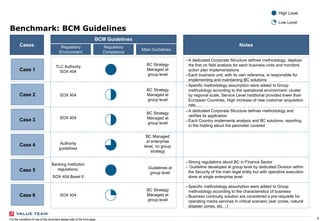
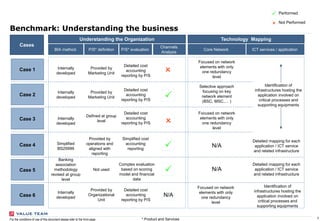
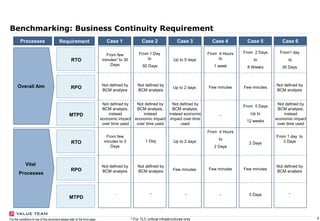
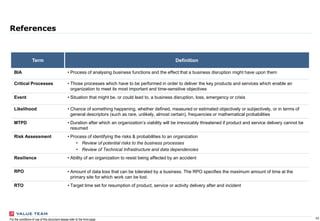
This document outlines the scope and purpose of a business continuity management (BCM) strategy report presented by Value Team S.p.A. It provides guidelines, benchmarking information, and a comparative analysis of different business continuity practices across industries, emphasizing the importance of resilience and preparedness against potential disruptions. The report serves as a high-level overview and does not replace specific assessments tailored to individual corporate needs.