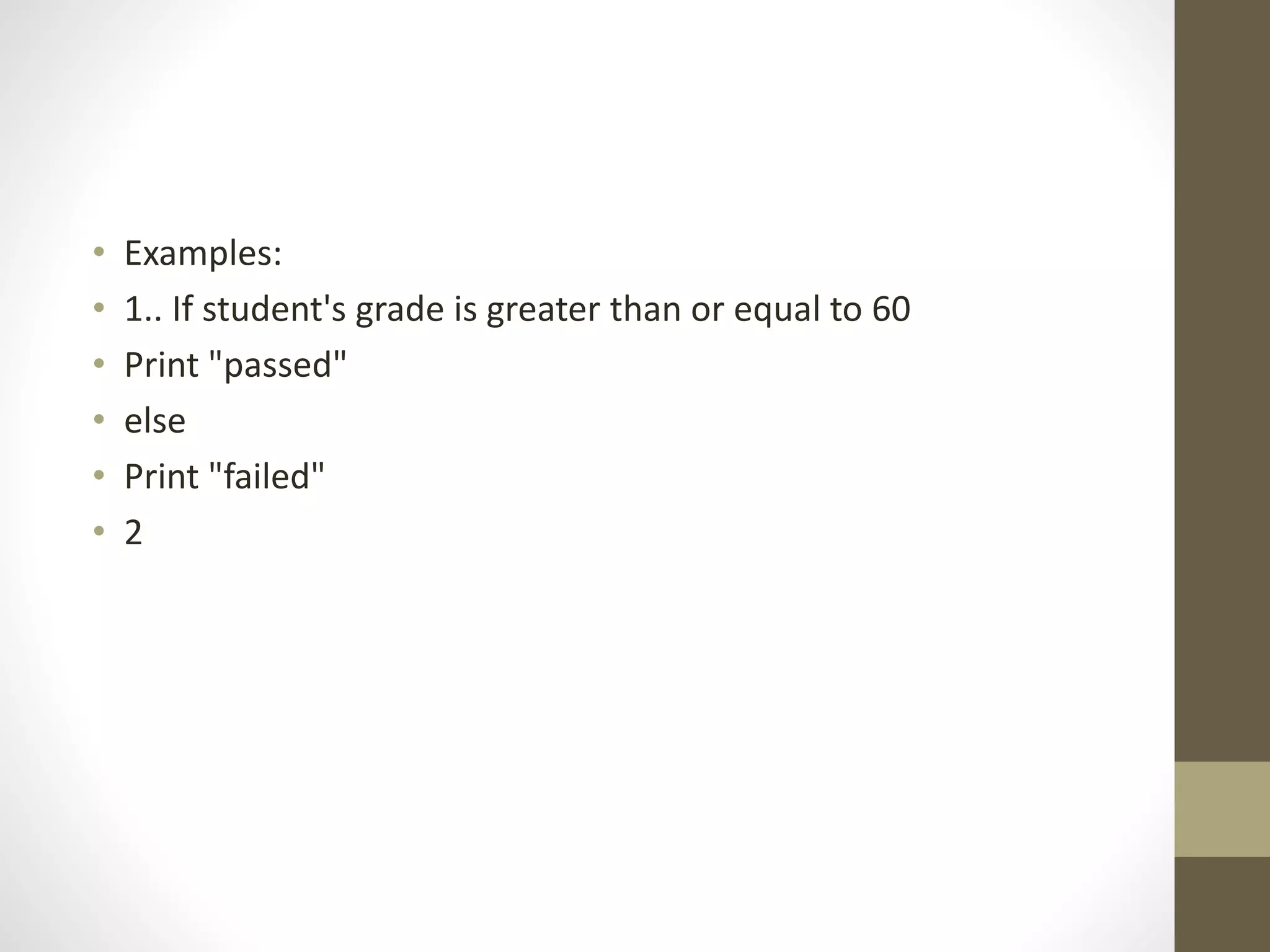This document outlines the key concepts and steps involved in programming logic and practices, including:
1) The main steps in the programming process are problem identification, designing algorithms and flowcharts, coding, compiling, debugging, execution and testing, and documentation.
