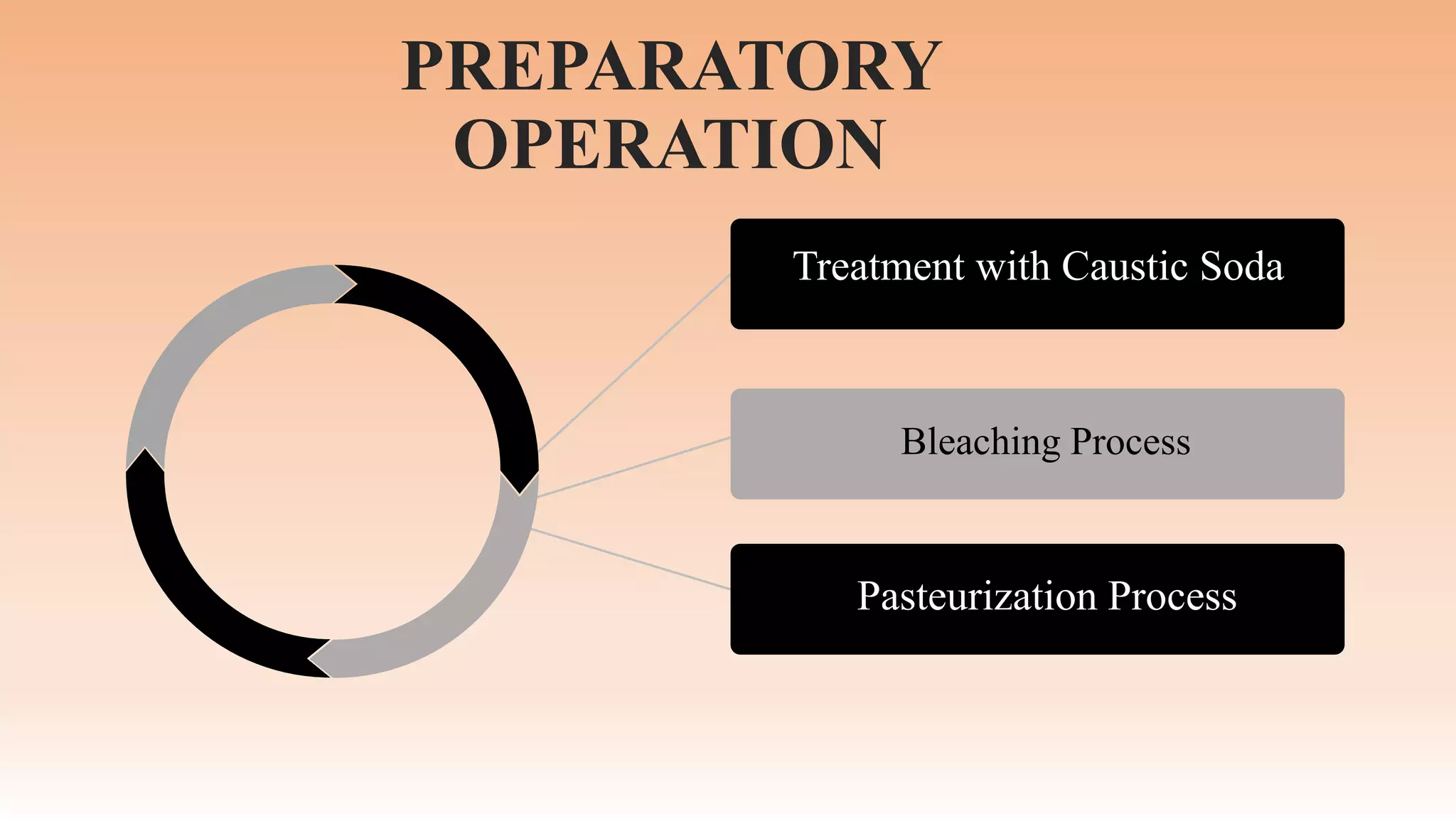
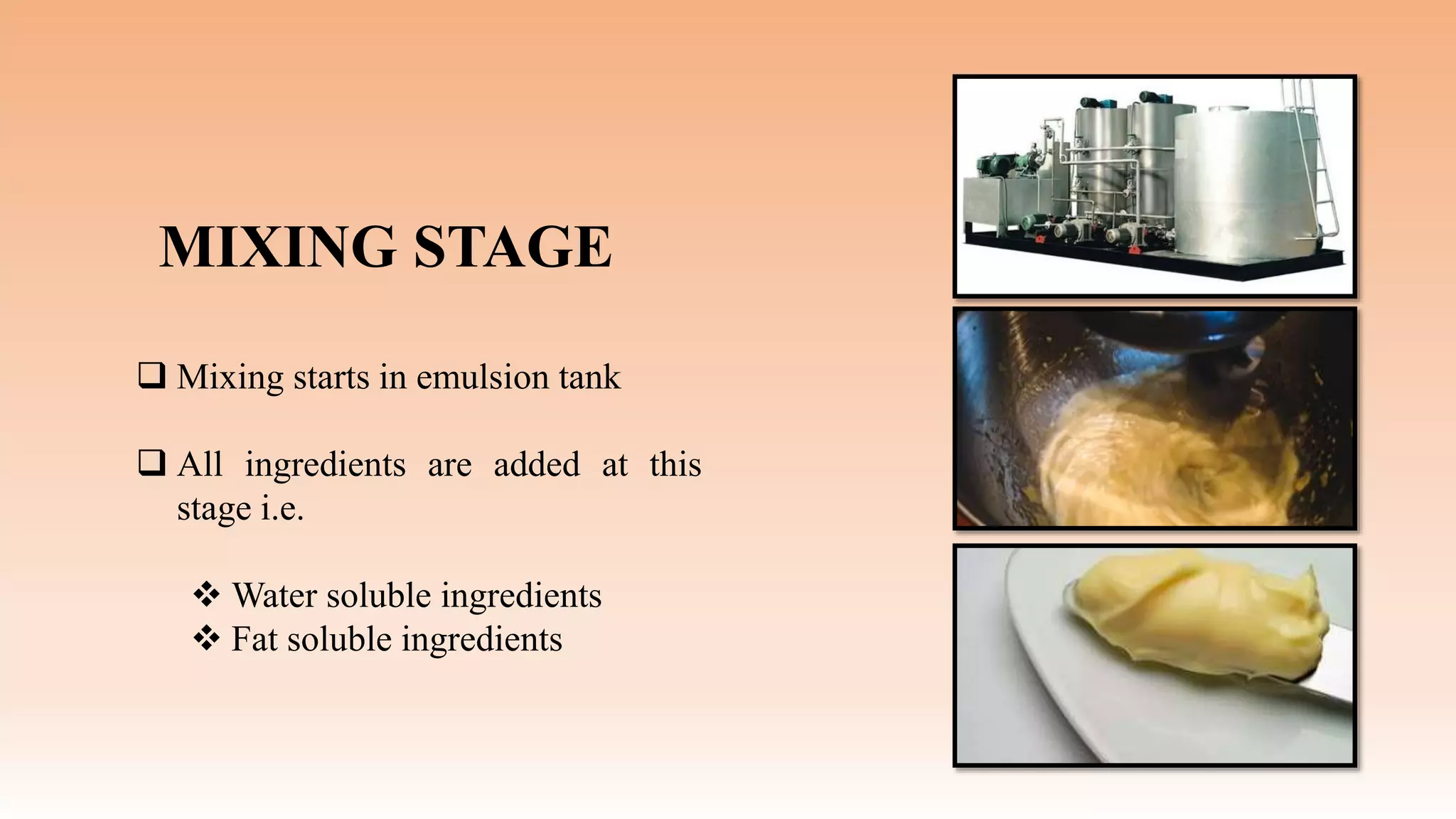
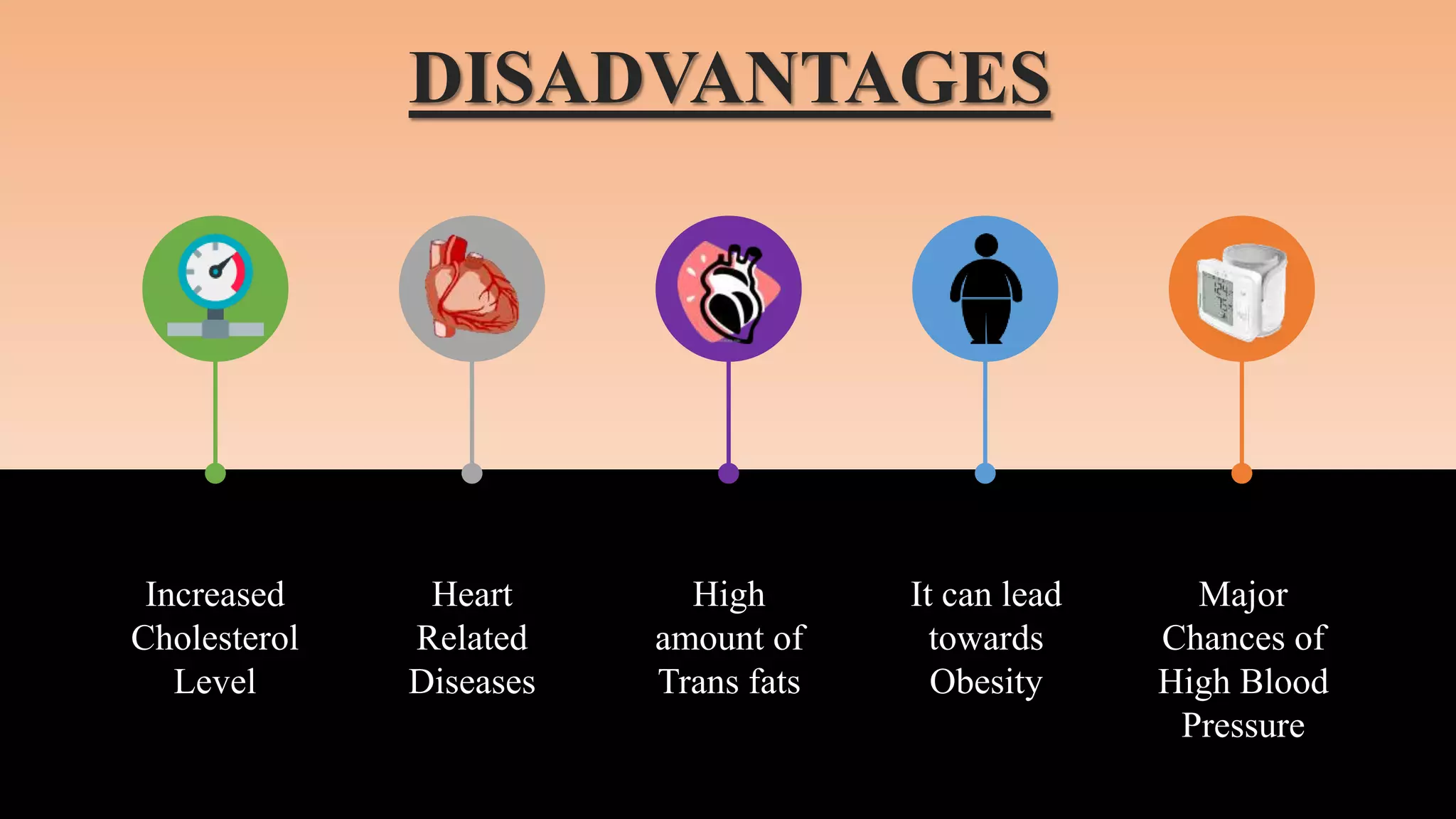
The document discusses the technology and processing of margarine, including its composition, production process, and the role of emulsifying agents. It outlines the history, raw materials, and steps involved in making margarine, emphasizing its advantages and disadvantages. Key ingredients include vegetable oils and emulsifiers, with production techniques ensuring the product's stability and shelf life.