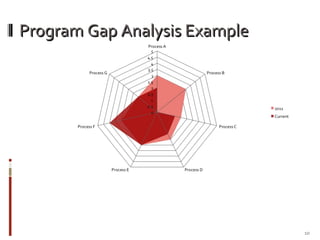
This document discusses assessing and improving IT security processes through a systematic process. It involves continually assessing existing processes, monitoring security programs, and adapting to evolving threats. Key steps include: assessing security processes and rating their effectiveness; identifying gaps; defining a strategy to close gaps; and executing a plan for improvement. Process improvement should be an ongoing cycle to reduce organizational risk over time.