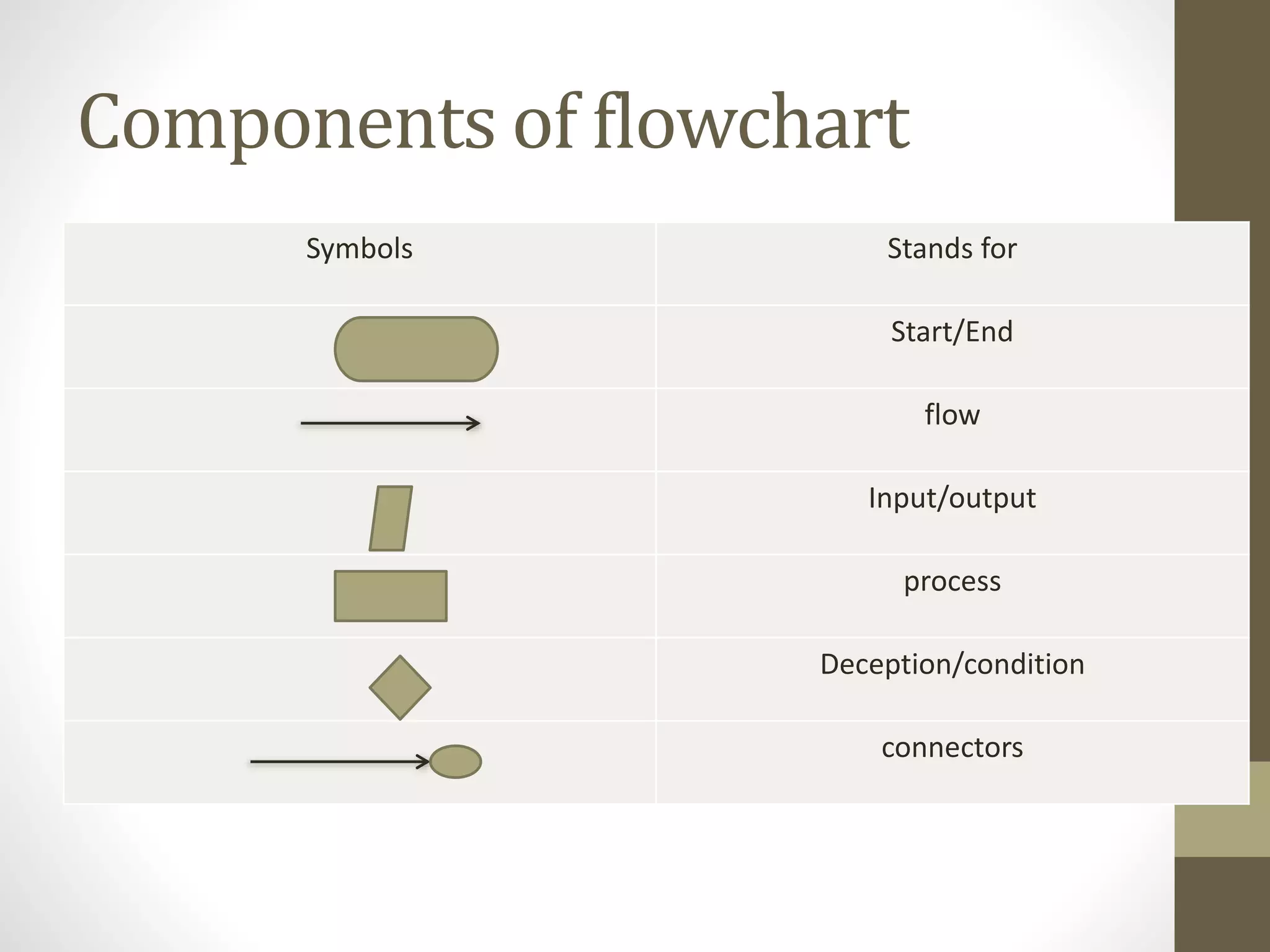
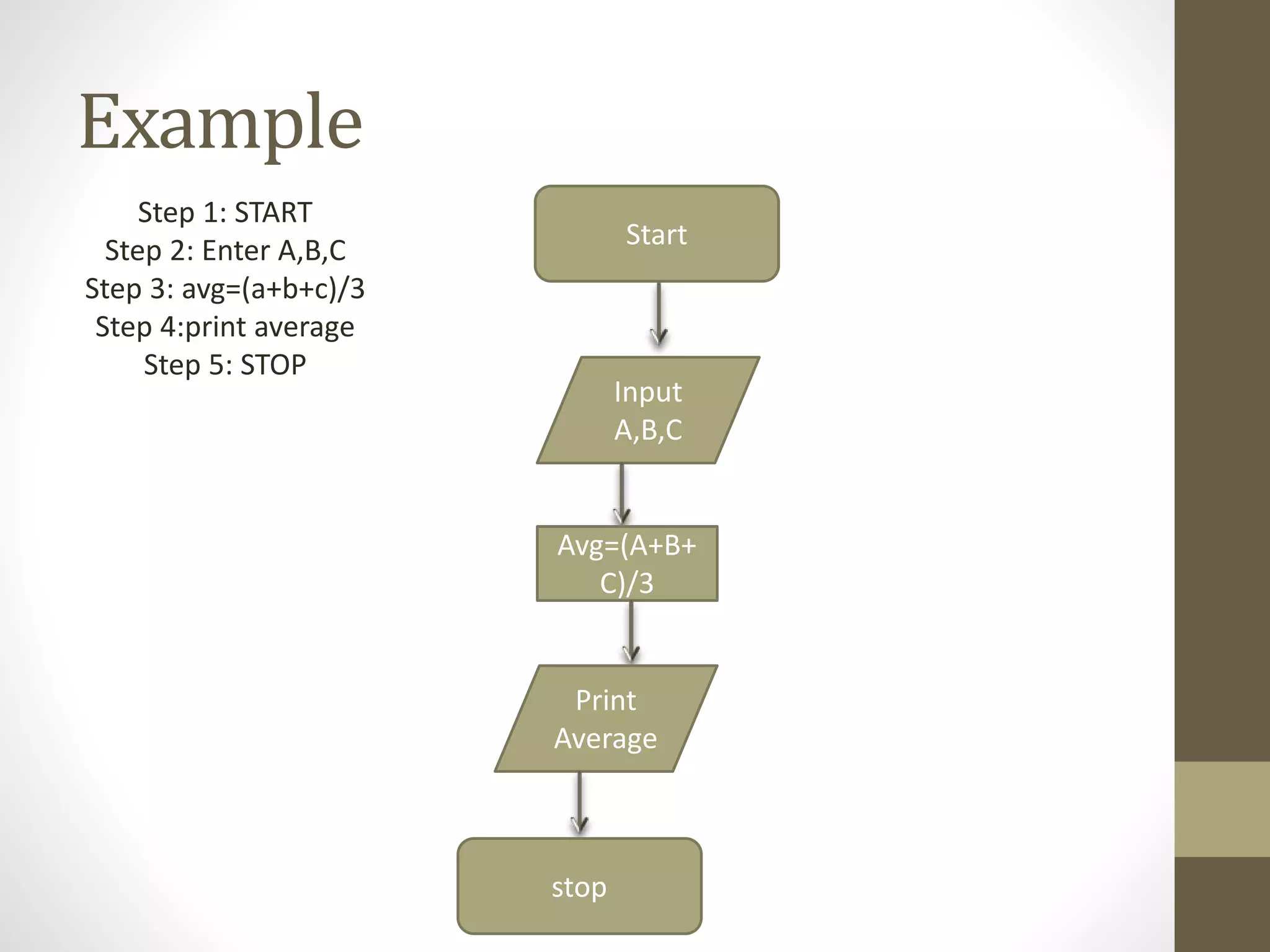
