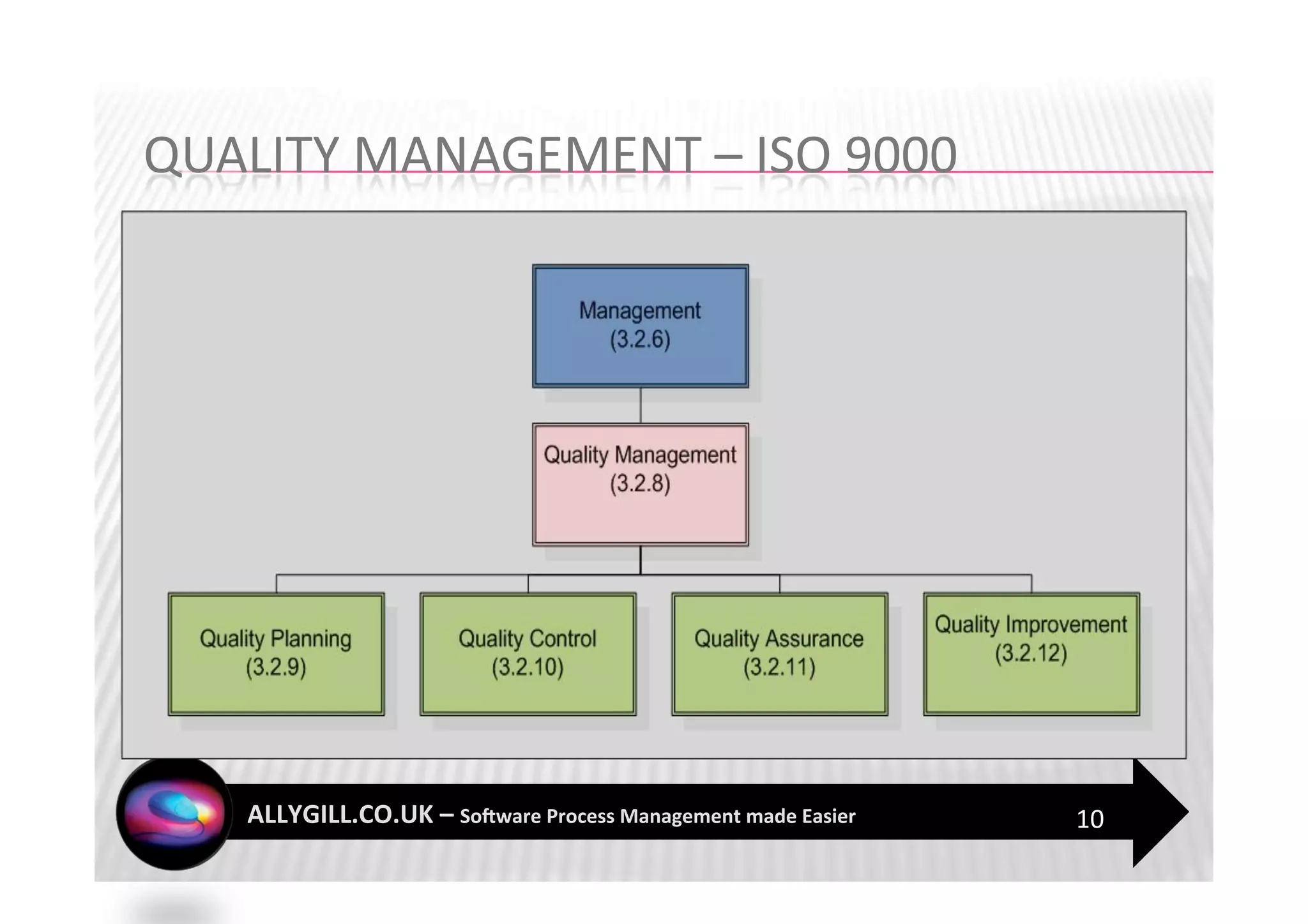
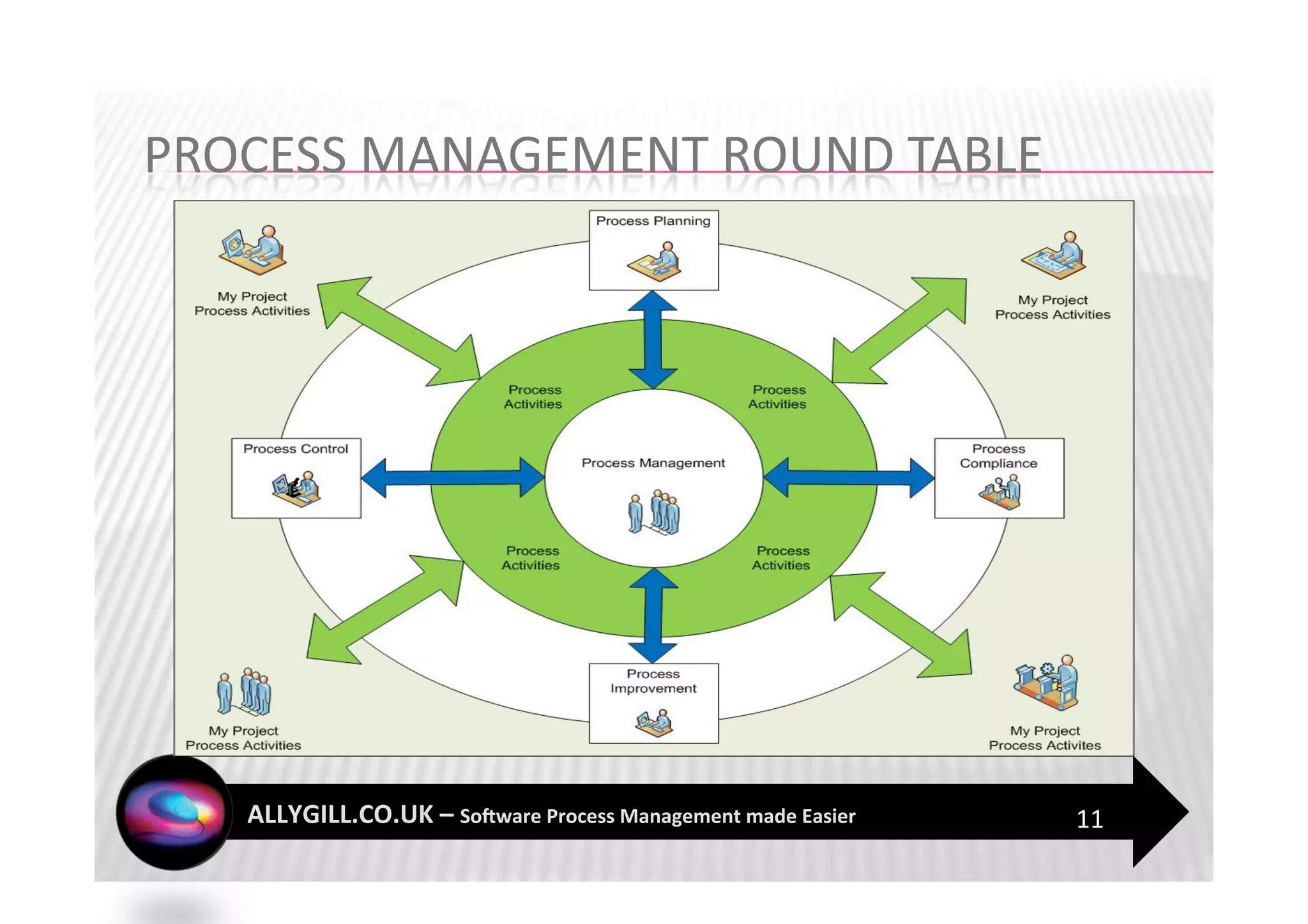
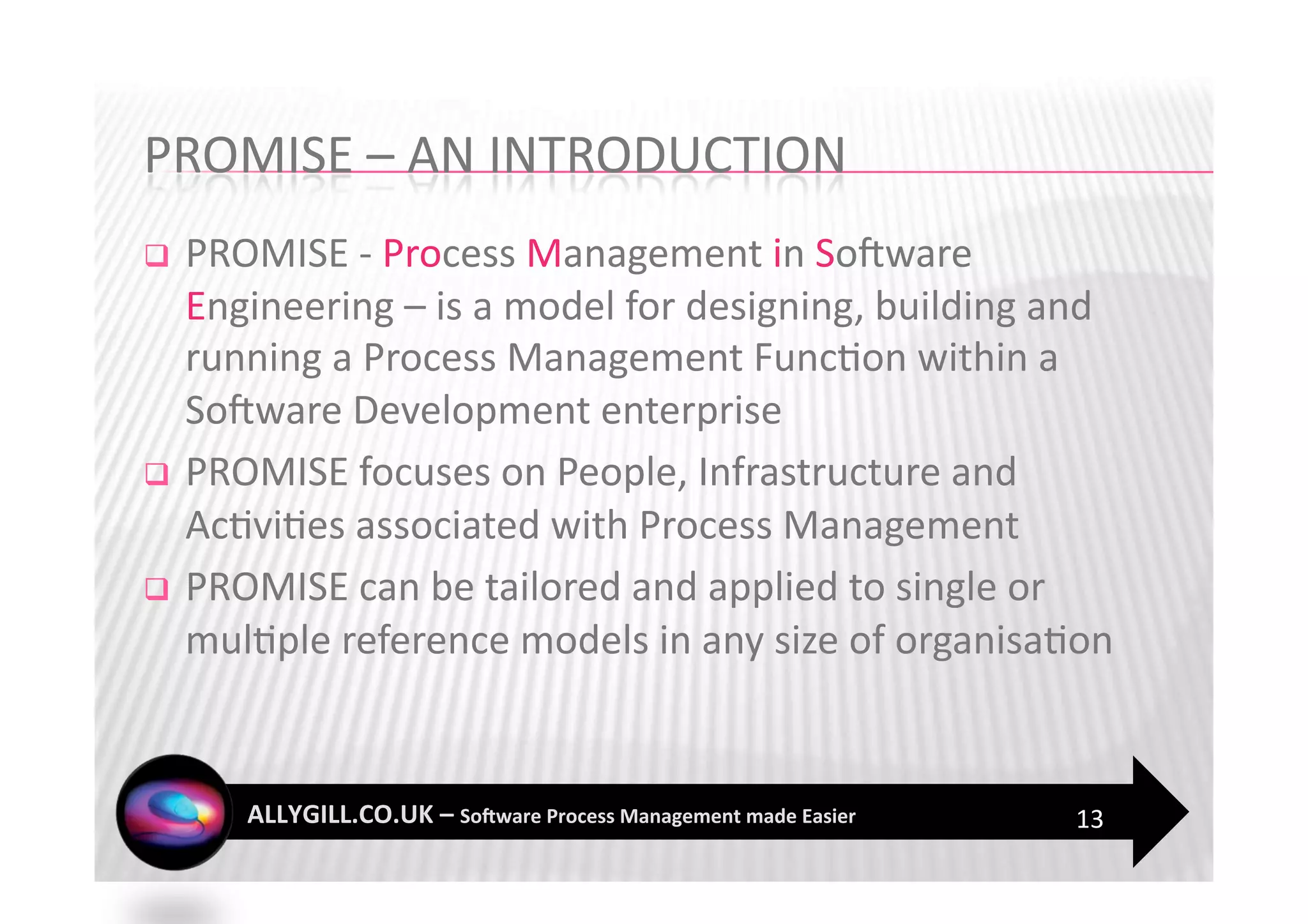
