This document provides an overview of professional nursing concepts and practice. It discusses several key concepts:
- Nursing aims to promote health and quality of life for individuals, families, and communities through caring for their physical, mental, and social well-being.
- Professional nursing practice is guided by ethical principles of respecting human dignity, maintaining patient confidentiality and autonomy, and more.
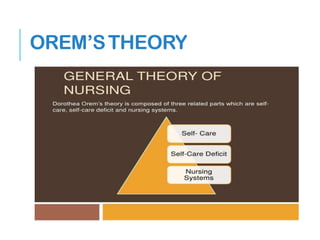
- Several theories are discussed that aim to understand different aspects of nursing, including Nightingale's environmental theory, Peplau's interpersonal relations theory, and models like the Health Belief Model.
- Overall the document outlines the core goals and philosophies of nursing as a patient-centered practice focused on providing holistic care.

























































![PEPLAU’STHEORY
in ReadingTheorist -Hildegard. E. Peplau Born
Pennsylvania [1909], USA
The theory explains the purpose of nursing is to
help others identify their felt difficulties.
Nurses should apply principles of human
relations to the problems that arise at all levels
of experience.
Peplau's theory explains the phases of
interpersonal process, roles in nursing
situations and methods for studying nursing as
an interpersonal process.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/professionalnursingconceptandpractice-200812063802/85/Professional-nursing-concept-and-practice-61-320.jpg)