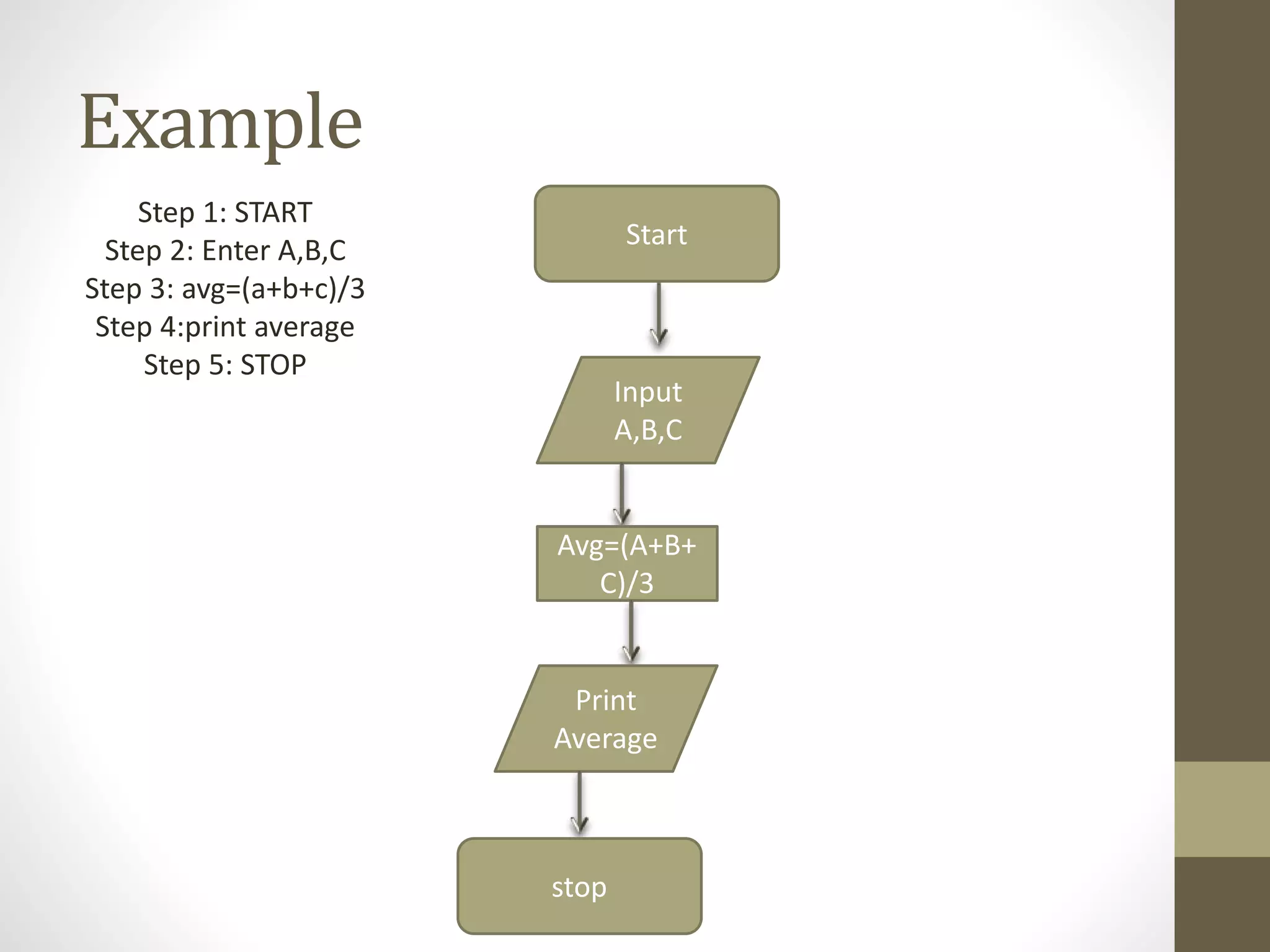
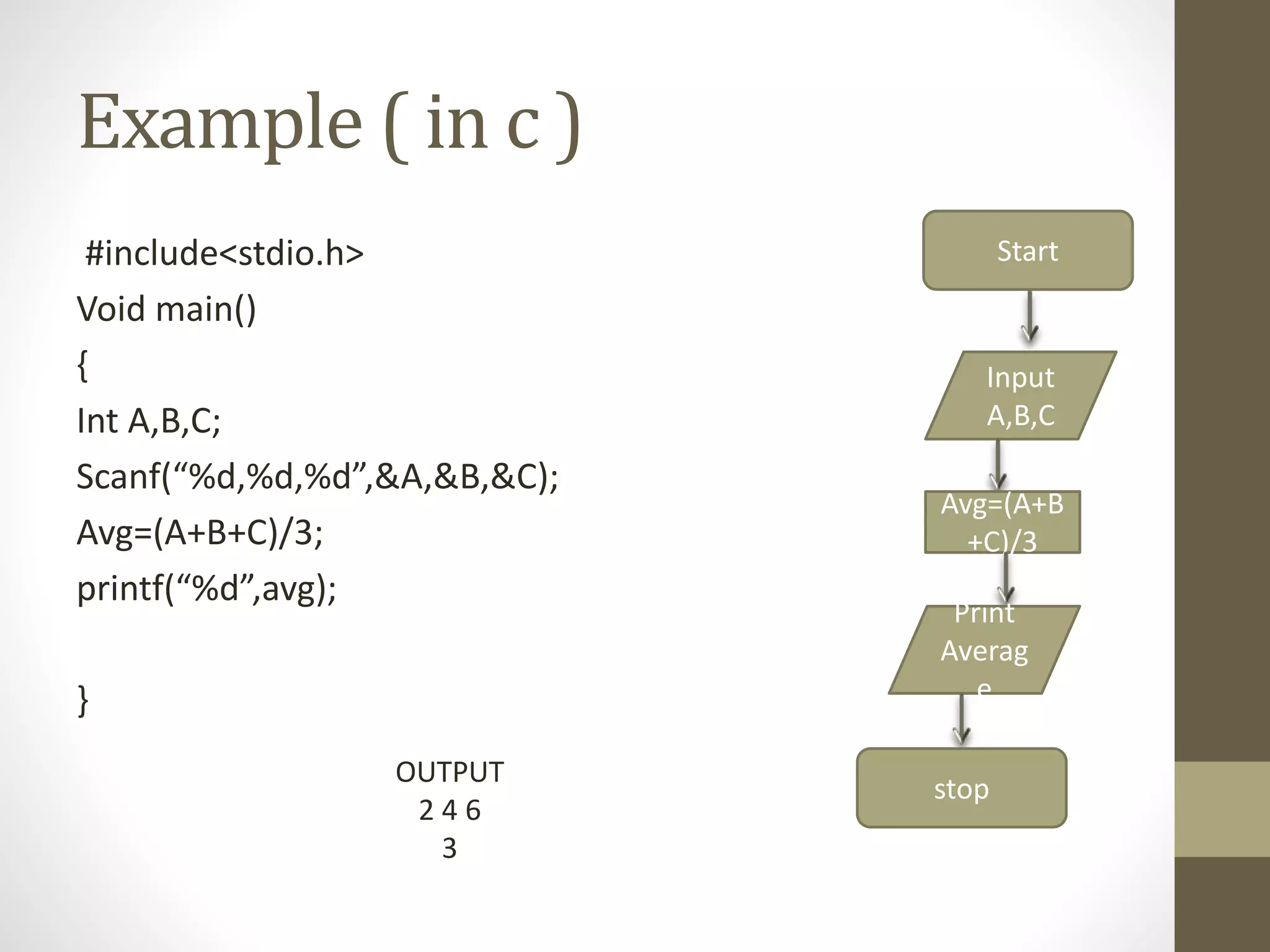
2) An algorithm is a series of steps to solve a problem, while a flowchart uses visual symbols to represent the flow of an algorithm. Pseudocode describes algorithms in plain language rather than code.
