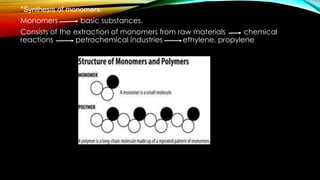
This document summarizes information about plastic materials from four students. It discusses the sourcing and synthesis of raw materials and monomers used to make plastics. It also describes various methods for shaping and finishing plastics, such as injection molding and vacuum forming. Finally, it outlines different types of plastics including thermoplastics and thermosets, and discusses some of their key physical, mechanical, chemical, and biological properties.