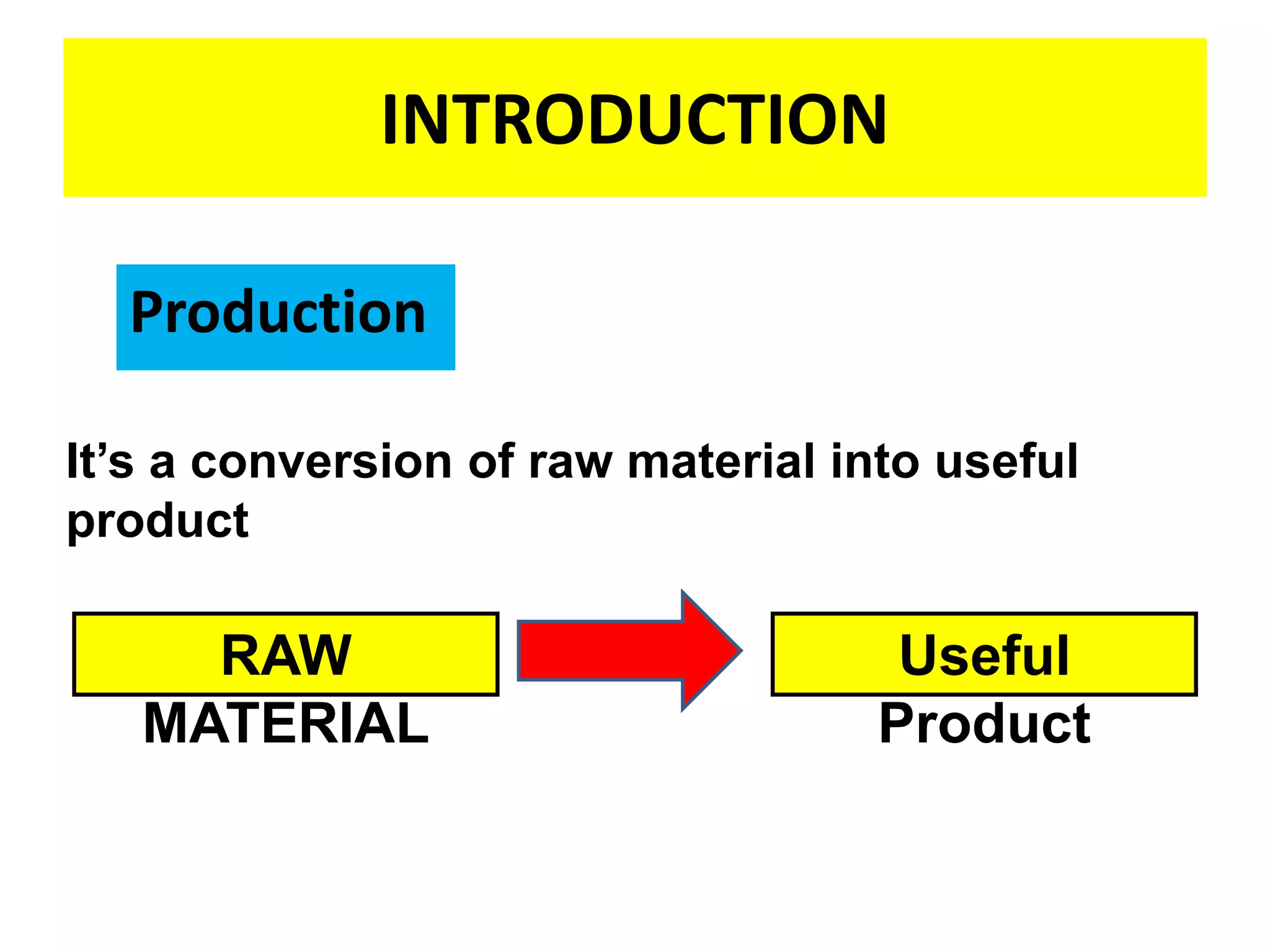
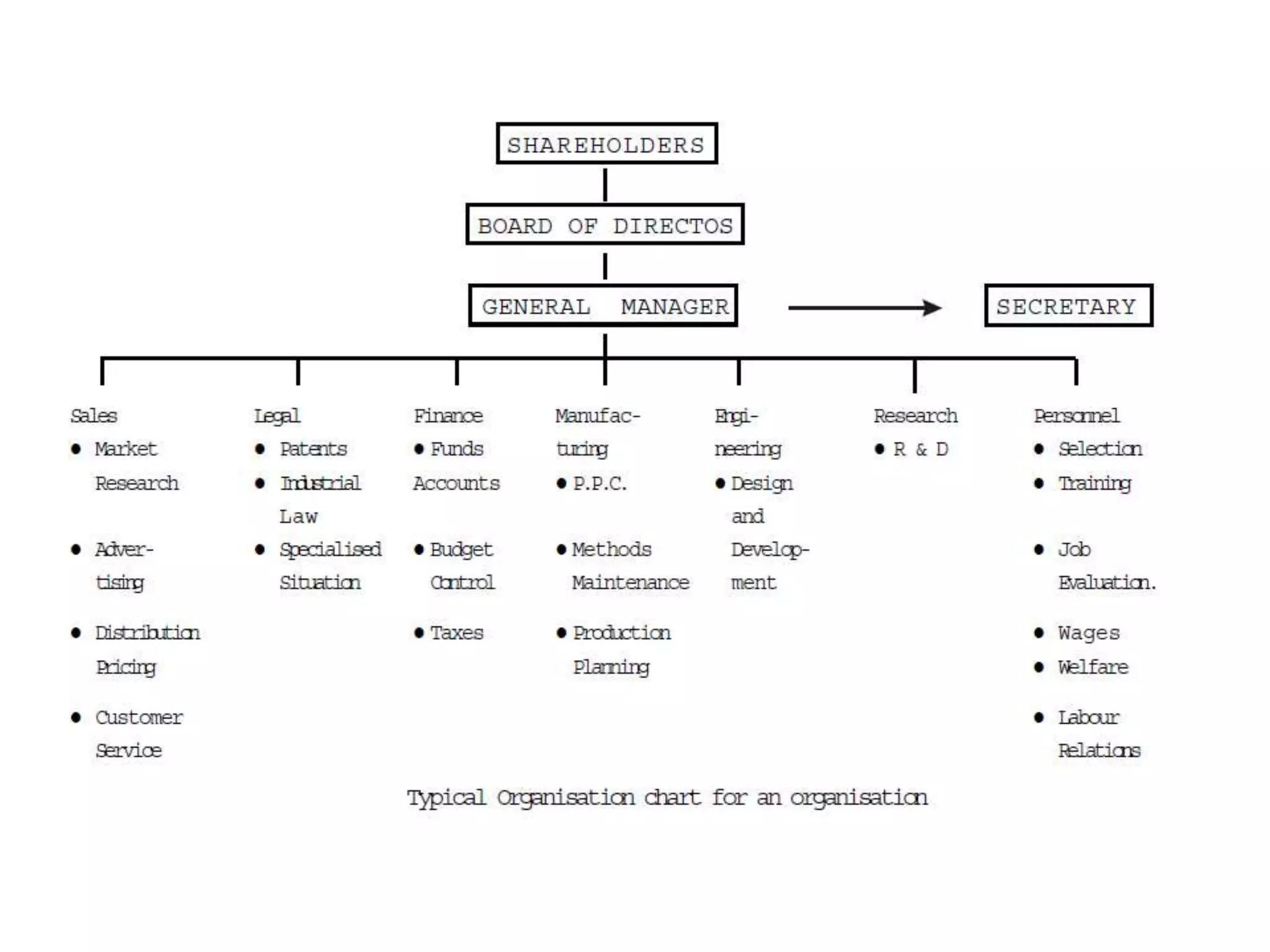
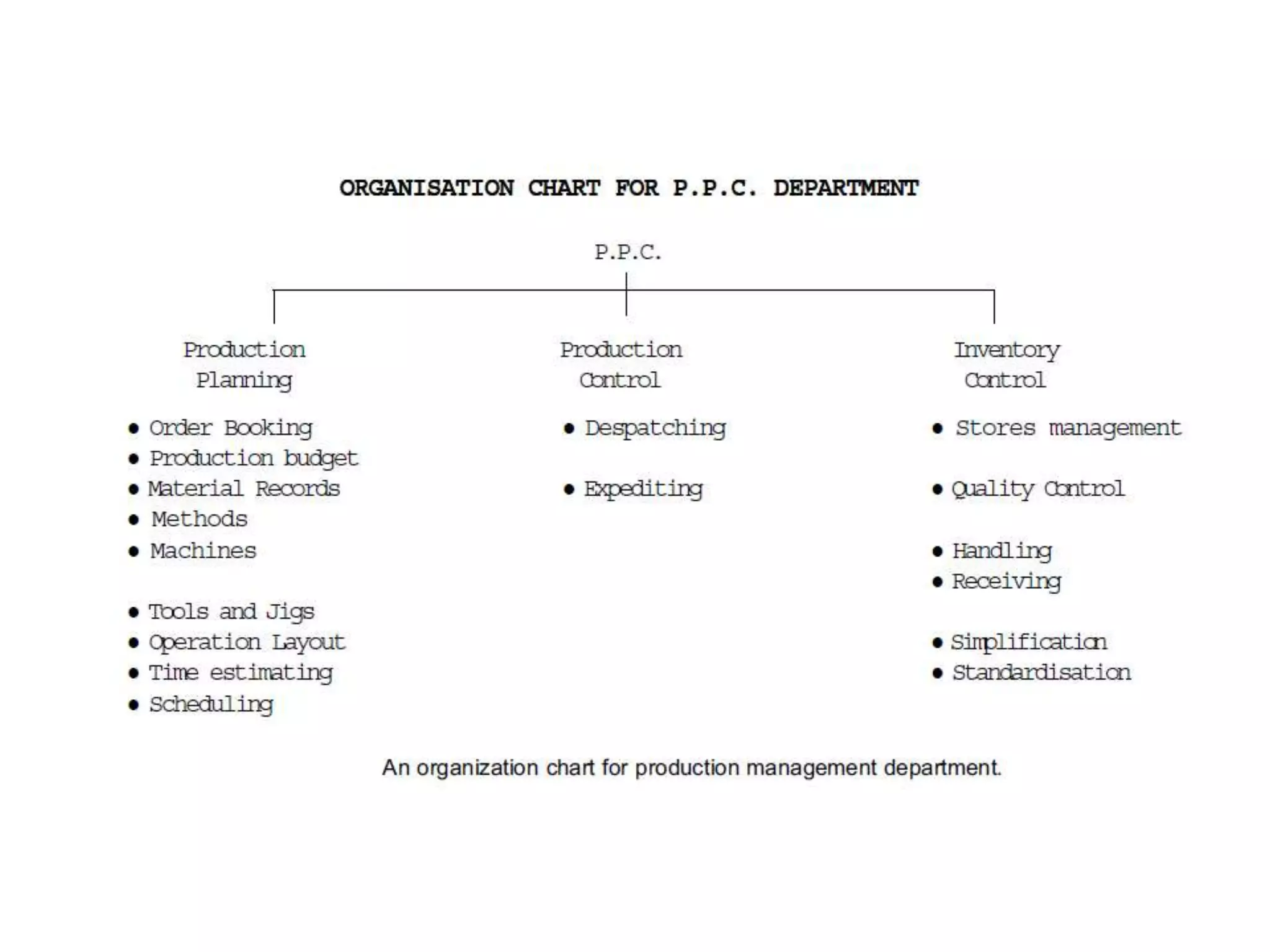
