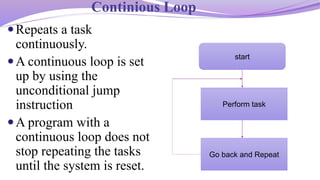
This document discusses different programming techniques used in microprocessors, specifically looping, counting, and indexing. It describes two types of loops - continuous loops which repeat tasks indefinitely, and conditional loops which repeat until a condition is met. Conditional loops often use counting and indexing. Counting involves incrementing or decrementing a counter register, while indexing points to memory locations using sequential numbers. An example is provided of using a counter, index, and addition to sum 10 data bytes stored in memory.