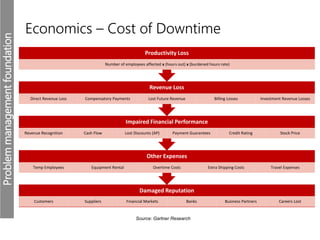
The document discusses the importance of budgeting in crisis management, emphasizing that understanding financial implications is critical for effective resource allocation and risk management. It outlines various cost categories associated with crises, including setup, repair, and return to service costs, as well as the broader financial impacts of downtime such as lost revenue and reputation damage. The piece highlights that, in a real-world context of limited resources, prioritizing funding for crisis management is essential for maintaining operational efficiency and mitigating risks.