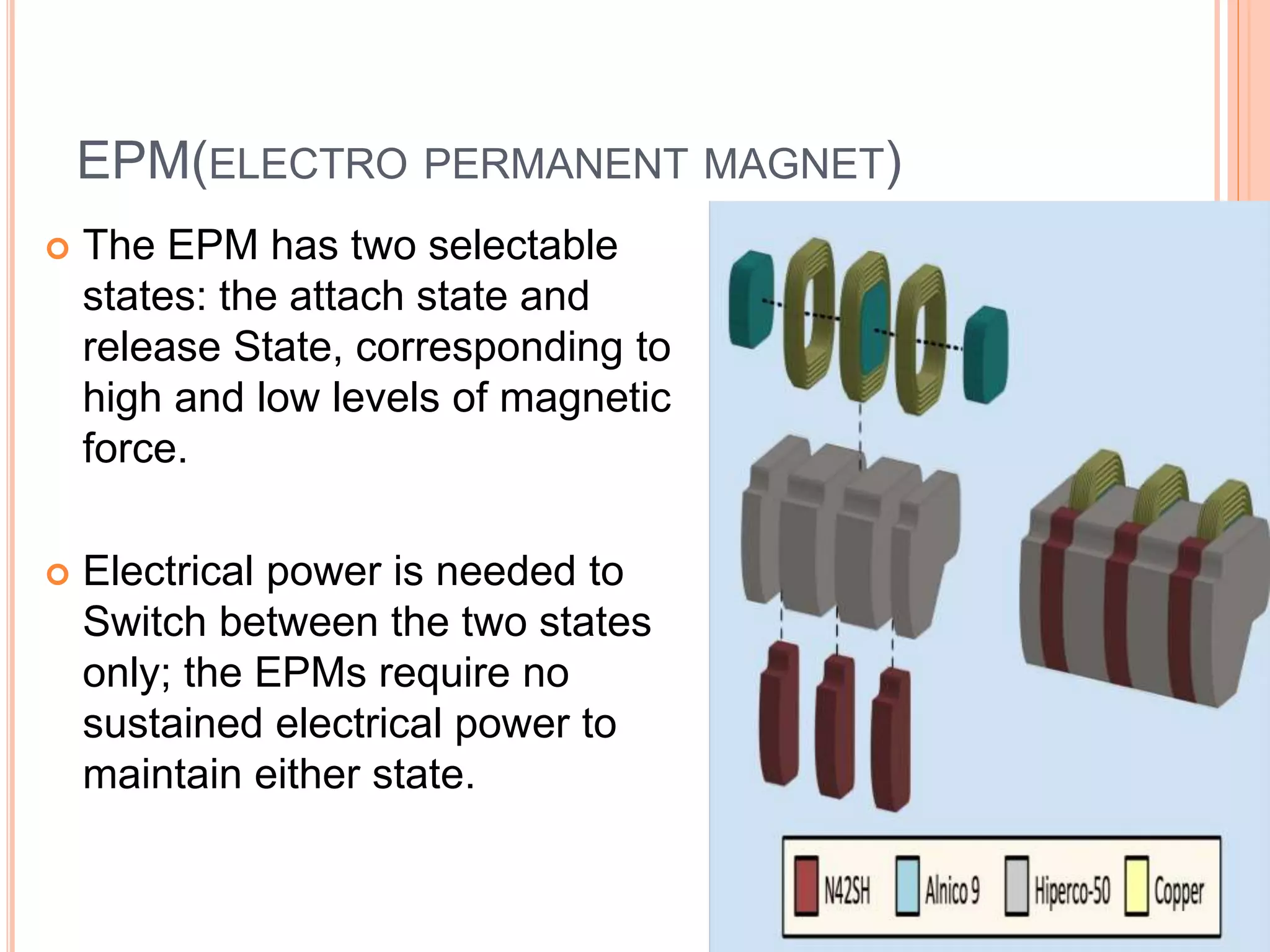
Project Ara is Google's initiative to create a modular smartphone platform. The phone consists of an endoskeleton frame with slots that house interchangeable modules. Modules come in different sizes and functions, like the front screen module or rear camera module, and are secured to the frame using electro permanent magnets. The goal is to make phones more customizable, upgradable, and sustainable by allowing users to replace individual components rather than the entire device.