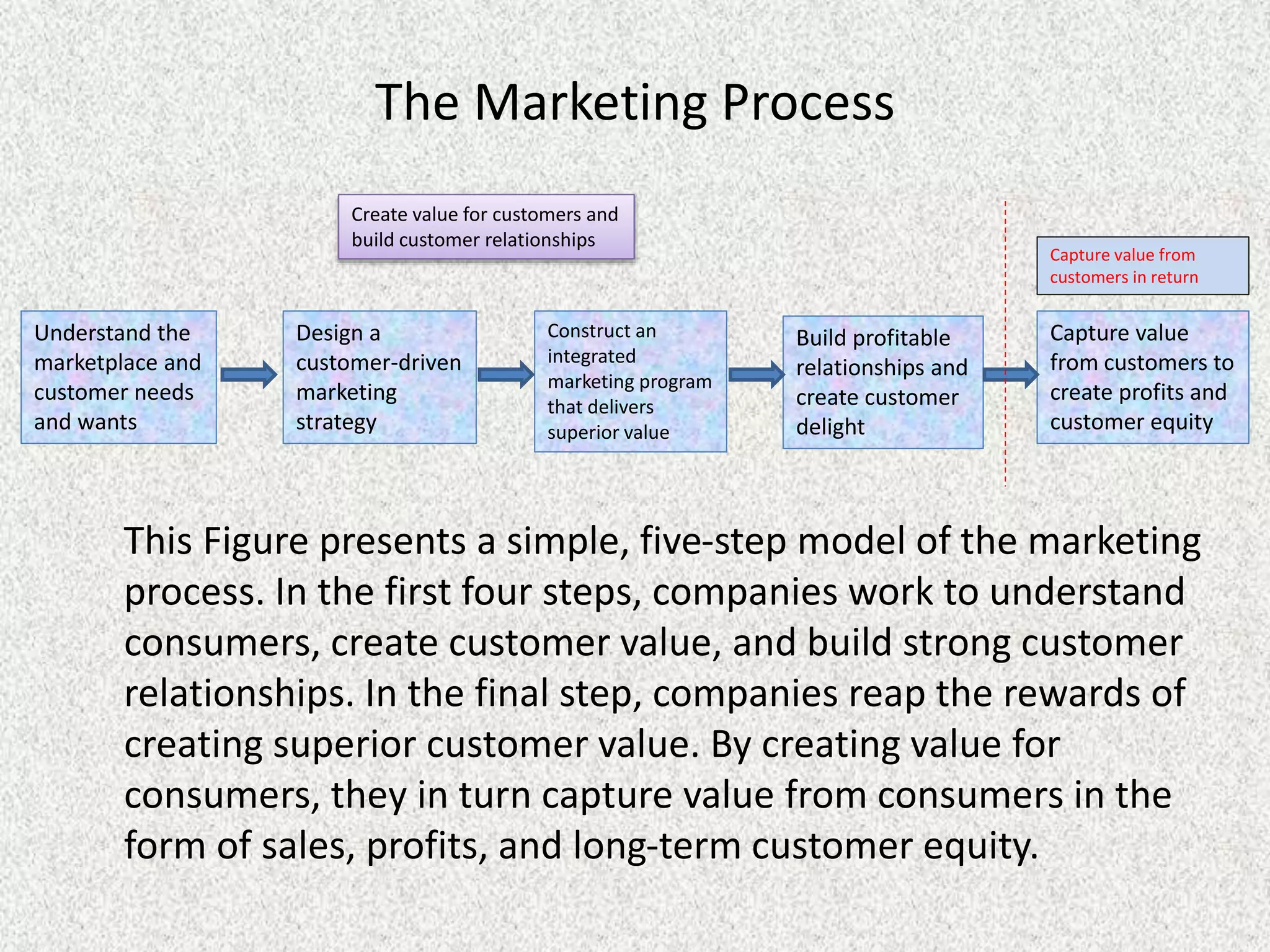
The document describes the marketing process as a 5-step model: 1) understand customer needs and marketplace, 2) design a customer-driven marketing strategy, 3) construct an integrated marketing program, 4) build profitable customer relationships and delight, 5) capture value from customers. It then discusses each step in more detail, focusing on understanding customer needs, wants, demands and the different concepts of marketing, exchanges, relationships and markets. Finally, it outlines 5 alternative marketing concepts that guide strategy: production, product, selling, marketing, and societal marketing concepts.