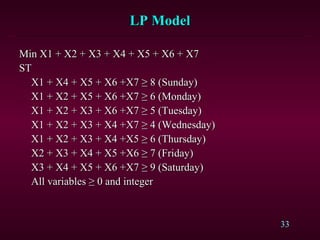
Linear programming (LP) is a technique used by operations managers to allocate scarce resources. LP involves defining an objective (e.g. maximize profit), decision variables (e.g. production levels), and constraints (e.g. resource limits). The objective and constraints must be expressed as linear equations. Common LP applications include determining optimal product mix, production plans, ingredient mixes, and resource allocation. LP problems are formulated by defining the objective and variables, writing the objective function, describing constraints, and specifying the mathematical model. Examples demonstrate how to set up LP models to maximize profit or minimize costs given production and resource constraints.