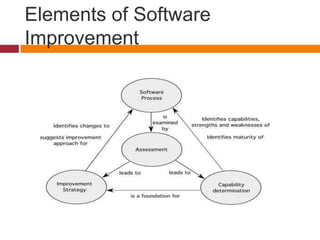
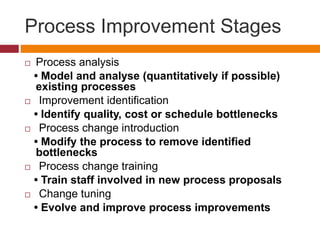
This document discusses software process improvement (SPI). SPI aims to introduce changes to achieve organizational objectives like quality improvement, cost reduction, and schedule acceleration. The key stages of SPI are process analysis, improvement identification, process change introduction, process change training, and change tuning. Process and product quality are closely related - a good process usually produces a good product. Process analysis techniques include using published process models, questionnaires/interviews, and ethnographic analysis. The document also notes some limitations of a specific improvement model in focusing only on project management rather than product development.