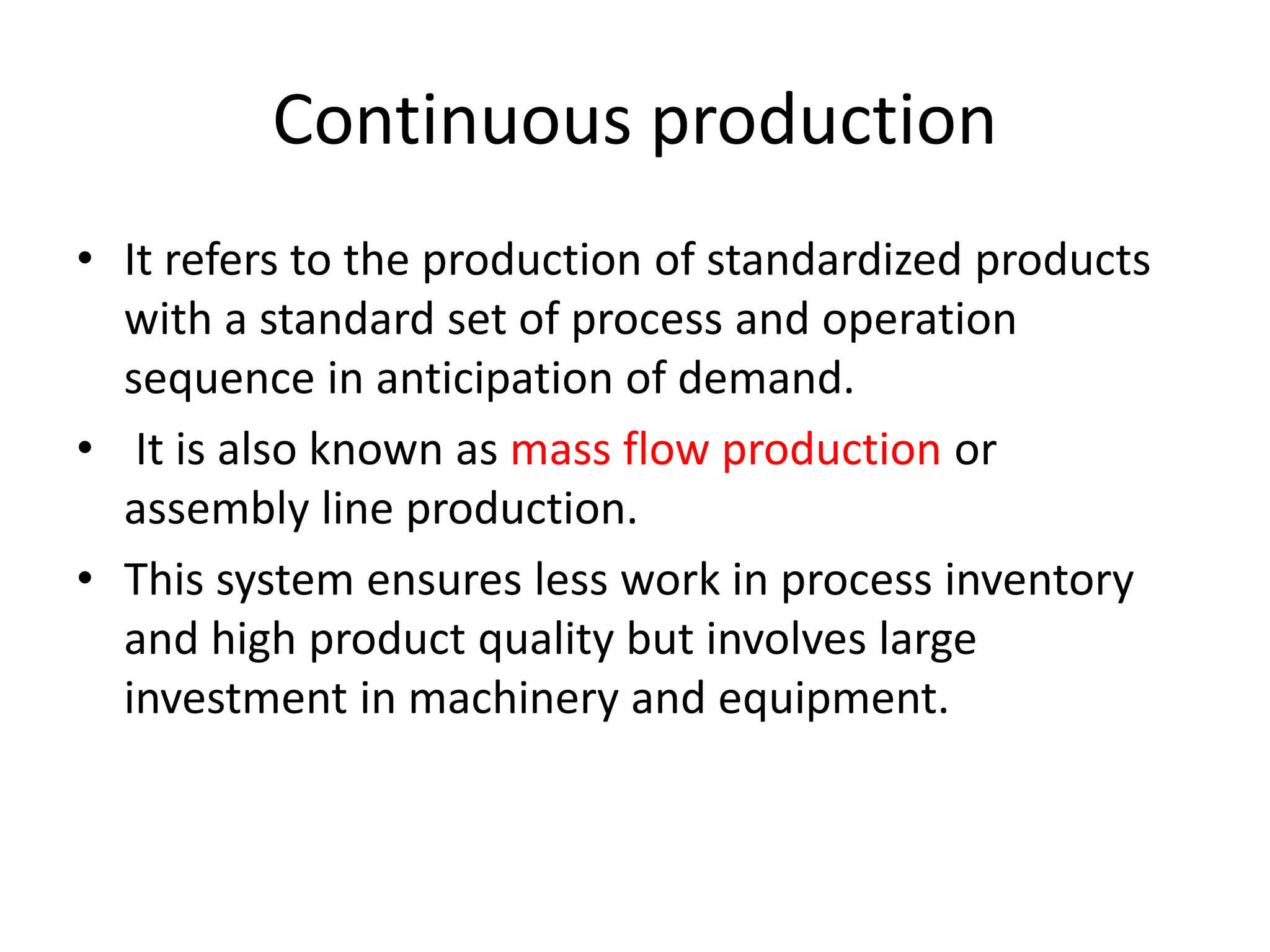
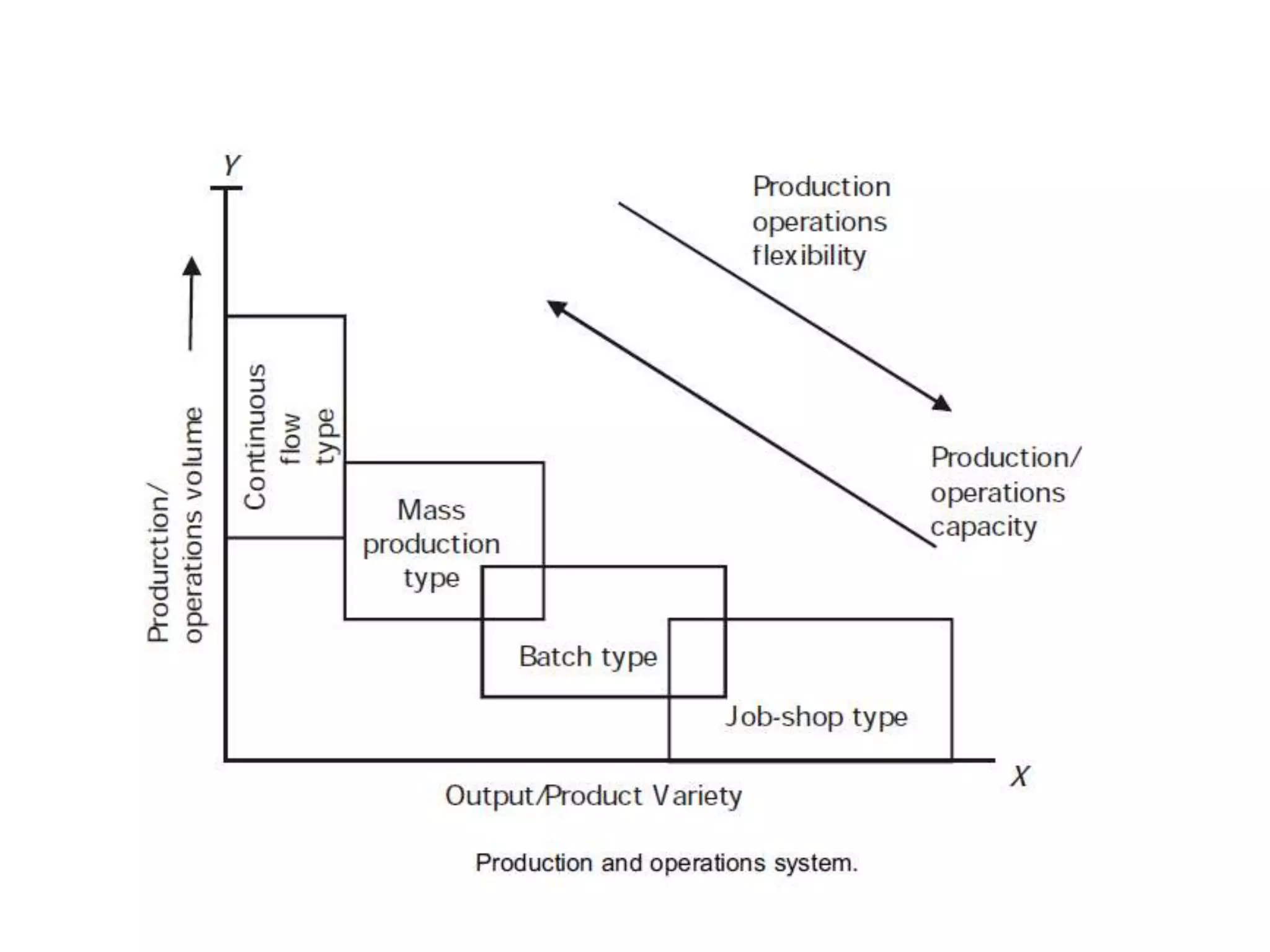
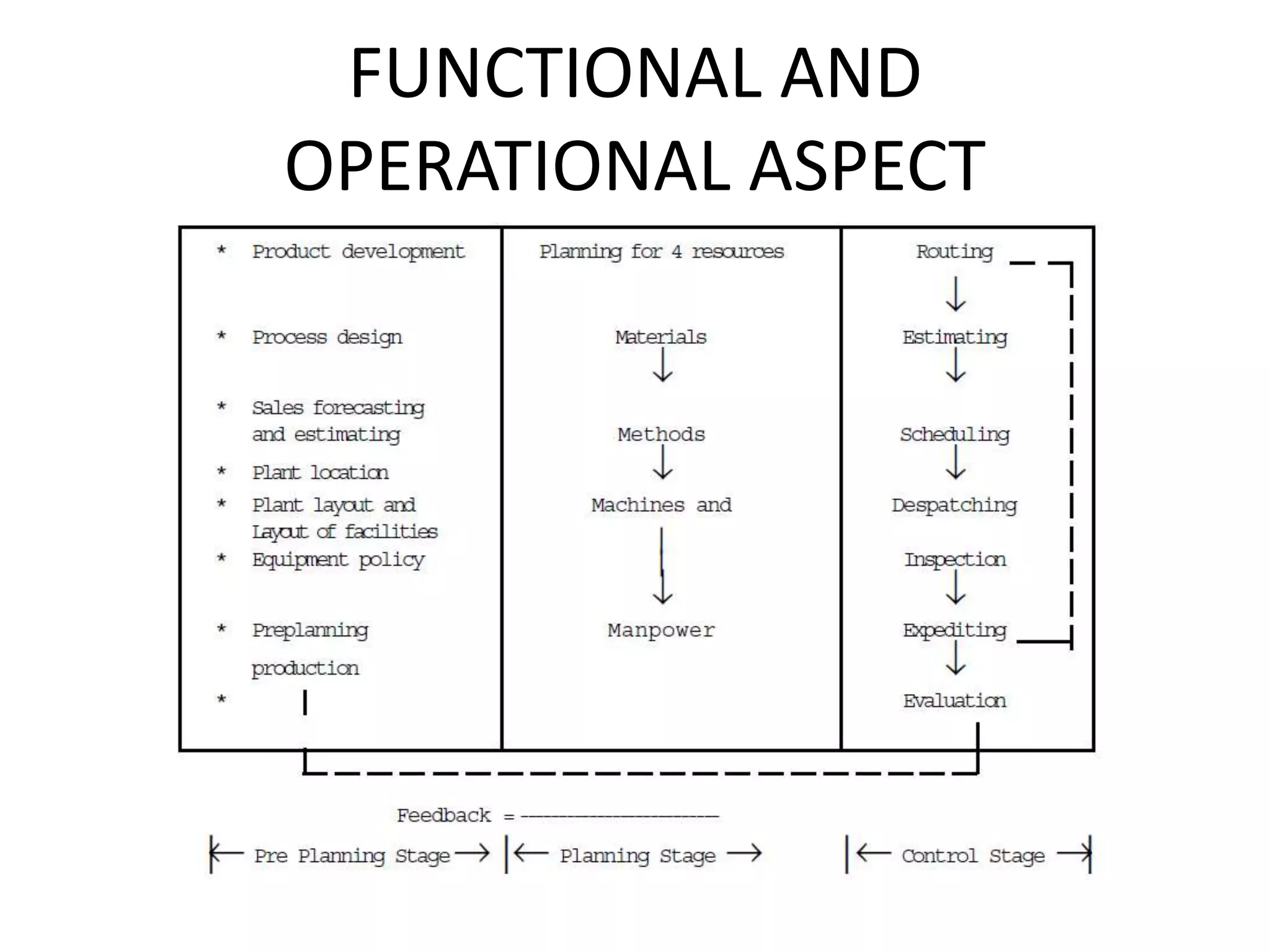
