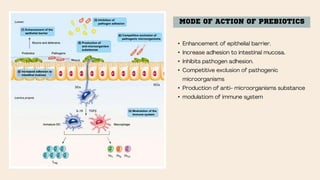
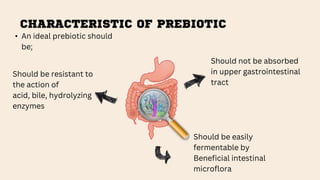
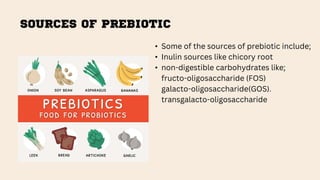
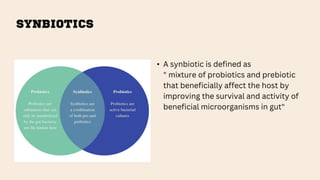
The document discusses the concepts of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics, defining each term and elaborating on their characteristics and health benefits. Probiotics are beneficial bacteria, while prebiotics are non-digestible food ingredients that promote their growth; synbiotics are a combination of both designed to enhance their effects. It highlights various sources, mechanisms, and health impacts such as improved gut health, reduced diarrhea, and protective effects against certain diseases.