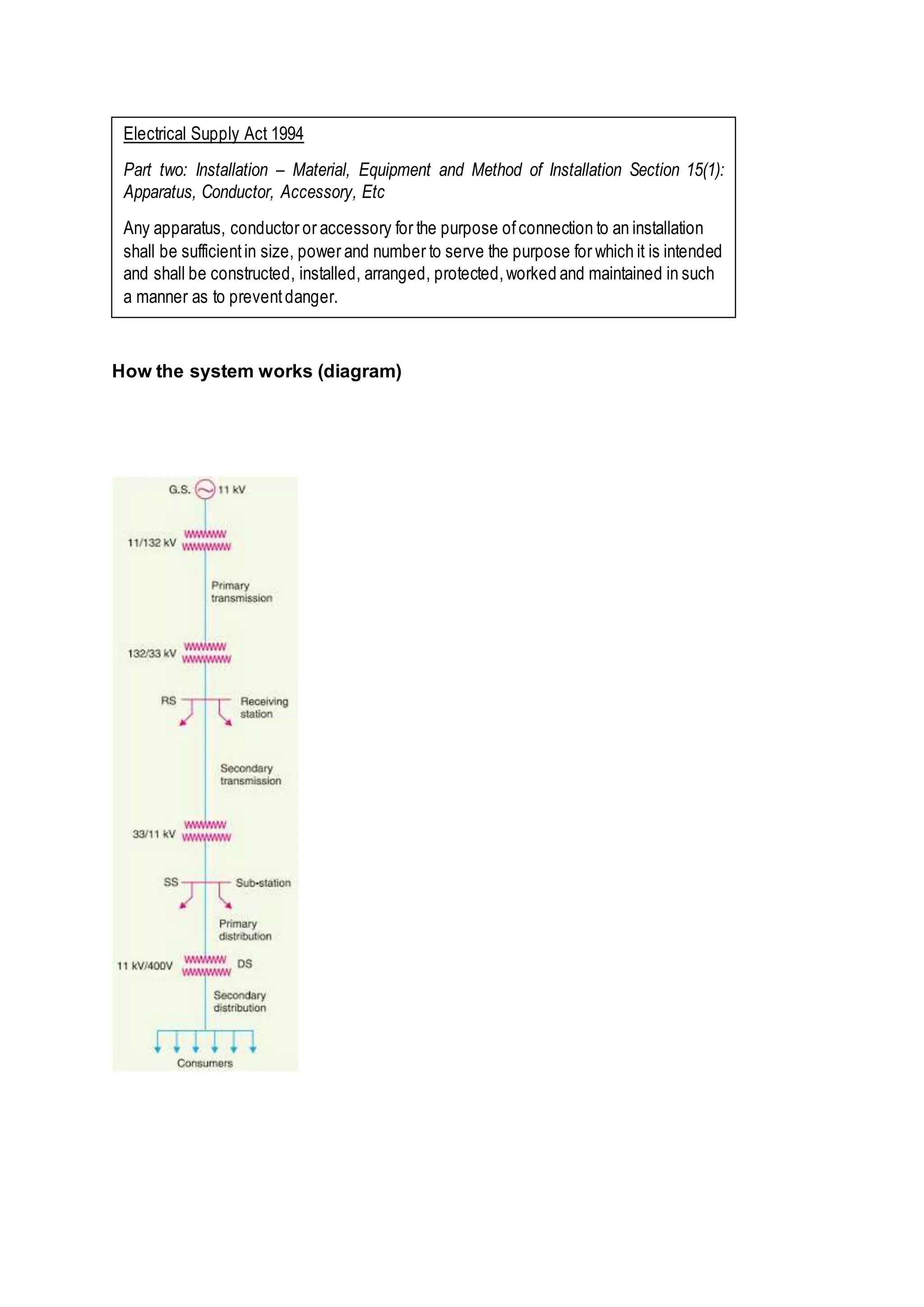
(1) The document provides details on the key building service systems - water supply, electrical supply, sewerage and sanitary, and rainwater/surface drainage - for a project, including descriptions of their components, materials, operation, and relevant regulatory requirements.
(2) It includes diagrams and drawings of the systems, as well as a table of contents listing sections on the introduction, components, operation, and UBBL/regulatory requirements for each system.
(3) The document serves as a reference for the building services for the project and ensures regulatory compliance for proper installation and maintenance of the critical water, electricity, sewerage, and drainage systems.