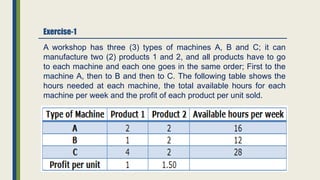
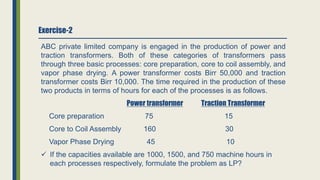
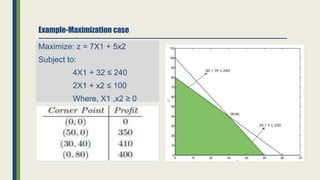
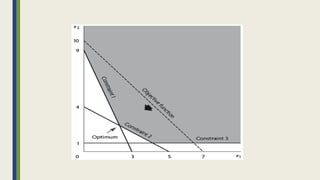
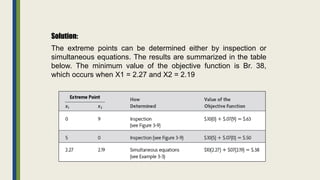
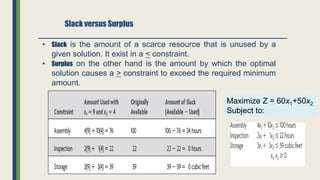
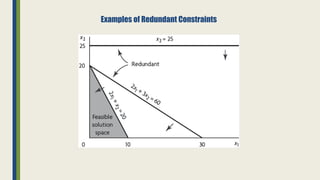
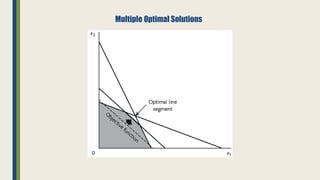
The document discusses linear programming and its key concepts. It begins by defining linear programming as using a mathematical model to allocate scarce resources to maximize profit or minimize cost. It then provides the steps to solve linear programming problems: [1] identify the problem as solvable by LP, [2] formulate a mathematical model, [3] solve the model, and [4] implement the solution. The document also discusses modeling techniques like defining decision variables, objective functions, and constraints. It provides examples of LP formulations and solutions using both graphical and algebraic methods. Finally, it discusses special issues that can arise like infeasible, unbounded, and redundant solutions or the existence of multiple optimal solutions.