Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX

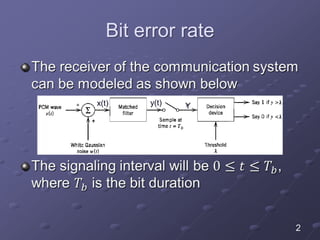

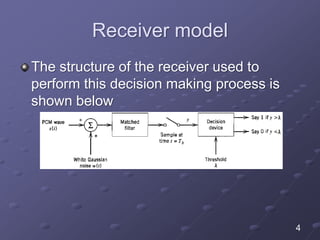








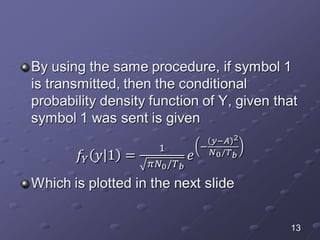
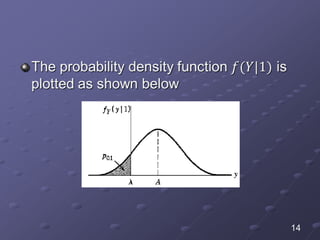






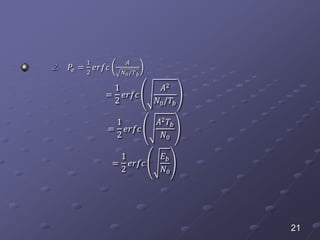
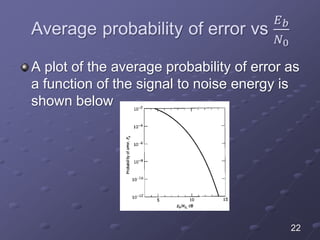











The document discusses bit error rate and the average probability of error in receiving digital signals over noise channels. It explains the two types of errors that can occur, shows the model of the receiver, and provides calculations and plots to show how the average probability of error decreases exponentially as the signal-to-noise ratio increases. Examples are included to illustrate applying the concepts.
































