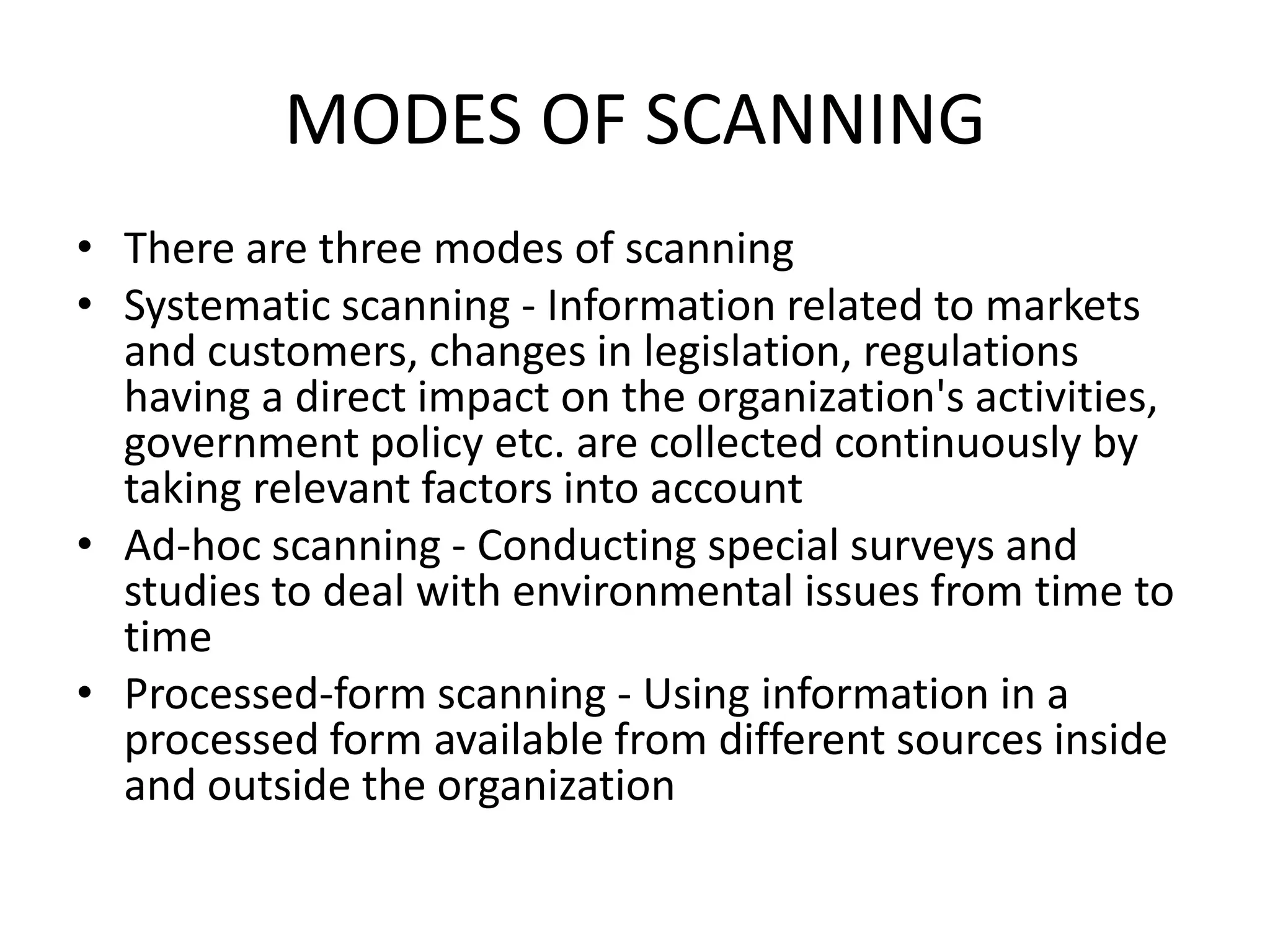
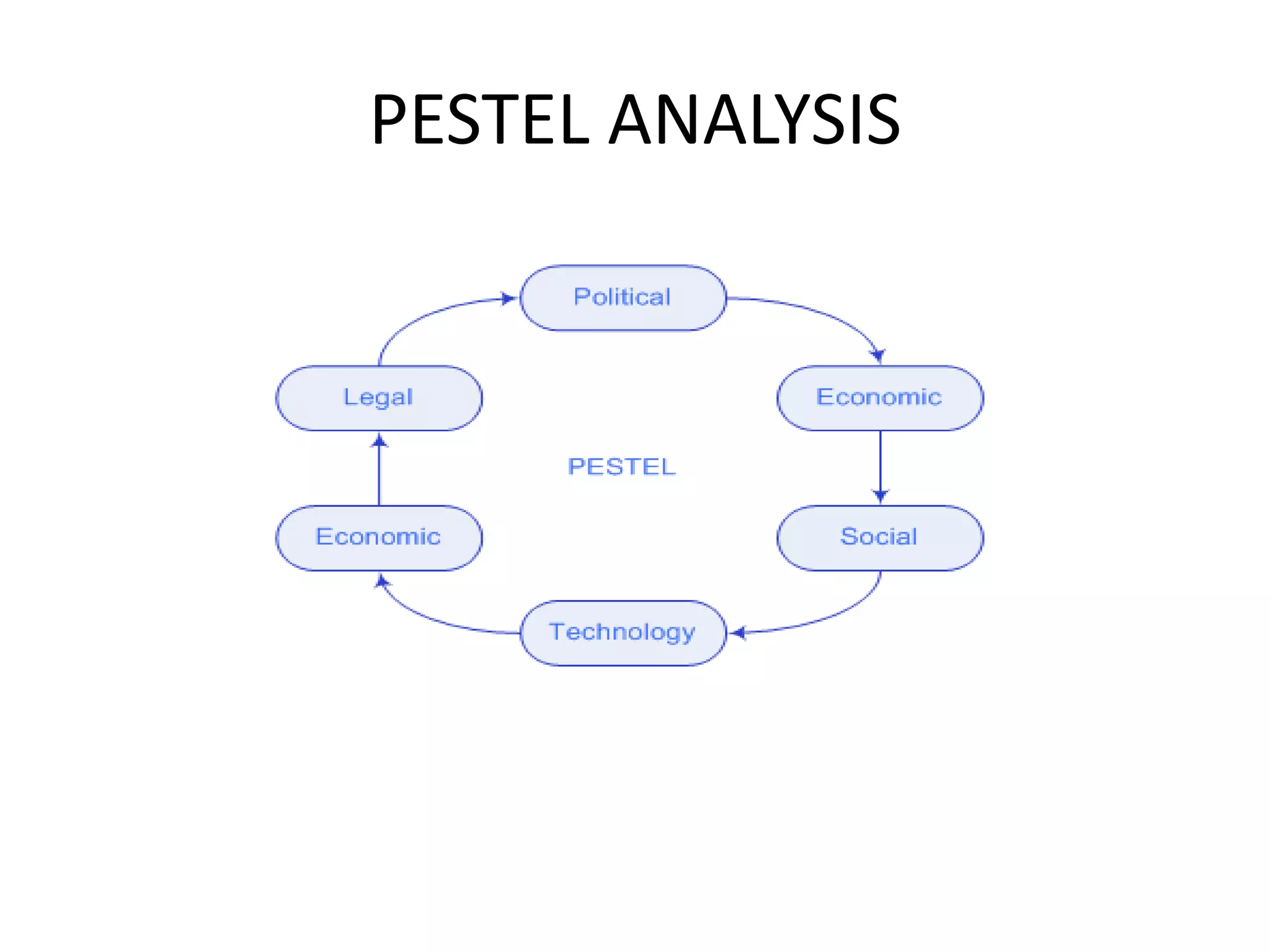
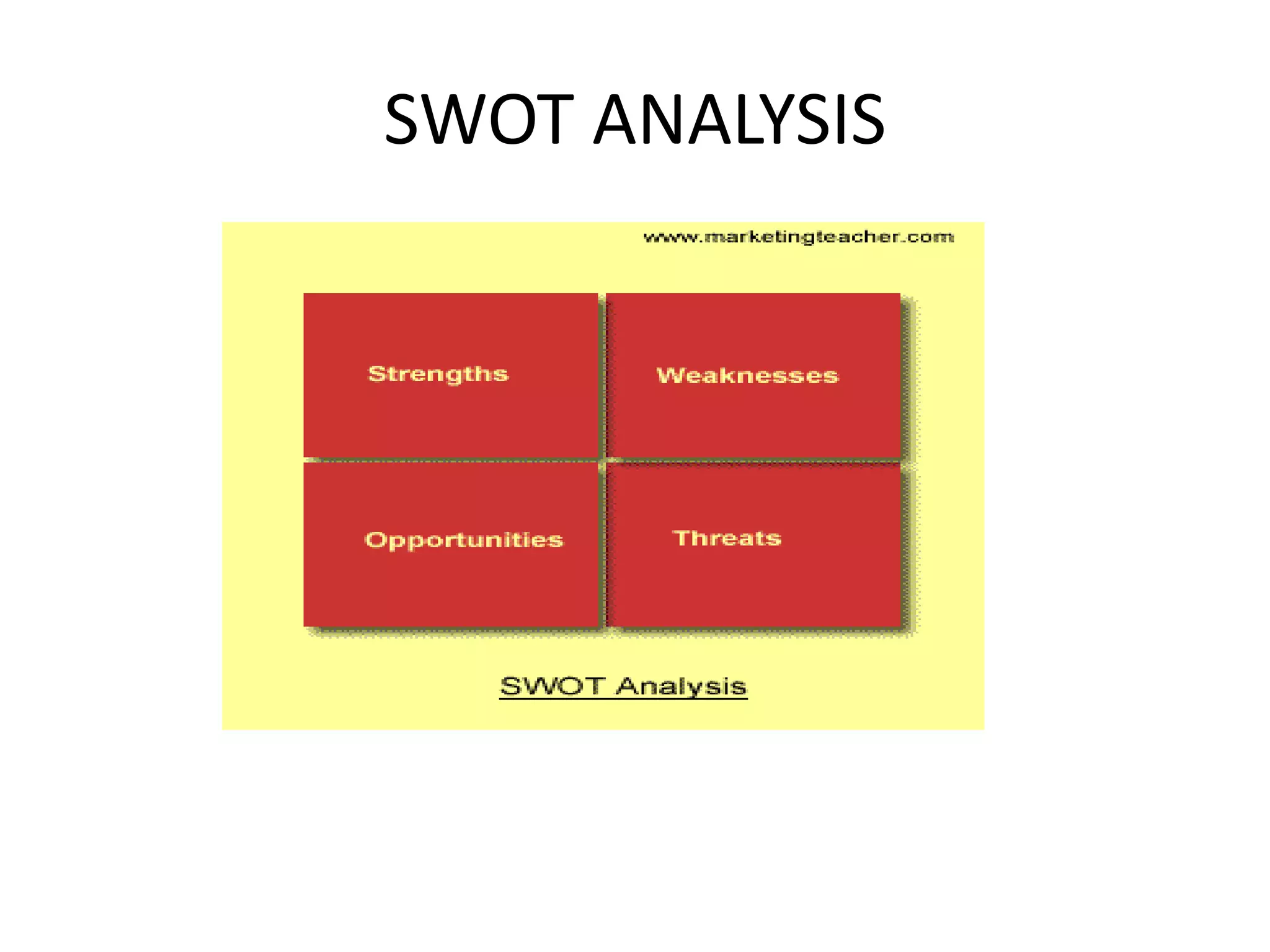
Environmental scanning involves studying political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental trends and events that could impact a business. There are three modes of scanning: systematic scanning of information directly relevant to a business; ad-hoc scanning through occasional surveys; and using processed information from internal and external sources. A PESTEL analysis examines these external factors through a political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal lens. A SWOT analysis identifies a business's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.