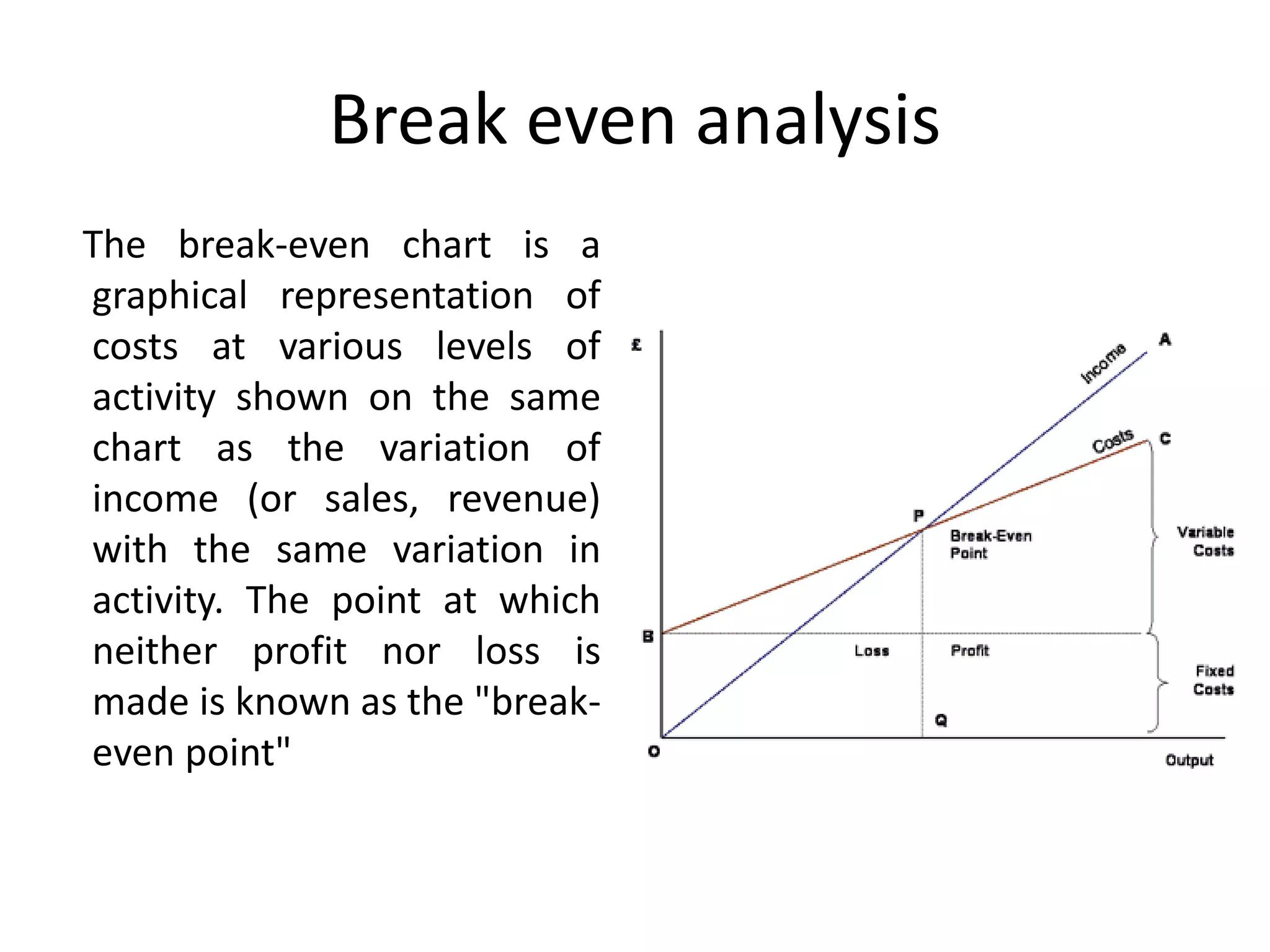
This document provides an introduction to production planning and control. It discusses objectives like minimizing costs and maximizing customer service. Production control functions include procurement, allocation, and utilization of resources to produce goods efficiently. Types of production discussed are continuous, job/unit, and intermittent. Other topics covered include product design, development, standardization, simplification, marketing aspects, functional/operational considerations, aesthetics, profit analysis, and break-even analysis.