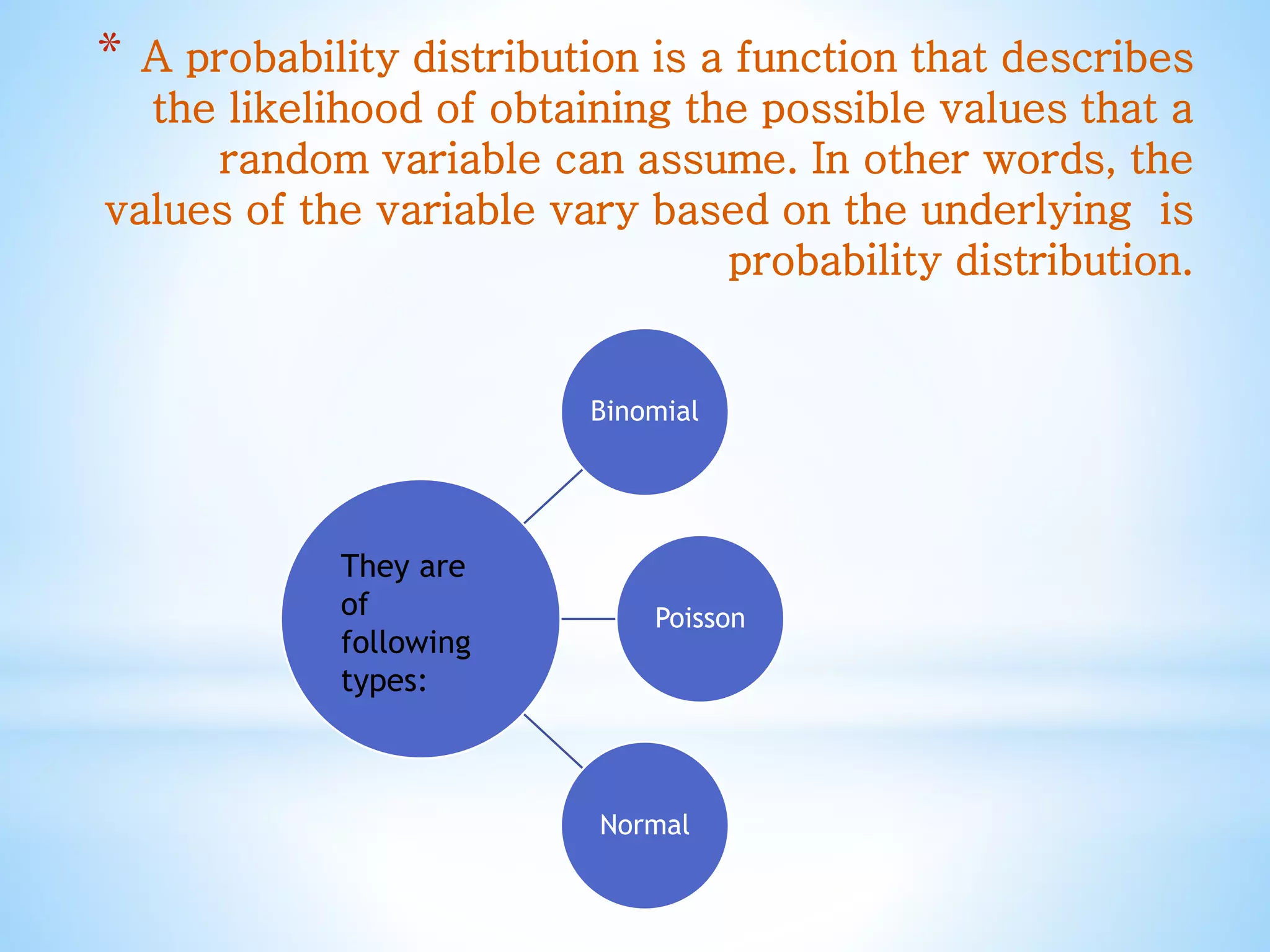
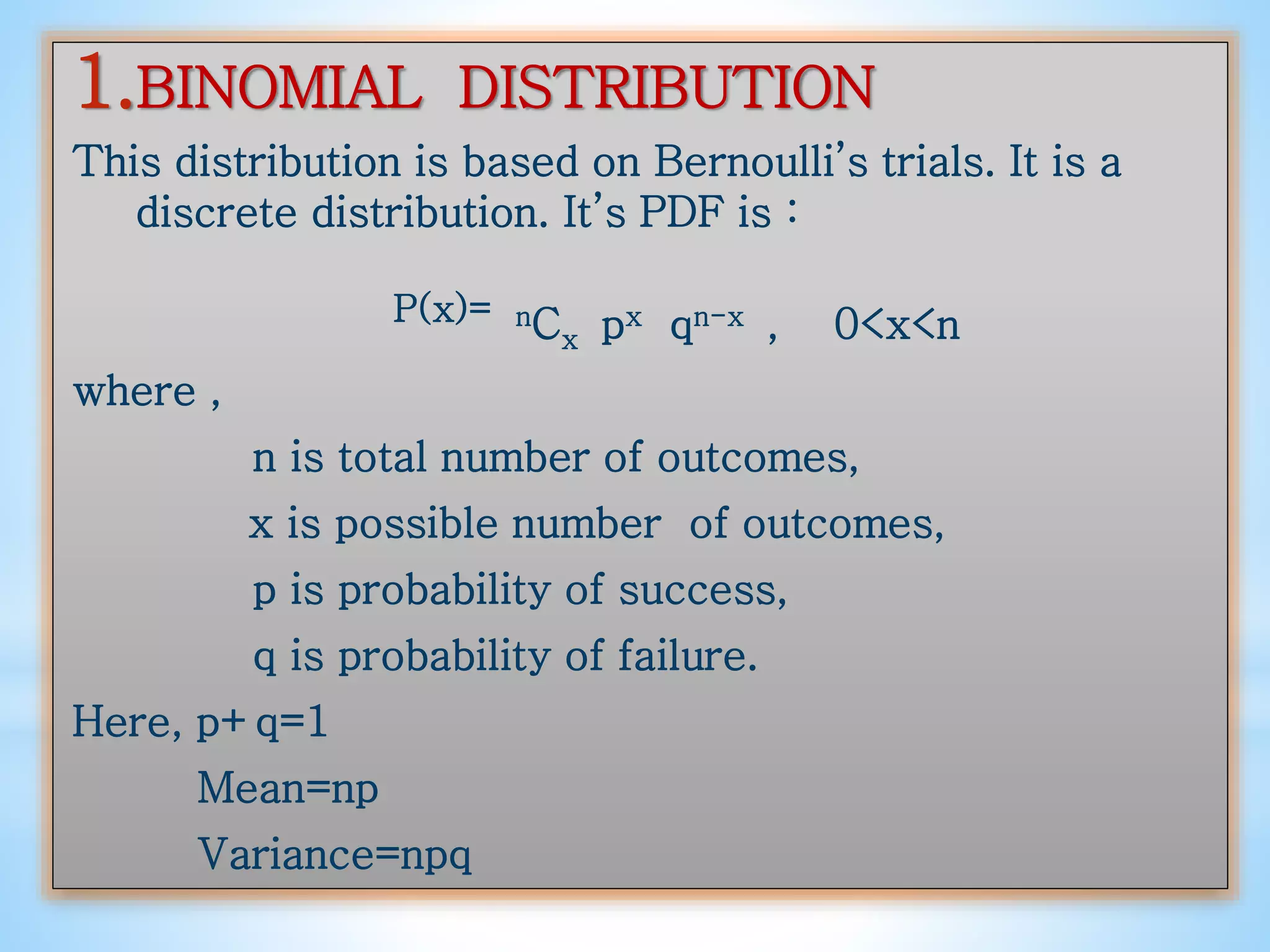
The presentation discusses probability distributions, explaining that they represent the likelihood of different outcomes for a random variable. It covers three main types: binomial, poisson, and normal distributions, detailing their properties and formulas. Each distribution has unique characteristics, such as the binomial's focus on discrete outcomes and the normal's continuity and symmetry.




![3. NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
It is a continuous probability distribution whose
Probability Mass Function(PMF) is:
P(x)= [1/
-∞<x<∞
It’s Mean= μ
Variance= σ2
Standard Deviation= σ
It is a limiting case of Binomial distribution. When n
becomes very large and P becomes close to ½ then
B.D tends to Normal distribution.
σ√2Π]*e[(-1/2)(x-μ/σ)2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mathsppt-200707103546/75/Probability-Distribution-7-2048.jpg)


