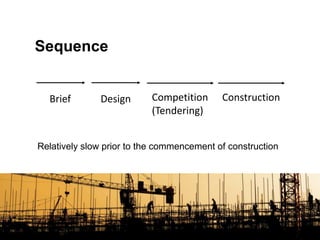
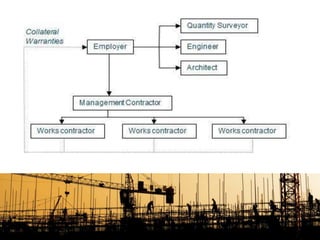
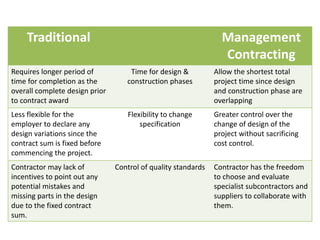
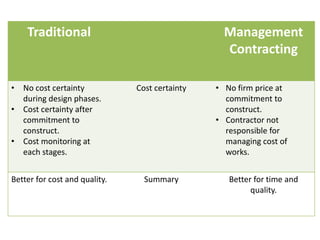
This document provides information about a group assignment for a professional practice course. The group members are listed. The project involves developing a 20-storey condominium in Kuala Lumpur to address the effects of the Malaysian economic downturn on property developers. Various construction procurement methods are discussed, including traditional procurement, management contracting, design-build, and cost reimbursement contracts. The advantages and disadvantages of each method are analyzed. Management contracting using a cost plus fixed fee contract is recommended to control costs while maintaining quality for the condominium project.























![• The management contractor(MC) is reimbursed
for completed work and plus a management
fees as his profit.
• To avoid any argument, the 2 parties should
specify how much is the reimbursable fees to
the MC before the project start
Type of Contract
[ Cost Reimbursement Contract ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/professional-practice-1-presentation-161204094022/85/Professional-practice-1-presentation-29-320.jpg)