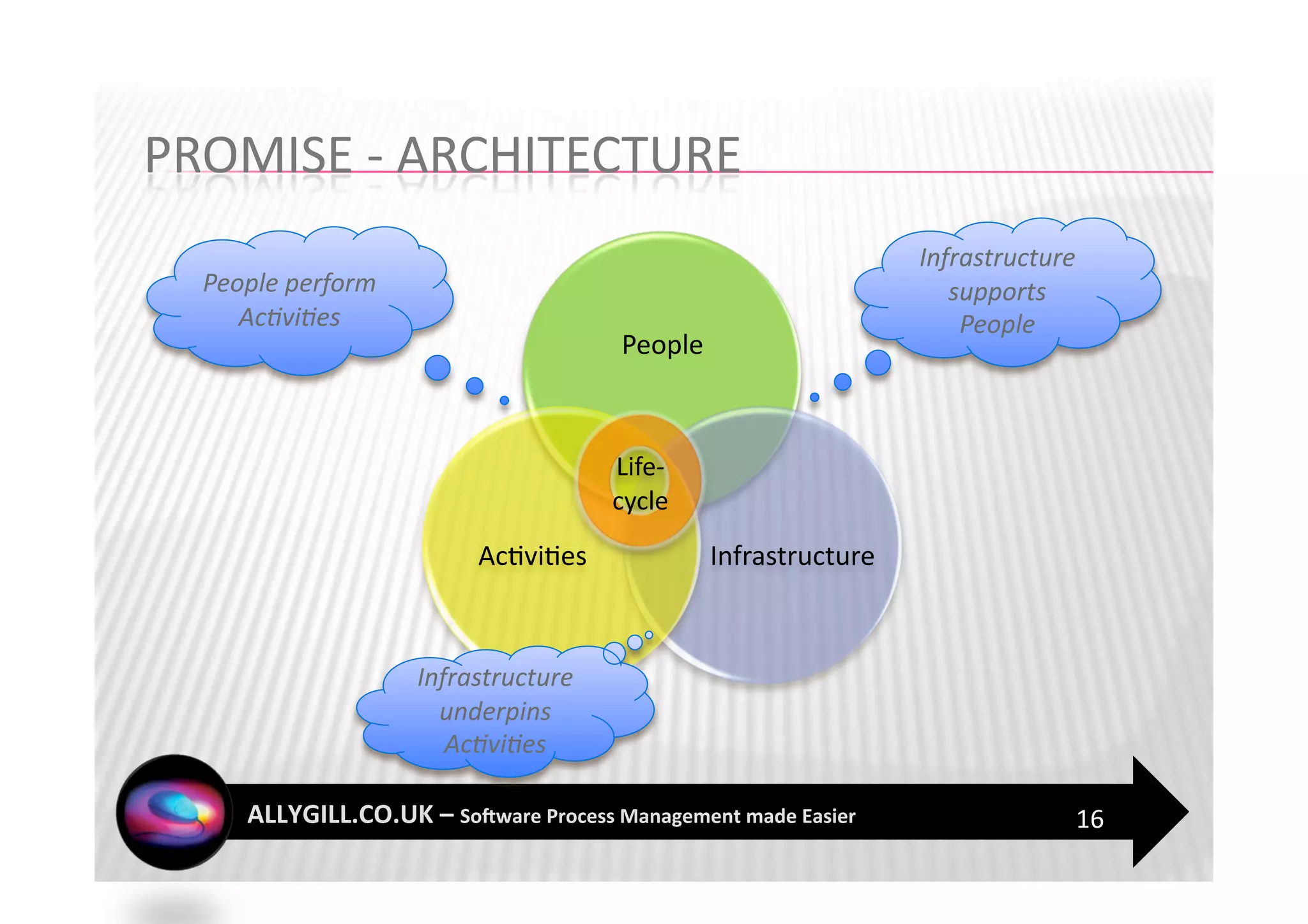
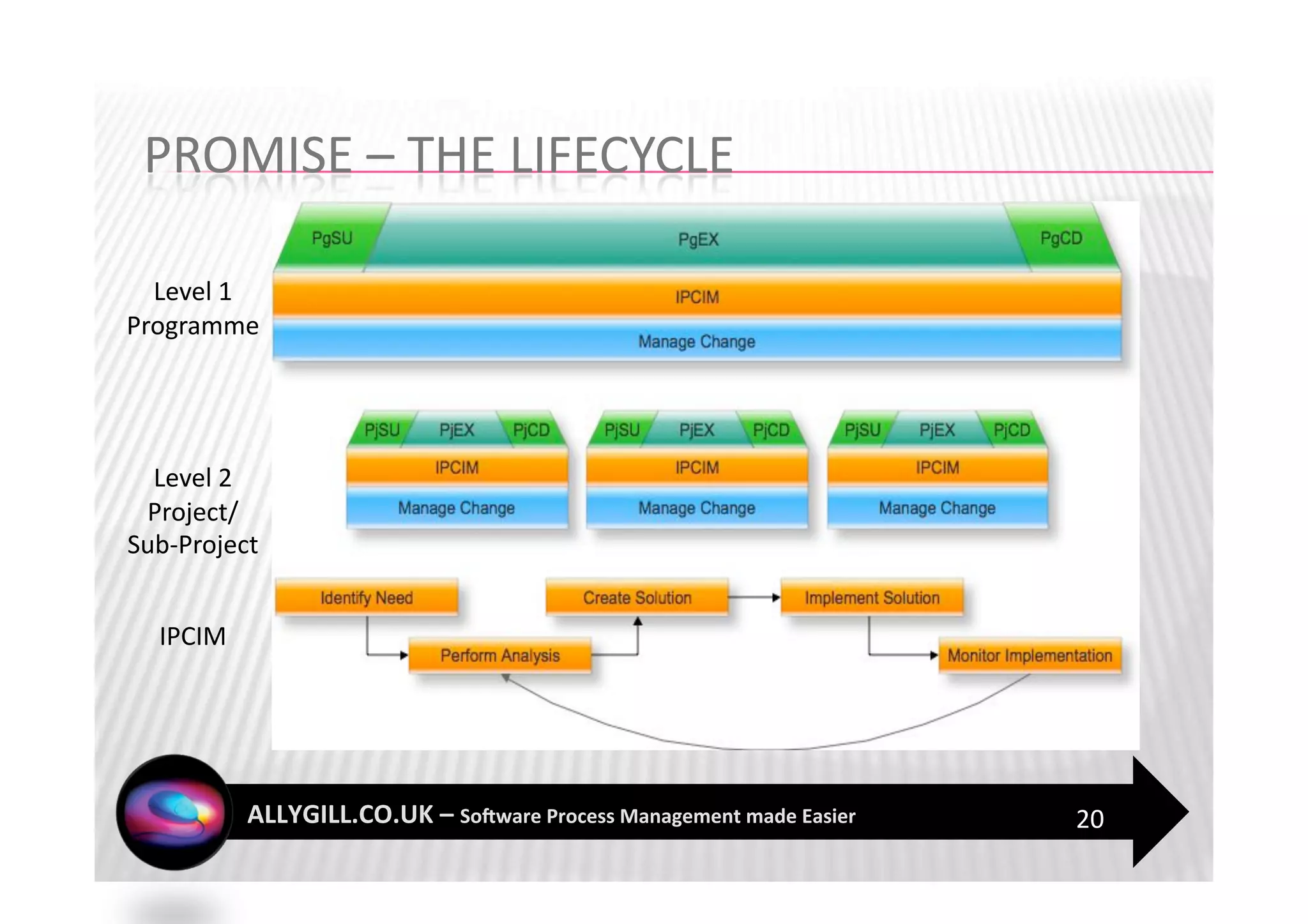
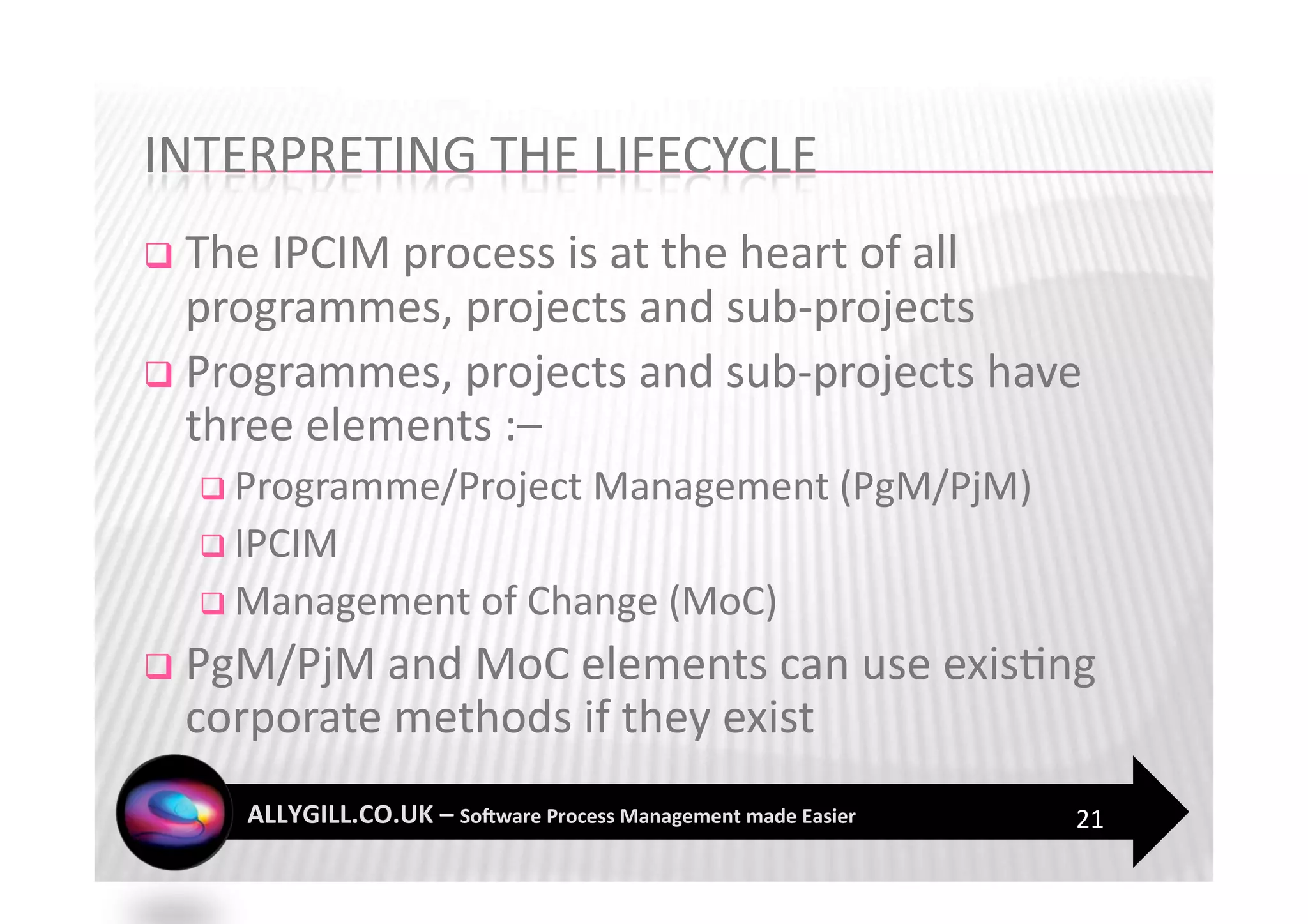
