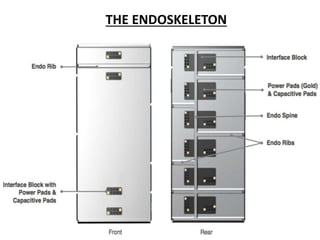
Project Ara, developed by Google, aims to create a customizable and modular smartphone platform with swappable parts to enhance sustainability and meet users' changing needs. The initiative, originally part of Motorola, promotes a democratic approach to hardware development, allowing users to choose and upgrade various phone modules easily. Despite its innovative promise, challenges such as size, weight, and component integration remain as the project strives to improve consumer appeal and functionality.