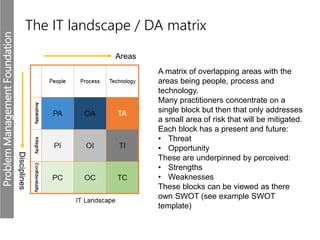
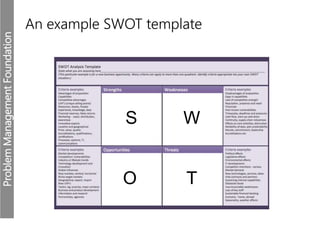
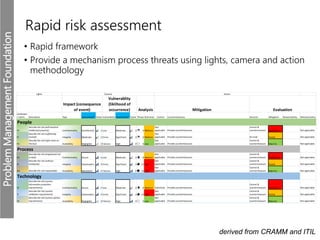
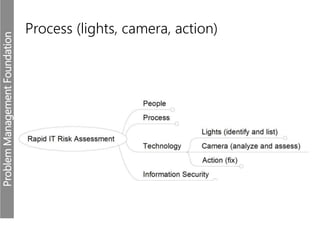
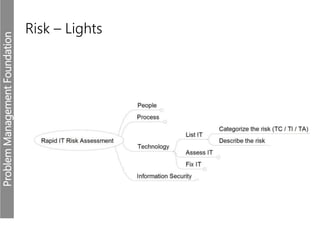
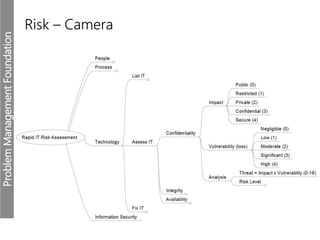
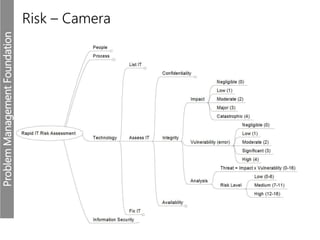
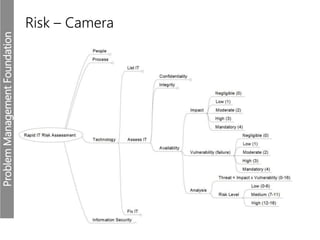
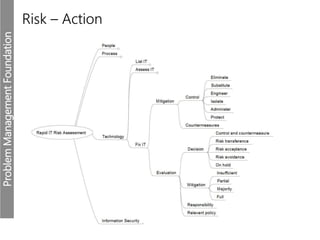
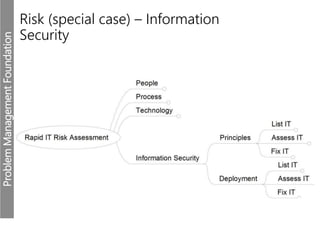
Meerkats watch for predators and other threats to warn their group. In the workplace, risks like problems must be evaluated and mitigated. An IT risk management methodology should be adopted to assess which problems need prioritized solutions. The Toyota logo represents customers, products, and technological progress, relevant areas in any risk landscape. A matrix model analyzes the intersections of people, processes, and technologies where strengths, weaknesses, threats, and opportunities reside.