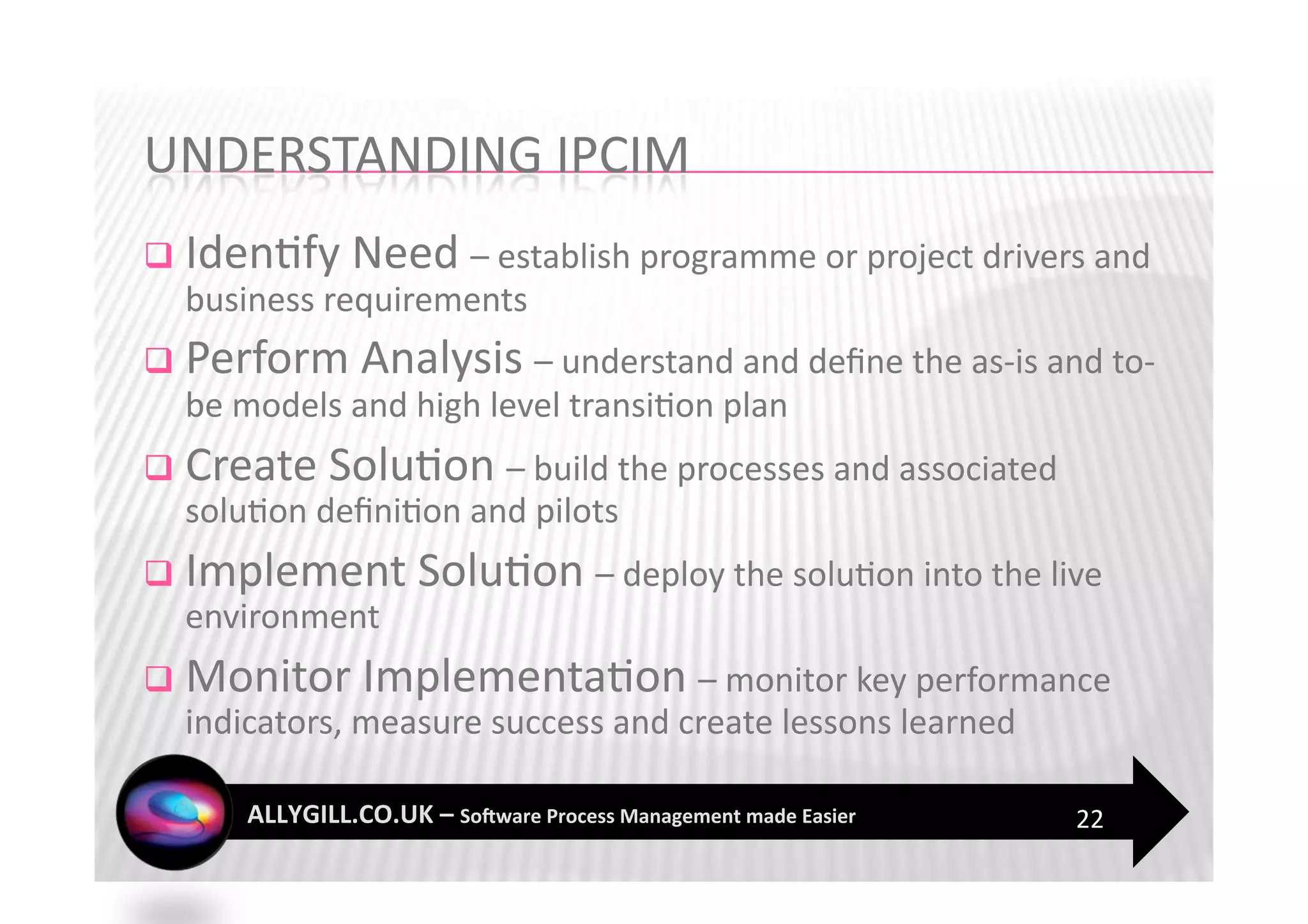
This document discusses software process management and the PROMISE model. It summarizes that many software process improvement programs fail because they lack long-term focus and management of change. PROMISE is presented as a model for building and sustaining an effective software process management function focused on people, infrastructure, and activities like process definition, monitoring, and improvement. The document advocates for a risk-based approach and integrating lessons learned to establish a process management culture.