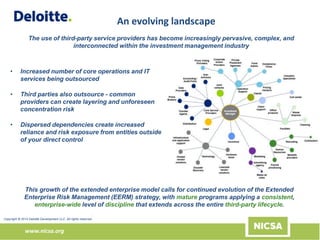
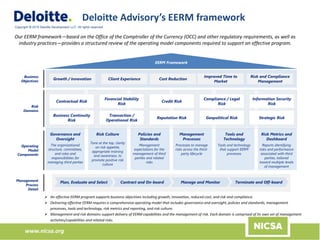
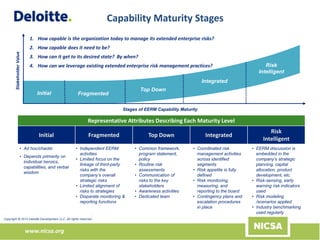
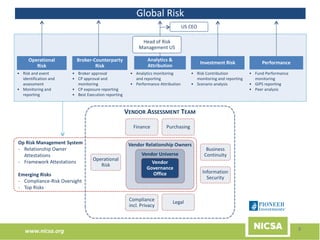
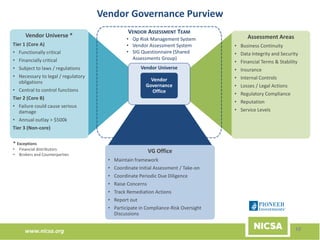
The document discusses the importance of third-party risk management in the investment management industry, highlighting the increasing complexity and interdependence of outsourced services. It introduces an evolving Extended Enterprise Risk Management (EERM) framework aimed at enhancing risk management processes through centralized execution and improved transparency across the third-party lifecycle. The framework emphasizes governance, oversight, and the integration of risk management with business objectives to effectively control and mitigate third-party risks.