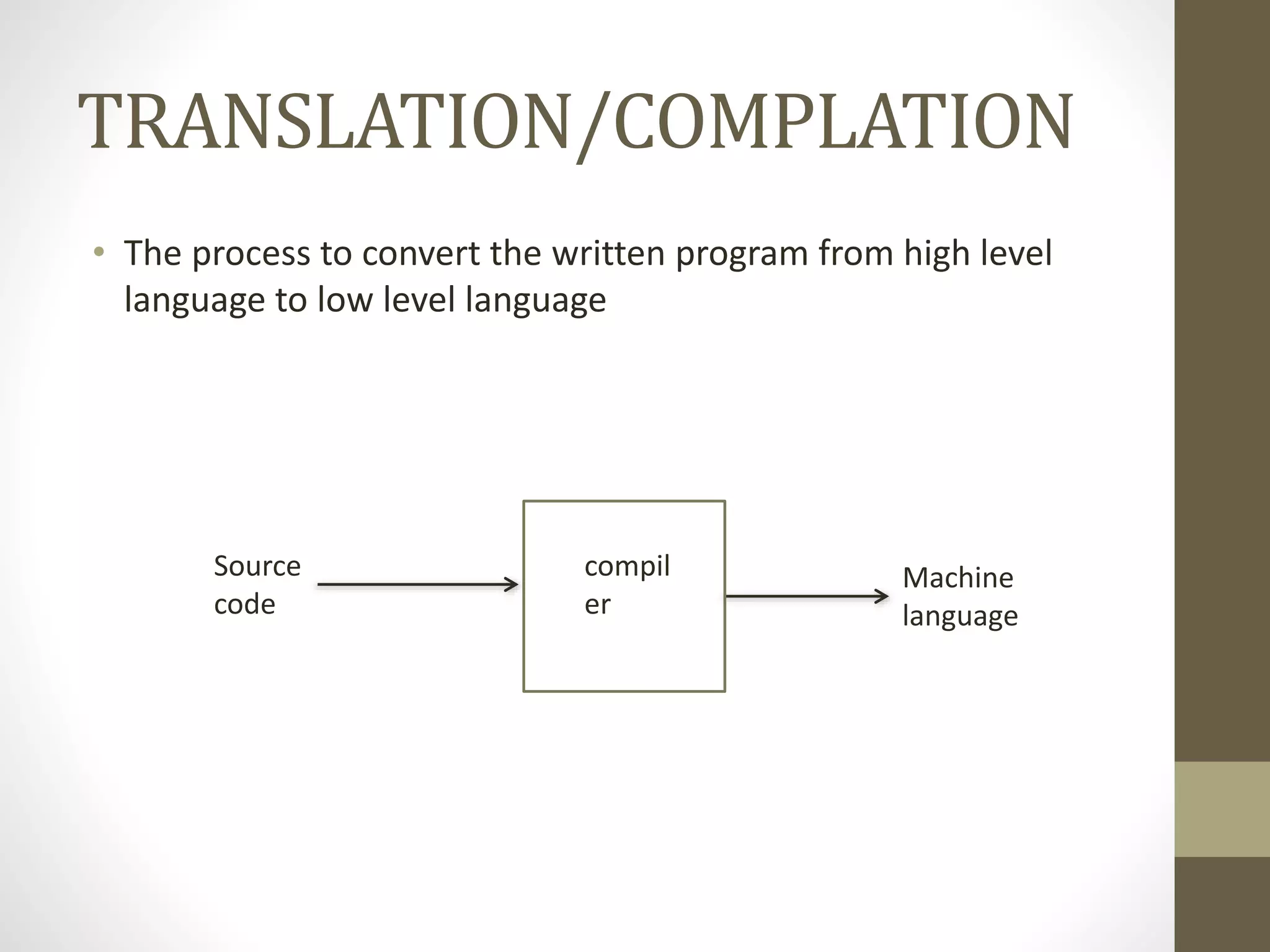
3) Coding involves writing instructions in a programming language based on the algorithm and flowchart. Compilation translates source code into machine code, while debugging detects and fixes errors.